Intro
Unlock the secrets of retract anatomy, exploring tendon, muscle, and joint interactions, and discover the intricacies of retractile structures in human physiology.
The human body is a complex and fascinating machine, comprising numerous intricate systems that work together in harmony to maintain overall health and function. Understanding the anatomy of the human body is essential for medical professionals, students, and anyone interested in learning about the inner workings of the body. In this article, we will delve into the world of anatomy, exploring its importance, key concepts, and fascinating facts.
Anatomy is the study of the structure and organization of living things, including the human body. It involves the examination of the relationships between different parts of the body, such as bones, muscles, organs, and tissues. By understanding anatomy, we can gain insights into how the body functions, how diseases and injuries affect the body, and how to develop effective treatments and interventions. Whether you are a medical professional, a student, or simply someone interested in learning about the human body, anatomy is a fascinating and essential subject.
The study of anatomy has been ongoing for centuries, with early anatomists such as Galen and Leonardo da Vinci making significant contributions to our understanding of the human body. Today, anatomy remains a vital part of medical education, with students spending countless hours studying and dissecting the human body to gain a deeper understanding of its complexities. However, anatomy is not just for medical professionals; it is also essential for anyone interested in maintaining good health and preventing disease. By understanding how the body works, we can take steps to prevent injuries, manage chronic conditions, and promote overall well-being.
Introduction to Anatomy
Anatomy is a vast and complex field, encompassing the study of the human body from the molecular level to the entire organism. It involves the examination of the relationships between different parts of the body, including the skeletal, muscular, nervous, and circulatory systems. By understanding these relationships, we can gain insights into how the body functions, how diseases and injuries affect the body, and how to develop effective treatments and interventions. In this section, we will explore the key concepts of anatomy, including the different types of anatomy, the importance of anatomy in medicine, and the tools and techniques used to study the human body.
Types of Anatomy
There are several types of anatomy, each focusing on a specific aspect of the human body. These include: * Gross anatomy: the study of the visible structures of the body, such as organs and tissues * Microscopic anatomy: the study of the microscopic structures of the body, such as cells and tissues * Developmental anatomy: the study of the development of the human body from conception to adulthood * Comparative anatomy: the study of the similarities and differences between different speciesThe Skeletal System
