Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of military squad ranks! This comprehensive guide explains the structure and roles of each rank, from Private to General, including Non-Commissioned Officers (NCOs) and Warrant Officers. Discover the responsibilities, insignia, and career progression within the armed forces, covering Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps ranks.
The military is a hierarchical organization with a well-defined rank structure. Understanding military squad ranks is essential for anyone interested in joining the armed forces or simply wanting to learn more about the inner workings of the military. In this article, we will delve into the world of military squad ranks, explaining the different levels, responsibilities, and requirements.
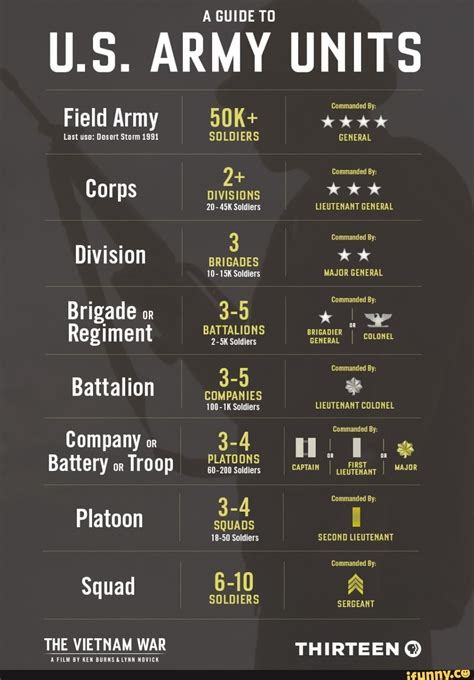
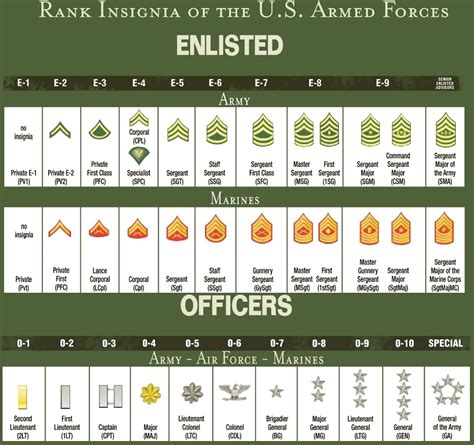
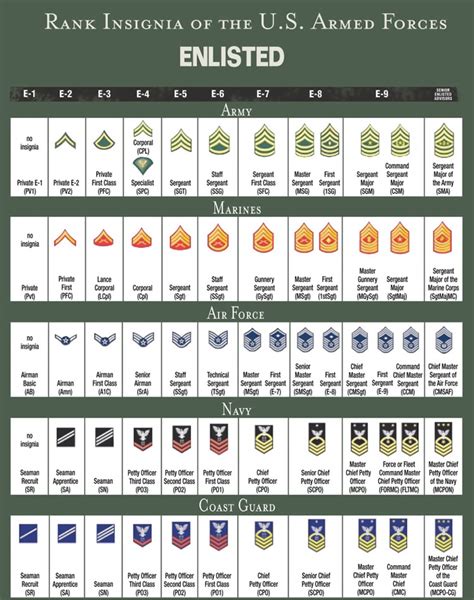
The military rank structure is designed to create a clear chain of command, with each rank having its unique responsibilities and authority. The ranks are divided into two main categories: enlisted and officer. Enlisted personnel make up the majority of the military, while officers are responsible for leading and commanding units.
