Intro
Discover the rich history and faith of the Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia. Learn about its formation, key events, and spiritual significance, as well as its impact on Russian diaspora communities worldwide. Explore the Churchs unique traditions, practices, and theology, and understand its role in preserving Russian Orthodox heritage abroad.
The Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia (ROCOR) is a semi-autonomous part of the Russian Orthodox Church, with its own administrative structure and a distinct history that spans over a century. The ROCOR has a significant presence in many countries around the world, including the United States, Australia, and Europe. In this article, we will delve into the history and faith of the ROCOR, exploring its origins, key events, and spiritual practices.
Early History of the ROCOR

The ROCOR was formed in the aftermath of the Russian Revolution of 1917, which led to the establishment of the Soviet Union and the persecution of the Russian Orthodox Church. Many Russian Orthodox clergy and laity were forced to flee their homeland, seeking refuge in other countries. In 1920, a group of Russian Orthodox bishops, led by Metropolitan Anthony (Khrapovitsky), gathered in Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) to discuss the future of the Russian Orthodox Church.
Establishment of the ROCOR
The bishops decided to establish a temporary church administration outside of Russia, which would serve the spiritual needs of Russian Orthodox Christians living abroad. This administration would later become the Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia. In 1922, the ROCOR was officially established, with its headquarters in Sremski Karlovci, Yugoslavia (now Serbia).
Growth and Development of the ROCOR
During the 1920s and 1930s, the ROCOR experienced significant growth, with the establishment of new parishes and monasteries in Europe, North America, and Australia. The ROCOR also established its own seminaries and theological institutions, which provided education and training for clergy and laity.
Relationship with the Moscow Patriarchate
The ROCOR's relationship with the Moscow Patriarchate, the governing body of the Russian Orthodox Church in Russia, has been complex and often tumultuous. In the early years, the ROCOR was seen as a rival to the Moscow Patriarchate, which was viewed as being under the control of the Soviet government. However, in 2007, the ROCOR and the Moscow Patriarchate signed the Act of Canonical Communion, which restored full communion between the two churches.
Spiritual Practices and Traditions

The ROCOR is known for its rich spiritual practices and traditions, which are rooted in Russian Orthodox theology and culture. Some of the key practices and traditions include:
- The veneration of icons and relics
- The celebration of the Divine Liturgy and other sacraments
- The observance of fasting periods, such as Lent and Advent
- The use of the Julian calendar to determine the dates of feasts and fasts
- The importance of monasticism and the role of monasteries in the life of the Church
Monasticism in the ROCOR
Monasticism plays a significant role in the life of the ROCOR, with many monasteries and convents located around the world. Monasteries in the ROCOR are known for their strict asceticism and their commitment to prayer and work. Some of the most famous monasteries in the ROCOR include the Holy Trinity Monastery in Jordanville, New York, and the Lesna Convent in France.
Challenges and Controversies
The ROCOR has faced several challenges and controversies throughout its history, including disagreements with the Moscow Patriarchate and internal conflicts. Some of the key challenges and controversies include:
- The ROCOR's relationship with the Moscow Patriarchate, which has been complex and often tumultuous
- Internal conflicts within the ROCOR, including disagreements over the role of the Church in society and the use of the Julian calendar
- The ROCOR's response to modernity and secularism, including issues related to ecumenism and the ordination of women
Conclusion
The Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia is a complex and multifaceted institution, with a rich history and a distinct spiritual tradition. Despite facing several challenges and controversies throughout its history, the ROCOR remains a vibrant and important part of the global Orthodox community.
ROCOR Image Gallery
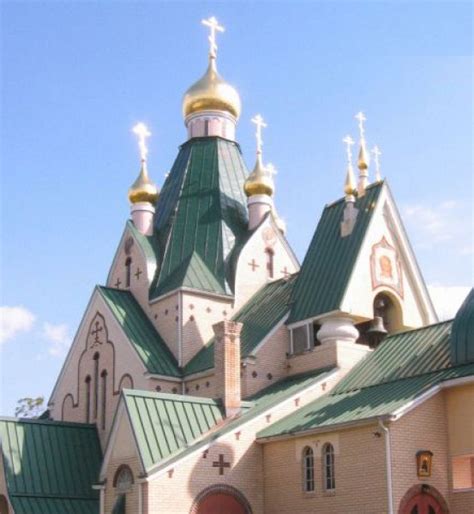
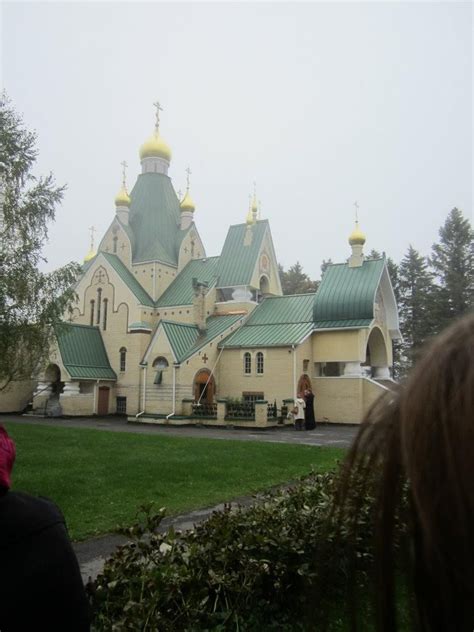
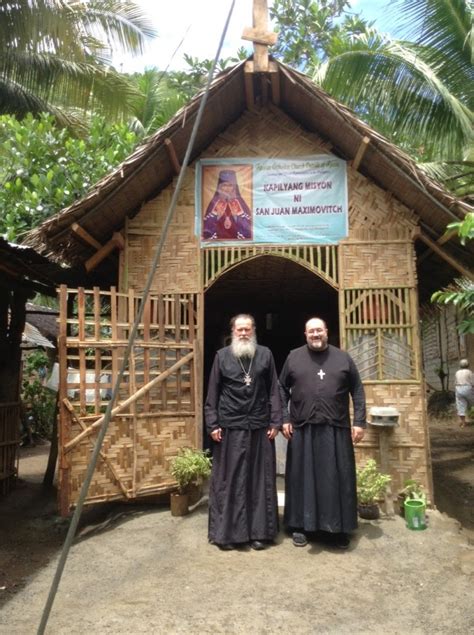









We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative overview of the Russian Orthodox Church Outside Russia. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments below, and to explore our website for more information on the ROCOR and other topics related to Orthodox Christianity.
