Intro
Discover the quirks of Italys boot-shaped geography and the humorous anecdotes surrounding it. From the toe to the heel, explore the countrys unique peninsula shape and the comedic misadventures that come with it. Learn about the fascinating history, geography, and cultural references that make Italys boot-shaped geography a laughing matter.
Italy's unique geography has been a subject of fascination for many, with its distinctive boot shape drawing comparisons and jokes from around the world. But what's behind this peculiar shape, and what does it mean for the country's climate, culture, and history?
Italy's geography is a complex mix of mountains, hills, and coastlines, shaped by millions of years of tectonic activity and erosion. The Apennine Mountains, which stretch from the northern regions of Liguria and Piedmont to the southernmost tip of Calabria, form the backbone of the country and give it its characteristic boot shape. This mountain range is not only a defining feature of Italy's geography but also plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, economy, and cultural identity.
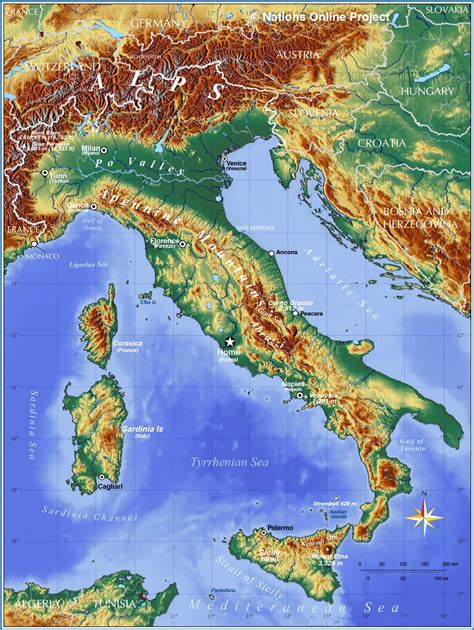
Climate and Geography: A Delicate Balance
Italy's geography has a profound impact on its climate, with the Apennine Mountains creating a rain shadow effect that divides the country into two distinct climatic zones. The northern regions, which are closer to the Alps, have a more temperate climate with cold winters and warm summers, while the southern regions have a Mediterranean climate with hot summers and mild winters. This diversity of climates supports a wide range of flora and fauna, making Italy one of the most biodiverse countries in Europe.
The country's geography also influences its economy, with the Apennine Mountains providing rich mineral deposits, fertile valleys, and picturesque coastlines that attract tourists from around the world. Italy's unique geography has also shaped its cultural identity, with the country's regions developing distinct traditions, languages, and cuisines that reflect their local environment and history.
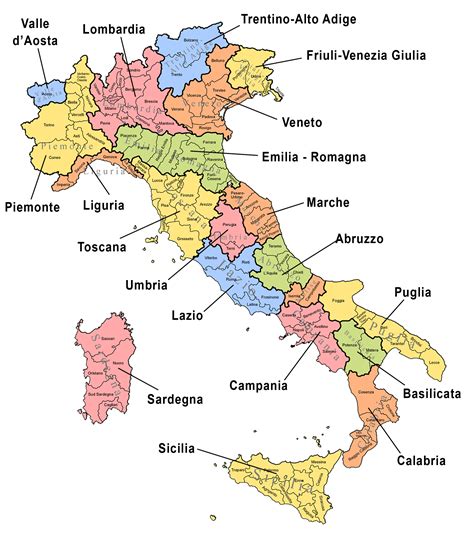
The Regions of Italy: A Geographical and Cultural Tour
Italy is divided into 20 regions, each with its unique geography, culture, and history. From the snow-capped mountains of the north to the sun-kissed beaches of the south, each region has its own distinct character and charm.
- Northern Italy: The northern regions of Liguria, Piedmont, and Lombardy are known for their stunning mountain scenery, picturesque lakes, and vibrant cities like Milan and Turin.
- Central Italy: The central regions of Tuscany, Umbria, and Marche are famous for their rolling hills, charming hilltop towns, and world-class wine production.
- Southern Italy: The southern regions of Campania, Apulia, and Calabria are known for their stunning coastlines, ancient ruins, and vibrant cities like Naples and Bari.
- Islands of Italy: The islands of Sicily and Sardinia are popular tourist destinations, with their beautiful beaches, crystal-clear waters, and rich cultural heritage.

The Apennine Mountains: A Spine of Stone
The Apennine Mountains are a rugged and scenic range that stretches from the northern regions of Liguria and Piedmont to the southernmost tip of Calabria. This mountain range is not only a defining feature of Italy's geography but also plays a crucial role in shaping its climate, economy, and cultural identity.
- Geology: The Apennine Mountains are a complex mix of limestone, granite, and sandstone, formed over millions of years of tectonic activity and erosion.
- Climate: The Apennine Mountains create a rain shadow effect that divides Italy into two distinct climatic zones, with the northern regions having a more temperate climate and the southern regions having a Mediterranean climate.
- Economy: The Apennine Mountains provide rich mineral deposits, fertile valleys, and picturesque coastlines that attract tourists from around the world.
- Culture: The Apennine Mountains have shaped Italy's cultural identity, with the country's regions developing distinct traditions, languages, and cuisines that reflect their local environment and history.

Italy's Geography in the Modern Era
Italy's geography continues to play a crucial role in shaping its economy, culture, and identity in the modern era. From tourism and agriculture to industry and infrastructure, the country's unique geography presents both opportunities and challenges.
- Tourism: Italy's stunning landscapes, picturesque towns, and rich cultural heritage make it one of the world's most popular tourist destinations.
- Agriculture: Italy's fertile valleys and mild climate make it an ideal place for growing a wide range of crops, from wheat and olives to grapes and tomatoes.
- Industry: Italy's geography has also shaped its industry, with the country's northern regions being home to some of the world's leading manufacturers of cars, machinery, and textiles.
- Infrastructure: Italy's geography has also presented challenges for infrastructure development, with the country's mountainous terrain making it difficult to build roads, railways, and other transportation networks.

Conclusion
Italy's geography is a complex and fascinating topic that has shaped the country's climate, economy, culture, and identity. From the Apennine Mountains to the Mediterranean coast, Italy's unique geography presents both opportunities and challenges for the country and its people. Whether you're interested in history, culture, or simply exploring one of the world's most beautiful countries, Italy's geography is sure to captivate and inspire.
Gallery of Italian Geography










We hope you enjoyed this article about Italy's geography. Whether you're interested in history, culture, or simply exploring one of the world's most beautiful countries, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below.
