Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of the US Army with our comprehensive guide to Army ranks. Learn about the different enlisted, warrant officer, and officer ranks, from Private to General. Understand rank insignia, pay grades, and responsibilities. Discover the progression path and requirements for advancement. Get a detailed overview of the US Army rank structure.
The United States Army is one of the most prestigious and respected institutions in the world, with a rich history and a proud tradition of service. One of the key aspects of the Army's structure is its system of ranks, which provides a clear hierarchy and chain of command. Understanding the different ranks in the US Army can be a complex task, but this comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed explanation of each rank, from the lowest to the highest.
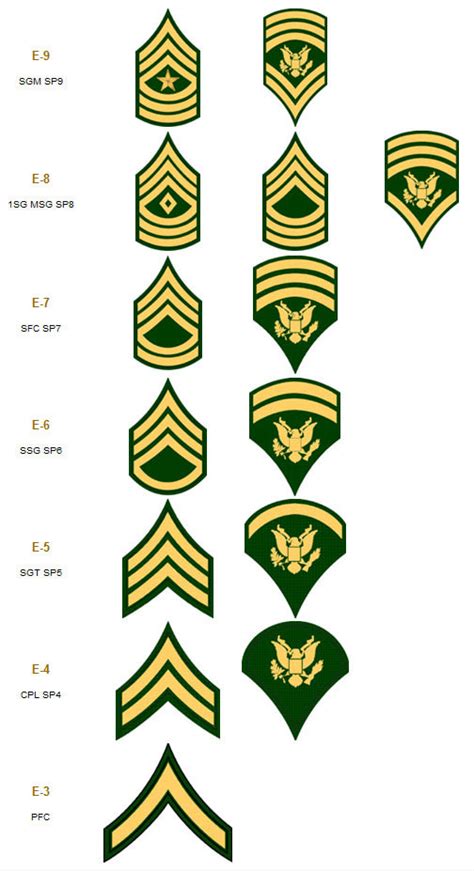
Enlisted Ranks
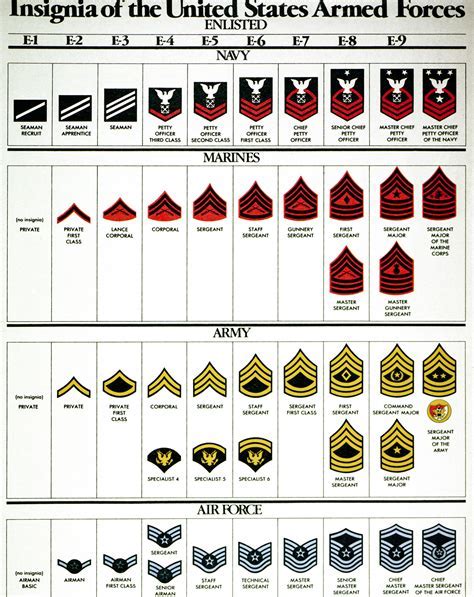

The enlisted ranks in the US Army are the backbone of the organization, making up the majority of its personnel. These ranks are divided into several categories, each with its own unique responsibilities and requirements.
Private (PVT)
The Private (PVT) is the lowest rank in the US Army, and it is the entry-level position for new recruits. Privates are typically assigned to a specific unit and are responsible for completing their initial training and education.
Private Second Class (PV2)
The Private Second Class (PV2) is the second-lowest rank in the US Army, and it is typically attained after a Private has completed their initial training and has gained some experience.
Private First Class (PFC)
The Private First Class (PFC) is a higher rank than the Private Second Class, and it is typically attained after a Private Second Class has demonstrated leadership potential and a strong work ethic.
Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL)
The Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) is a junior non-commissioned officer (NCO) rank, and it is typically attained after a Private First Class has completed advanced training and has demonstrated leadership abilities.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks
The Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) ranks in the US Army are responsible for leading and training enlisted personnel. These ranks are divided into several categories, each with its own unique responsibilities and requirements.
Sergeant (SGT)
The Sergeant (SGT) is a senior NCO rank, and it is typically attained after a Specialist/Corporal has completed advanced training and has demonstrated strong leadership abilities.
Staff Sergeant (SSG)
The Staff Sergeant (SSG) is a higher rank than the Sergeant, and it is typically attained after a Sergeant has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
Sergeant First Class (SFC)
The Sergeant First Class (SFC) is a senior NCO rank, and it is typically attained after a Staff Sergeant has completed advanced training and has demonstrated strong leadership abilities.