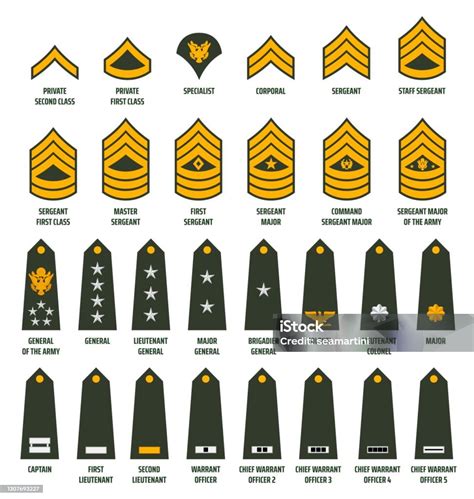
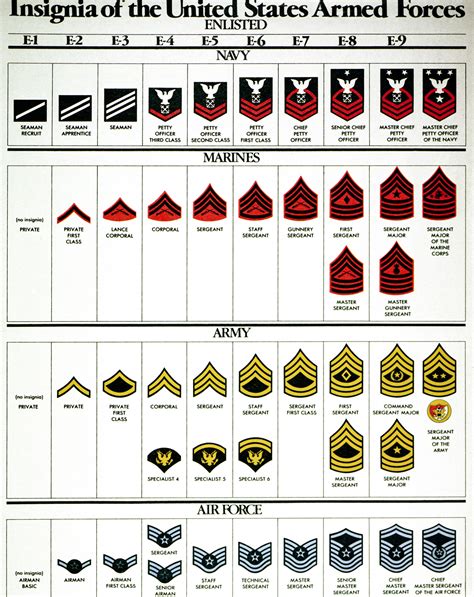
Enlisted Ranks
Enlisted personnel are the backbone of the military, responsible for carrying out the day-to-day tasks and operations. The enlisted ranks are further divided into several levels, each with its own set of responsibilities and requirements.

- Private (PVT): The lowest rank in the military, privates are responsible for following orders and completing tasks assigned by their superiors.
- Private First Class (PFC): A higher rank than private, private first classes are responsible for leading small teams and making decisions in the absence of their superiors.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): Specialists and corporals are responsible for specialized tasks, such as communication or medical care. They may also lead small teams.
- Sergeant (SGT): Sergeants are non-commissioned officers (NCOs) who are responsible for leading teams and making tactical decisions.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) are enlisted personnel who have demonstrated leadership potential and have been promoted to higher ranks. NCOs are responsible for leading teams and making tactical decisions.
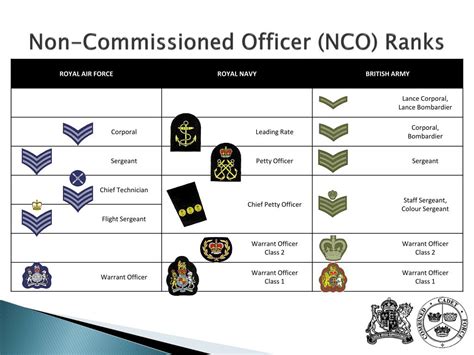
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): Staff sergeants are senior NCOs who are responsible for leading larger teams and making strategic decisions.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): Sergeant first classes are senior NCOs who are responsible for leading teams and making tactical decisions.
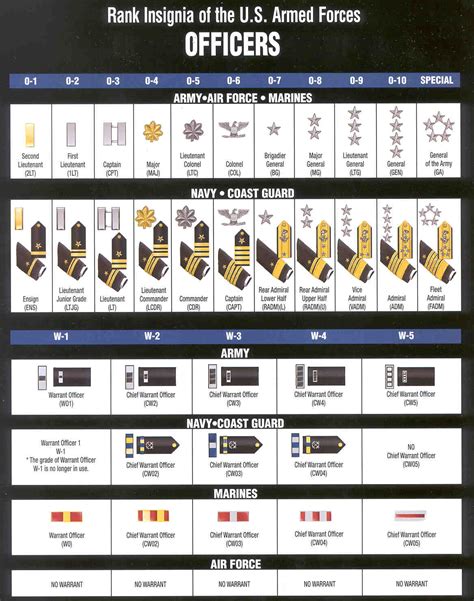
Officer Ranks
Officer ranks are reserved for those who have completed officer training and have been commissioned as officers. Officers are responsible for leading and commanding units.
