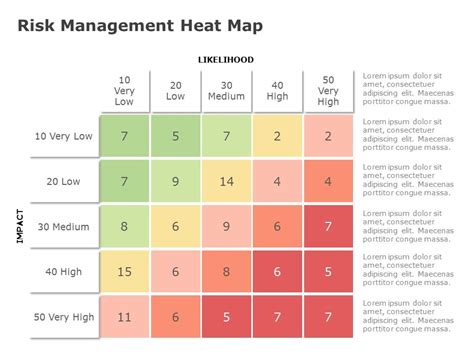
Creating a risk management heat map template is an essential step in identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks within an organization. A heat map is a visual representation of data that uses colors to indicate the level of risk, making it easier to understand and communicate complex risk information. In this article, we will guide you through the 5 steps to create a risk management heat map template.
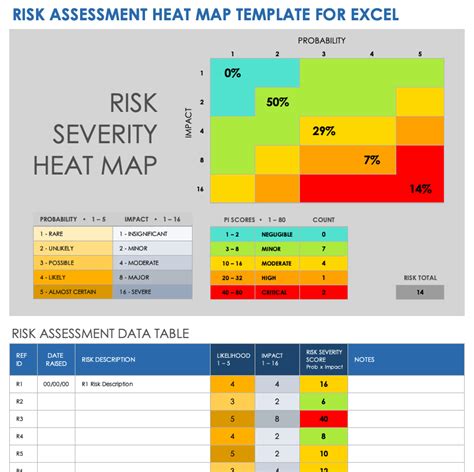
Step 1: Identify Risks and Define Criteria
The first step in creating a risk management heat map template is to identify the risks that your organization faces. This involves gathering data from various sources, including historical data, industry trends, and stakeholder feedback. Once you have identified the risks, define the criteria that will be used to assess and prioritize them. Common criteria include:
- Likelihood of occurrence
- Potential impact
- Velocity of impact
- Persistency of impact
- Detectability of impact
Step 2: Determine the Heat Map Matrix
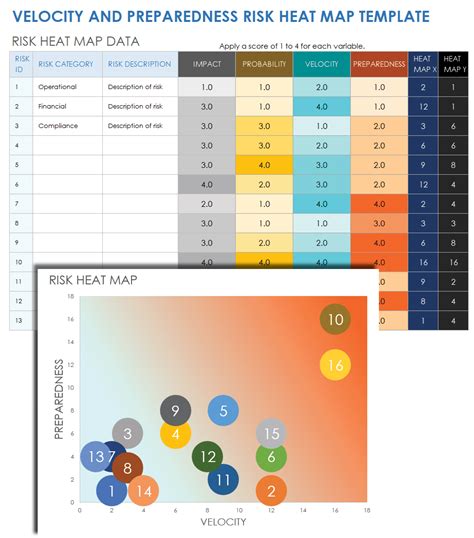
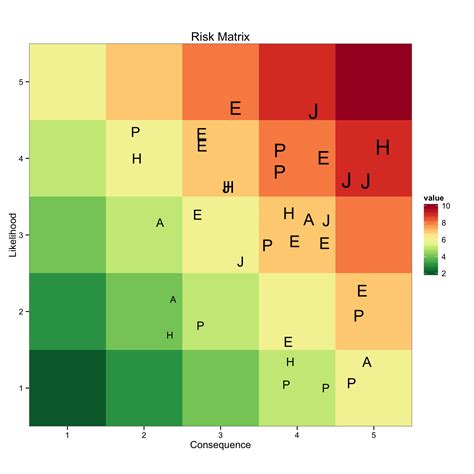
A heat map matrix is a table that consists of rows and columns, with each cell representing a specific combination of risk criteria. The matrix is typically divided into four quadrants, each representing a different level of risk:
- High risk (red)
- Medium risk (yellow)
- Low risk (green)
- Very low risk (blue)
The heat map matrix can be customized to suit your organization's specific needs and risk profile.
Step 3: Assess and Score Risks
Once you have identified the risks and defined the heat map matrix, assess and score each risk based on the criteria defined in Step 1. This involves assigning a score to each risk for each criterion, using a scale such as 1-5 or 1-10. The scores are then used to determine the overall risk level and plot the risk on the heat map matrix.
Step 4: Plot Risks on the Heat Map
Using the scores obtained in Step 3, plot each risk on the heat map matrix. The x-axis typically represents the likelihood of occurrence, while the y-axis represents the potential impact. Each risk is represented by a bubble or a dot on the matrix, with the size and color of the bubble indicating the level of risk.
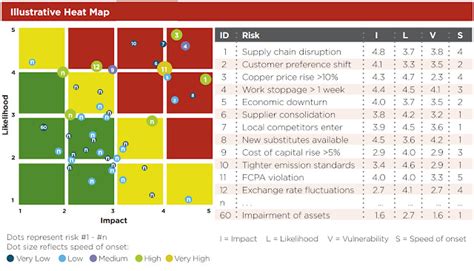
Step 5: Review and Update the Heat Map
The final step is to review and update the heat map regularly. This involves reviewing the risks plotted on the heat map, updating the scores and risk levels as necessary, and ensuring that the heat map remains relevant and accurate.
Benefits of a Risk Management Heat Map Template
A risk management heat map template provides several benefits, including:
- Improved risk visibility and communication
- Enhanced risk prioritization and decision-making
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness in risk management
- Better alignment of risk management with organizational objectives
Common Challenges and Limitations
While a risk management heat map template is a powerful tool for managing risks, there are several common challenges and limitations to consider, including:
- Data quality and availability
- Subjectivity in risk assessment and scoring
- Difficulty in prioritizing risks
- Limited visibility and communication
Best Practices for Implementing a Risk Management Heat Map Template
To get the most out of a risk management heat map template, follow these best practices:
- Use a standardized risk assessment framework
- Ensure data quality and availability
- Involve stakeholders in the risk assessment and prioritization process
- Review and update the heat map regularly
- Use the heat map to inform risk mitigation and management decisions
Conclusion
Creating a risk management heat map template is a critical step in identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks within an organization. By following the 5 steps outlined in this article, you can create a heat map template that provides a clear and visual representation of your organization's risk profile. Remember to review and update the heat map regularly, and use it to inform risk mitigation and management decisions.
Call to Action
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to creating a risk management heat map template. If you have any questions or need further guidance, please leave a comment below. Share this article with your colleagues and peers to help them improve their risk management practices.
Risk Management Heat Map Template Gallery