Warrant Officer Ranks
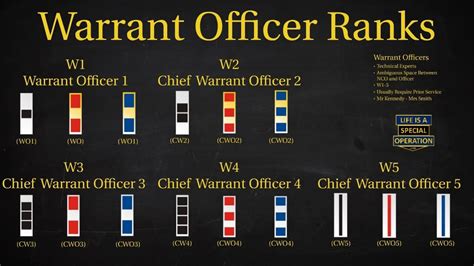
The Warrant Officer ranks in the US Army are technical experts in a specific field, and they are responsible for providing guidance and advice to commanders.
Warrant Officer 1 (WO1)
The Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) is the lowest Warrant Officer rank, and it is typically attained after a Sergeant First Class has completed advanced training and has demonstrated technical expertise.
Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2)
The Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) is a higher rank than the Warrant Officer 1, and it is typically attained after a Warrant Officer 1 has completed advanced training and has demonstrated technical expertise.
Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3)
The Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) is a senior Warrant Officer rank, and it is typically attained after a Chief Warrant Officer 2 has completed advanced training and has demonstrated technical expertise.
Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4)
The Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) is the highest Warrant Officer rank, and it is typically attained after a Chief Warrant Officer 3 has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional technical expertise.
Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5)
The Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) is a rare and exceptional rank, and it is typically attained after a Chief Warrant Officer 4 has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional technical expertise.
Officer Ranks
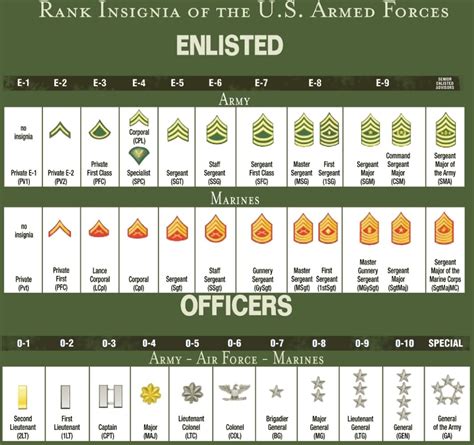
The Officer ranks in the US Army are responsible for leading and commanding units, and they are divided into several categories, each with its own unique responsibilities and requirements.
Second Lieutenant (2LT)
The Second Lieutenant (2LT) is the lowest Officer rank, and it is typically attained after completing Officer Candidate School (OCS) or the United States Military Academy (USMA).
First Lieutenant (1LT)
The First Lieutenant (1LT) is a higher rank than the Second Lieutenant, and it is typically attained after a Second Lieutenant has completed advanced training and has demonstrated leadership abilities.
Captain (CPT)
The Captain (CPT) is a senior Officer rank, and it is typically attained after a First Lieutenant has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
Major (MAJ)
The Major (MAJ) is a higher rank than the Captain, and it is typically attained after a Captain has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
Lieutenant Colonel (LTC)
The Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) is a senior Officer rank, and it is typically attained after a Major has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
Colonel (COL)
The Colonel (COL) is a higher rank than the Lieutenant Colonel, and it is typically attained after a Lieutenant Colonel has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
Brigadier General (BG)
The Brigadier General (BG) is a one-star general officer rank, and it is typically attained after a Colonel has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
Major General (MG)
The Major General (MG) is a two-star general officer rank, and it is typically attained after a Brigadier General has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
Lieutenant General (LTG)
The Lieutenant General (LTG) is a three-star general officer rank, and it is typically attained after a Major General has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
General (GEN)
The General (GEN) is the highest rank in the US Army, and it is typically attained after a Lieutenant General has completed advanced training and has demonstrated exceptional leadership abilities.
US Army Ranks Image Gallery
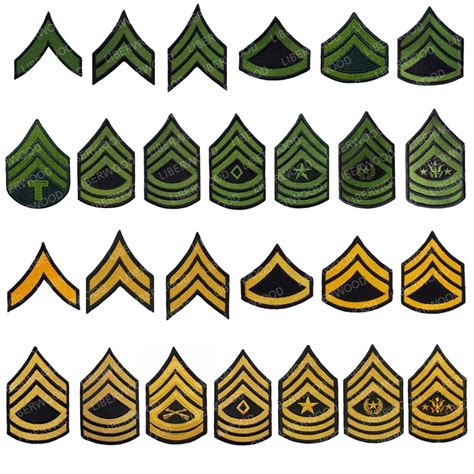








In conclusion, the US Army's rank structure is a complex and nuanced system that provides a clear hierarchy and chain of command. Understanding the different ranks and their responsibilities is essential for anyone looking to join the Army or advance their career. Whether you're a new recruit or a seasoned veteran, this comprehensive guide has provided a detailed explanation of each rank, from the lowest to the highest.