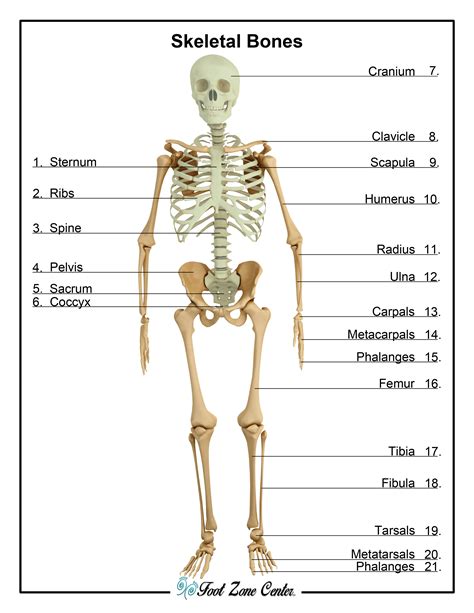
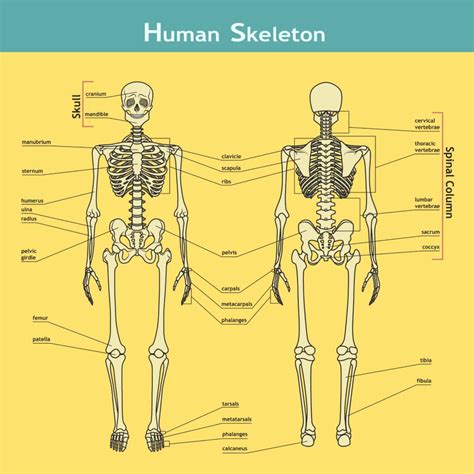
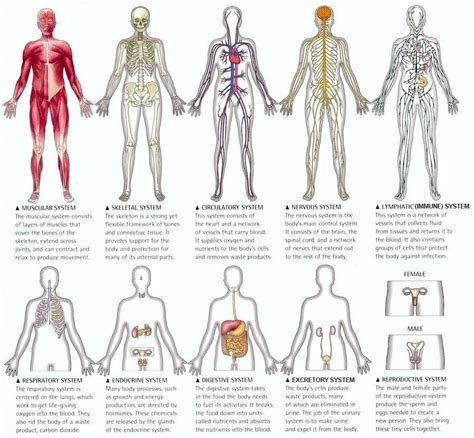
The skeletal system is one of the most fascinating and essential systems in the human body. Comprising 206 bones, the skeletal system provides support, protection, and movement for the body. It also produces blood cells, stores minerals, and regulates the body's pH levels. The skeletal system is divided into two main categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the bones of the skull, spine, ribcage, and sternum, while the appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system performs several essential functions, including: * Support: providing a framework for the body * Protection: protecting internal organs, such as the brain and heart * Movement: providing attachment points for muscles, allowing for movement and locomotion * Blood cell production: producing blood cells in the bone marrow * Mineral storage: storing minerals, such as calcium and phosphorusThe Muscular System

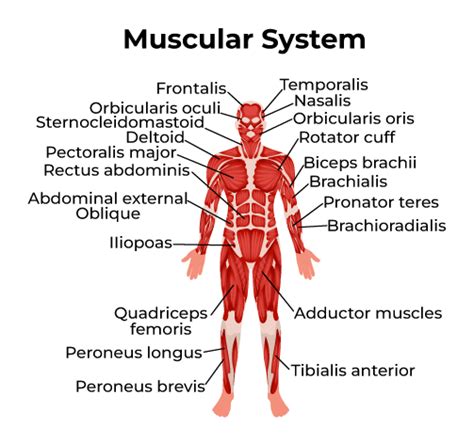
The muscular system is responsible for movement, support, and stability in the human body. Comprising over 600 muscles, the muscular system works in conjunction with the skeletal system to produce movement and maintain posture. There are three types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for voluntary movements, such as walking and running. Smooth muscles are found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the digestive tract, and are responsible for involuntary movements, such as peristalsis. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
Functions of the Muscular System
The muscular system performs several essential functions, including: * Movement: producing movement and locomotion * Support: providing support and stability for the body * Posture: maintaining posture and preventing injury * Blood pressure regulation: regulating blood pressure through the contraction and relaxation of blood vesselsThe Nervous System
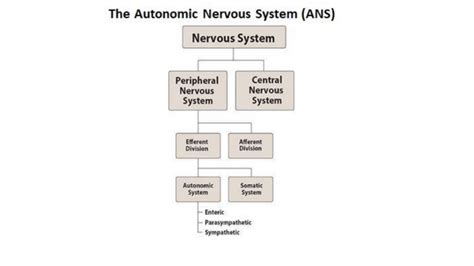
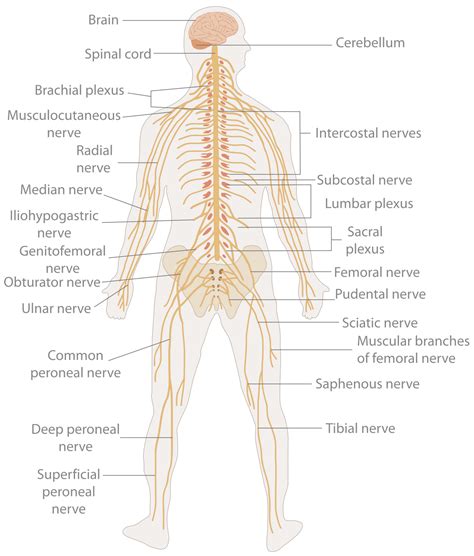
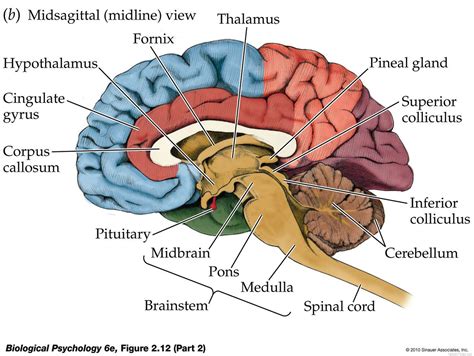
The nervous system is responsible for controlling and coordinating the body's functions, including movement, sensation, perception, and cognition. Comprising the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, the nervous system is a complex and highly specialized system that enables us to interact with the world around us. The nervous system is divided into two main categories: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes the nerves that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body.
Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system performs several essential functions, including: * Control: controlling and coordinating the body's functions * Sensation: detecting and interpreting sensory information * Perception: interpreting and understanding sensory information * Cognition: enabling thought, learning, and memoryThe Circulatory System
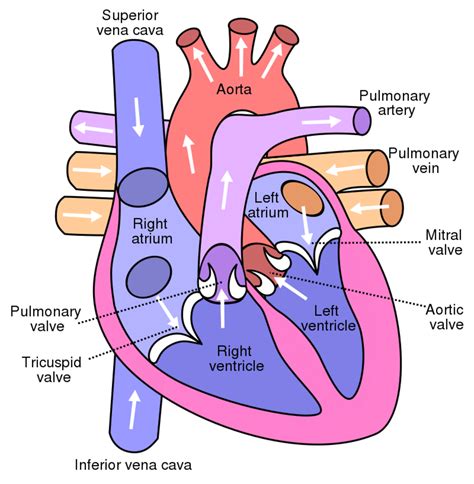
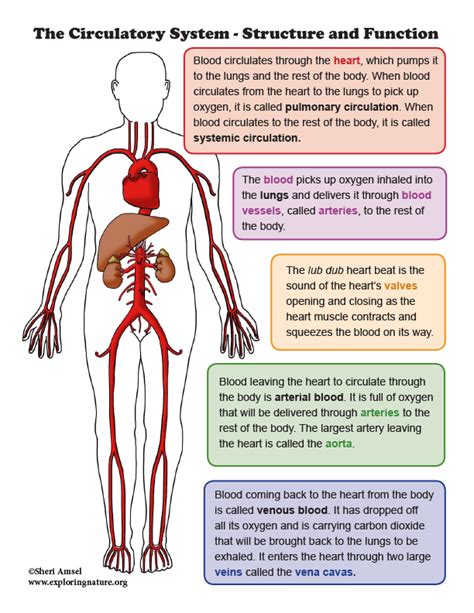
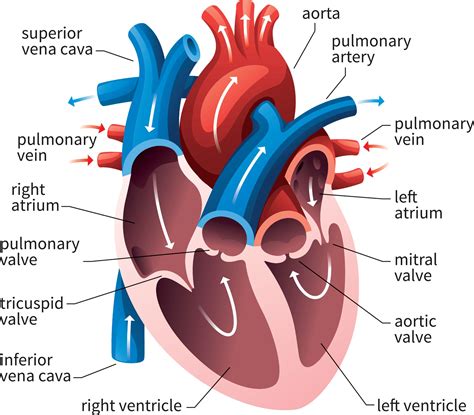
The circulatory system is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. Comprising the heart, blood vessels, and blood, the circulatory system is a vital system that enables the body to function properly. The circulatory system is divided into two main categories: the pulmonary circulation and the systemic circulation. The pulmonary circulation includes the blood vessels that carry blood between the heart and lungs, while the systemic circulation includes the blood vessels that carry blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
Functions of the Circulatory System
The circulatory system performs several essential functions, including: * Oxygenation: delivering oxygen to the body's tissues * Nutrient delivery: delivering nutrients to the body's tissues * Waste removal: removing waste products from the body's tissues * Regulation: regulating body temperature, pH, and blood pressureAnatomy Image Gallery
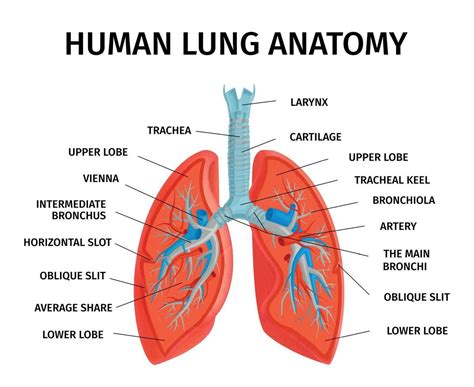
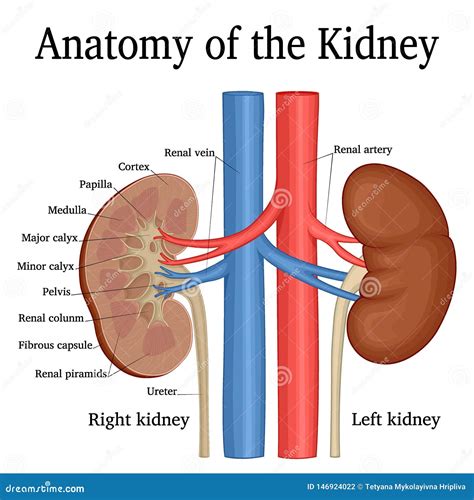
In conclusion, anatomy is a fascinating and essential subject that enables us to understand the complexities of the human body. By studying anatomy, we can gain insights into how the body functions, how diseases and injuries affect the body, and how to develop effective treatments and interventions. Whether you are a medical professional, a student, or simply someone interested in learning about the human body, anatomy is a vital and captivating subject that has the potential to inspire and educate. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about anatomy in the comments below, and to explore further the many wonders of the human body.
