Intro
Explore the Navy Enlisted Ranks hierarchy, from E-1 to E-9, in this comprehensive guide. Learn about each ranks responsibilities, requirements, and pay grade. Discover the differences between Seaman, Petty Officer, and Chief Petty Officer ranks, and how to advance in the US Navys enlisted rank structure.
The United States Navy is one of the most prestigious and respected naval forces in the world, with a rich history and a strong tradition of excellence. For those who are interested in joining the Navy, understanding the enlisted ranks is essential. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to Navy enlisted ranks, including the different ranks, their responsibilities, and the requirements for advancement.
Navy Enlisted Rank Structure
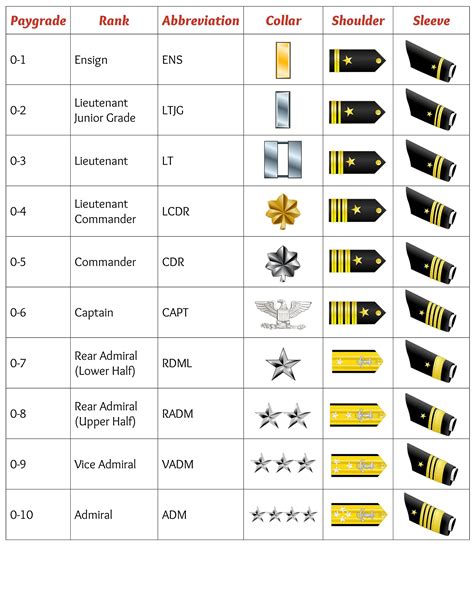
The Navy enlisted rank structure is divided into nine pay grades, ranging from E-1 (Seaman Recruit) to E-9 (Master Chief Petty Officer). Each rank has its own set of responsibilities, requirements, and benefits.
Pay Grades E-1 to E-3: Junior Enlisted Ranks
The junior enlisted ranks in the Navy are the entry-level positions, and they are responsible for learning the basics of naval operations and performing tasks as assigned by their superiors.
- E-1 (Seaman Recruit): This is the lowest enlisted rank in the Navy, and it is the starting point for all new recruits. Seaman Recruits are responsible for learning the basics of naval operations and completing boot camp.
- E-2 (Seaman Apprentice): Seaman Apprentices are one step above Seaman Recruits and are responsible for learning specific skills and trades.
- E-3 (Seaman): Seamen are responsible for performing specific tasks and duties as assigned by their superiors.
Pay Grades E-4 to E-6: Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks

The NCO ranks in the Navy are responsible for leading and supervising junior enlisted personnel.
- E-4 (Petty Officer Third Class): Petty Officers Third Class are responsible for leading small teams and performing specific tasks and duties.
- E-5 (Petty Officer Second Class): Petty Officers Second Class are responsible for leading larger teams and performing more complex tasks and duties.
- E-6 (Petty Officer First Class): Petty Officers First Class are responsible for leading and supervising junior personnel and performing advanced tasks and duties.
Pay Grades E-7 to E-9: Senior Enlisted Ranks
The senior enlisted ranks in the Navy are the highest ranks that can be achieved by enlisted personnel.
- E-7 (Chief Petty Officer): Chief Petty Officers are responsible for leading and supervising junior personnel and performing advanced tasks and duties.
- E-8 (Senior Chief Petty Officer): Senior Chief Petty Officers are responsible for leading and supervising larger teams and performing complex tasks and duties.
- E-9 (Master Chief Petty Officer): Master Chief Petty Officers are the highest enlisted rank in the Navy and are responsible for leading and supervising senior personnel and performing advanced tasks and duties.
Requirements for Advancement

Advancement in the Navy is based on performance, time in grade, and completion of required training and education. To be eligible for advancement, sailors must meet the following requirements:
- Performance: Sailors must demonstrate good performance and a strong work ethic to be eligible for advancement.
- Time in Grade: Sailors must have a certain amount of time in their current grade before they can be eligible for advancement.
- Training and Education: Sailors must complete required training and education to be eligible for advancement.
Special Ratings and NECs

In addition to the regular enlisted ranks, the Navy also has special ratings and NECs (Navy Enlisted Classifications) that are used to identify specific skills and trades.
- Special Ratings: Special ratings are used to identify sailors who have specialized skills and trades, such as aviation, submarines, and special operations.
- NECs: NECs are used to identify sailors who have specific skills and trades, such as electronics, mechanics, and administration.
Gallery of Navy Enlisted Ranks
Navy Enlisted Ranks Image Gallery








In conclusion, understanding the Navy enlisted ranks is essential for anyone who is interested in joining the Navy. By knowing the different ranks, their responsibilities, and the requirements for advancement, sailors can plan their careers and achieve their goals. Whether you are a junior enlisted sailor or a senior enlisted leader, the Navy offers a wide range of opportunities for advancement and professional development.
