Intro
Identify deception with ease! Learn the 5 telltale signs of shenanigans and malarkey in our expert guide. From detecting insincere flattery to recognizing manipulation tactics, well arm you with the knowledge to spot nonsense and lies. Boost your critical thinking skills and stay vigilant against deceitful behavior with our informative article.
Are you tired of being duped by misleading information, pseudoscience, and outright fabrications? In today's world, it's easier than ever to spread misinformation, and it's up to us to be vigilant and critical thinkers. Spotting shenanigans and malarkey requires a keen eye, a healthy dose of skepticism, and a solid understanding of how to evaluate information. Here are five ways to help you separate fact from fiction and avoid getting taken in by nonsense.
1. Be Wary of Emotional Appeals
Emotional appeals are a powerful tool used to sway people's opinions and decisions. They often involve storytelling, vivid imagery, or emotional manipulation to create a strong reaction. While emotions can be a legitimate way to connect with others, they can also be used to deceive and manipulate. Be cautious of information that relies heavily on emotional appeals, especially if it lacks concrete evidence or logical reasoning.
For instance, consider a charity ad that features a heartbreaking image of a malnourished child, accompanied by a plea for donations. While the image may evoke strong emotions, it's essential to look beyond the emotional appeal and investigate the charity's legitimacy, transparency, and effectiveness. Remember, a well-crafted emotional appeal can be just as convincing as a well-crafted lie.
How to Spot Emotional Appeals
- Look for vivid imagery, storytelling, or sensational language.
- Check if the information is backed by concrete evidence or logical reasoning.
- Be wary of appeals that target your emotions rather than your rational thinking.
- Investigate the source and credibility of the information.
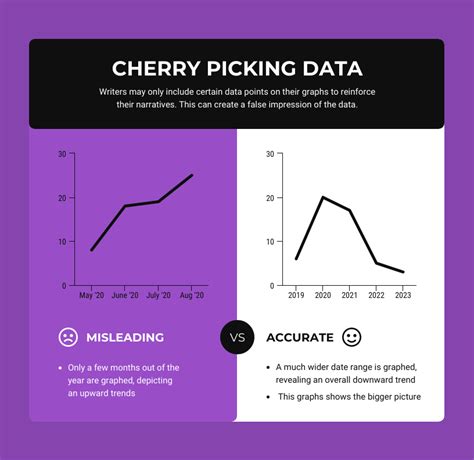
2. Watch Out for Cherry-Picked Data
Cherry-picked data is a common tactic used to misrepresent information and support a particular agenda. It involves selectively presenting data that supports a claim while ignoring or downplaying contradictory evidence. This can create a misleading narrative that convinces people of a false or exaggerated truth.
For example, consider a news article that claims a new diet is the key to weight loss, citing a study that shows a significant reduction in weight among participants. However, upon closer inspection, you find that the study was small, poorly designed, and had a high dropout rate. Moreover, the article ignores other studies that found no significant weight loss associated with the diet.
How to Spot Cherry-Picked Data
- Look for selective presentation of data that supports a particular claim.
- Check if the data is based on a small or biased sample size.
- Investigate if the study or data has been peer-reviewed or replicated.
- Be wary of studies that have a clear conflict of interest or agenda.
3. Be Cautious of Unqualified or Biased Sources

Unqualified or biased sources can be a significant source of misinformation. This includes sources that lack expertise or credentials in the relevant field, as well as those with a clear conflict of interest or agenda. Be cautious of sources that present themselves as authorities but lack the necessary qualifications or credentials.
For instance, consider a celebrity endorsement of a health supplement. While the celebrity may be well-known and influential, they are unlikely to have the necessary expertise or credentials to endorse a health supplement. Similarly, be wary of sources that have a clear conflict of interest, such as a pharmaceutical company promoting a new medication.
How to Spot Unqualified or Biased Sources
- Check the source's credentials and expertise in the relevant field.
- Look for any potential conflicts of interest or agendas.
- Investigate if the source has a history of promoting misinformation or pseudoscience.
- Be wary of sources that rely on anecdotal evidence or personal testimonials.
4. Don't Fall for the Appeal to Authority

The appeal to authority is a common tactic used to convince people of a particular claim or idea. It involves citing the opinions or endorsements of authority figures, such as experts, celebrities, or thought leaders. While authority figures can be a valuable source of information, they are not infallible, and their opinions should be subject to scrutiny and evaluation.
For example, consider a claim that a new medication is safe and effective, citing the endorsement of a well-known doctor. While the doctor may be an authority in their field, their endorsement is not necessarily a guarantee of the medication's safety or efficacy. It's essential to look beyond the appeal to authority and evaluate the evidence for yourself.
How to Spot the Appeal to Authority
- Be cautious of claims that rely heavily on the opinions or endorsements of authority figures.
- Check if the authority figure has expertise in the relevant field.
- Investigate if the authority figure has a conflict of interest or agenda.
- Look for evidence-based information that supports the claim.
5. Be Skeptical of Unfalsifiable Claims

Unfalsifiable claims are statements that cannot be proven or disproven through empirical evidence or logical reasoning. These claims are often used to promote pseudoscience, superstition, or other forms of misinformation. Be skeptical of claims that are too vague, too broad, or too absolute to be tested or falsified.
For instance, consider a claim that a new energy drink can improve mental clarity and focus. While the claim may sound appealing, it's impossible to test or falsify, as mental clarity and focus are subjective experiences that cannot be measured or quantified. Be wary of claims that are too good (or bad) to be true, as they may be based on unfalsifiable assumptions or evidence.
How to Spot Unfalsifiable Claims
- Be cautious of claims that are too vague, too broad, or too absolute.
- Check if the claim can be tested or falsified through empirical evidence or logical reasoning.
- Investigate if the claim is based on anecdotal evidence or personal testimonials.
- Be wary of claims that rely on unproven assumptions or evidence.
Gallery of Critical Thinking









In conclusion, spotting shenanigans and malarkey requires a critical and discerning mindset. By being aware of emotional appeals, cherry-picked data, unqualified or biased sources, the appeal to authority, and unfalsifiable claims, you can make more informed decisions and avoid falling prey to misinformation. Remember to always evaluate evidence critically, consider multiple perspectives, and avoid bias and assumptions. With these skills, you'll be well-equipped to navigate the complex information landscape and make informed choices in your personal and professional life.
We'd love to hear from you! Share your thoughts and experiences with spotting shenanigans and malarkey in the comments below.