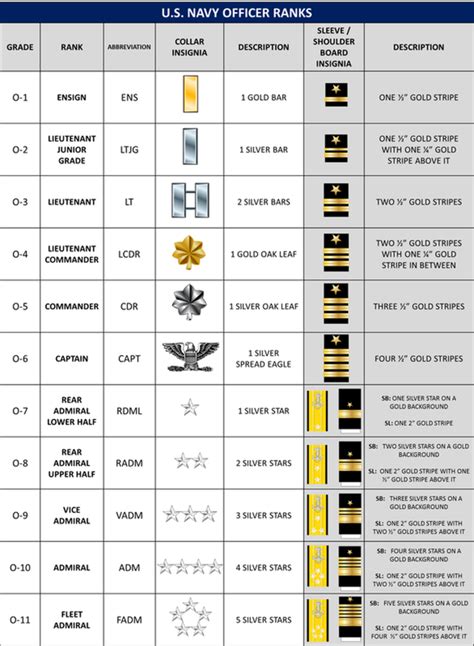
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The lowest rank among officers, second lieutenants are responsible for leading platoons and making tactical decisions.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): First lieutenants are responsible for leading companies and making strategic decisions.
- Captain (CPT): Captains are senior officers who are responsible for leading battalions and making tactical decisions.
Senior Officer Ranks
Senior officer ranks are reserved for those who have demonstrated exceptional leadership potential and have been promoted to higher ranks. Senior officers are responsible for leading and commanding larger units.
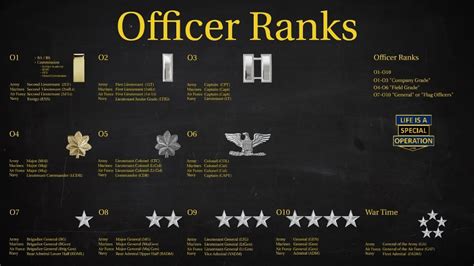
- Major (MAJ): Majors are senior officers who are responsible for leading brigades and making strategic decisions.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): Lieutenant colonels are senior officers who are responsible for leading regiments and making tactical decisions.
- Colonel (COL): Colonels are senior officers who are responsible for leading divisions and making strategic decisions.
General Officer Ranks
General officer ranks are the highest ranks in the military, reserved for those who have demonstrated exceptional leadership potential and have been promoted to the highest ranks. General officers are responsible for leading and commanding entire armies.

- Brigadier General (BG): Brigadier generals are one-star generals who are responsible for leading brigades and making strategic decisions.
- Major General (MG): Major generals are two-star generals who are responsible for leading divisions and making tactical decisions.
- Lieutenant General (LTG): Lieutenant generals are three-star generals who are responsible for leading corps and making strategic decisions.
- General (GEN): Generals are four-star generals who are responsible for leading entire armies and making strategic decisions.
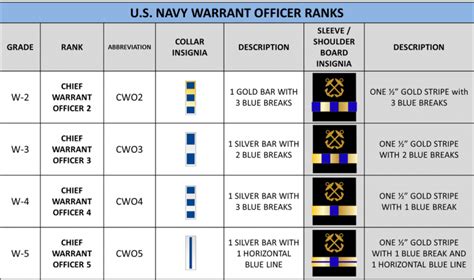
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts who have specialized skills and knowledge. They are responsible for providing technical guidance and support to units.

- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): Warrant officer 1 is the lowest rank among warrant officers, responsible for providing technical guidance and support to units.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): Chief warrant officer 2 is a higher rank than warrant officer 1, responsible for providing technical guidance and support to units.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): Chief warrant officer 3 is a higher rank than chief warrant officer 2, responsible for providing technical guidance and support to units.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): Chief warrant officer 4 is a higher rank than chief warrant officer 3, responsible for providing technical guidance and support to units.
- Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5): Chief warrant officer 5 is the highest rank among warrant officers, responsible for providing technical guidance and support to units.
Military Squad Ranks Image Gallery




In conclusion, understanding military squad ranks is essential for anyone interested in joining the armed forces or simply wanting to learn more about the inner workings of the military. From enlisted personnel to general officers, each rank has its unique responsibilities and authority. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to military squad ranks, and we encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
