Random selection is a crucial aspect of data analysis, statistical modeling, and even gaming. In Excel, there are several ways to select random data points, numbers, or items from a list. Whether you're a data analyst, a researcher, or a gamer, this article will guide you through five different methods to select randomly in Excel.
Method 1: Using the RAND Function
The RAND function is a simple and straightforward way to generate random numbers in Excel. This function returns a random number between 0 and 1. To use the RAND function, follow these steps:
- Select the cell where you want to generate the random number.
- Type "=RAND()" and press Enter.
- The cell will display a random number between 0 and 1.
- To generate a random integer, multiply the RAND function by the maximum number you want to generate. For example, "=RAND()*100" will generate a random integer between 0 and 100.
Example: Generating Random Numbers for a Lottery
Suppose you want to generate random numbers for a lottery drawing. You can use the RAND function to generate six unique random numbers between 1 and 49.
| A | |
|---|---|
| 1 | =RAND()*49+1 |
| 2 | =RAND()*49+1 |
| 3 | =RAND()*49+1 |
| 4 | =RAND()*49+1 |
| 5 | =RAND()*49+1 |
| 6 | =RAND()*49+1 |
To ensure that the numbers are unique, you can use the following formula:
=IF(COUNTIF(A:A, RAND()*49+1)>0, RAND()*49+1, RAND()*49+1)
This formula checks if the generated number already exists in column A. If it does, it generates a new number.
Method 2: Using the RANK and RAND Functions
This method involves ranking a list of items randomly using the RANK and RAND functions. Here's how:
- Select the list of items you want to rank randomly.
- In a new column, enter the formula "=RAND()" next to each item.
- Use the RANK function to rank the items based on the random numbers. For example, "=RANK(A2, A:A)" will rank the item in cell A2 based on the random number in cell B2.
- Sort the list by the random numbers to get the randomly ranked list.
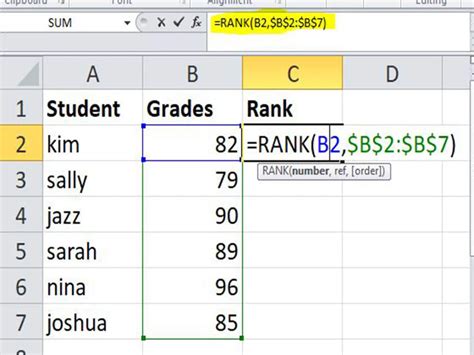
Example: Randomly Ranking a List of Students
Suppose you have a list of students and you want to rank them randomly for a school project. You can use the RANK and RAND functions to achieve this.
| Student | Random Number | Rank |
|---|---|---|
| John | =RAND() | =RANK(A2, A:A) |
| Mary | =RAND() | =RANK(A3, A:A) |
| David | =RAND() | =RANK(A4, A:A) |
| Emily | =RAND() | =RANK(A5, A:A) |
| James | =RAND() | =RANK(A6, A:A) |
Sort the list by the random numbers to get the randomly ranked list of students.
Method 3: Using the INDEX and RAND Functions
This method involves using the INDEX and RAND functions to select a random item from a list. Here's how:
- Select the list of items you want to select randomly.
- Use the INDEX function to return a random item from the list. For example, "=INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1)" will return a random item from column A.
- To ensure that the item is unique, you can use the following formula:
=IF(COUNTIF(A:A, INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1))>0, INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1), INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1))
This formula checks if the selected item already exists in column A. If it does, it selects a new item.

Example: Selecting a Random Winner for a Contest
Suppose you have a list of contestants for a contest and you want to select a random winner. You can use the INDEX and RAND functions to achieve this.
| Contestant |
|---|
| John |
| Mary |
| David |
| Emily |
| James |
Use the following formula to select a random winner:
=INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1)
To ensure that the winner is unique, you can use the formula:
=IF(COUNTIF(A:A, INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1))>0, INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1), INDEX(A:A, RAND()*COUNT(A:A)+1))
Method 4: Using VBA Macros
You can also use VBA macros to select random data points or items from a list in Excel. Here's an example of a VBA macro that selects a random item from a list:
Sub SelectRandomItem() Dim myList As Range Set myList = Range("A1:A10") Dim randomItem As Range Set randomItem = myList.Cells(Int((myList.Count) * Rnd) + 1) MsgBox randomItem.Value End Sub
To run this macro, follow these steps:
- Open the Visual Basic Editor by pressing Alt+F11 or by navigating to Developer > Visual Basic.
- In the Visual Basic Editor, click Insert > Module to insert a new module.
- Paste the VBA macro code into the module.
- Click Run > Run Sub/UserForm to run the macro.
Method 5: Using Power Query
Power Query is a powerful data manipulation tool in Excel that allows you to select random data points or items from a list. Here's an example of how to use Power Query to select a random item from a list:
- Select the list of items you want to select randomly.
- Go to the Data tab and click From Table/Range.
- In the Power Query Editor, click Add Column > Custom Column.
- Enter the following formula:
= Table.Sample(tbl, 1)
This formula selects a random item from the table.
- Click OK to close the Power Query Editor.
- The random item will be displayed in a new column.
Example: Selecting a Random Sample for Data Analysis
Suppose you have a large dataset and you want to select a random sample for data analysis. You can use Power Query to achieve this.
| ID | Name | Age |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | 25 |
| 2 | Mary | 31 |
| 3 | David | 42 |
| 4 | Emily | 28 |
| 5 | James | 35 |
Use the following formula to select a random sample:
= Table.Sample(tbl, 10)
This formula selects a random sample of 10 items from the table.
Random Selection in Excel Image Gallery






We hope this article has helped you learn five different ways to select randomly in Excel. Whether you're a data analyst, a researcher, or a gamer, these methods can help you generate random numbers, select random items from a list, and even create random samples for data analysis. Do you have any questions or need further assistance? Please leave a comment below.
