Discover 5 ways solvolysis reactions enhance chemical processes, including nucleophilic substitution, hydrolysis, and elimination, with applications in organic chemistry and synthesis.
The study of solvolysis reactions is a crucial aspect of organic chemistry, as it provides valuable insights into the mechanisms of chemical reactions and the properties of molecules. Solvolysis reactions involve the cleavage of a molecule using a solvent, and they play a significant role in various industrial and biological processes. In this article, we will delve into the world of solvolysis reactions and explore five key ways in which they occur.
Solvolysis reactions are essential in understanding the behavior of molecules in different environments. By studying these reactions, chemists can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence the stability and reactivity of molecules. This knowledge can be applied in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and biotechnology. Furthermore, solvolysis reactions are also important in understanding biological processes, such as enzyme-catalyzed reactions and the metabolism of drugs.
The importance of solvolysis reactions cannot be overstated, as they have far-reaching implications in various areas of science and technology. For instance, solvolysis reactions are used in the synthesis of complex molecules, such as pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. They are also used in the development of new materials, such as polymers and nanomaterials. In addition, solvolysis reactions play a crucial role in understanding environmental processes, such as the degradation of pollutants and the fate of chemicals in the environment.
Introduction to Solvolysis
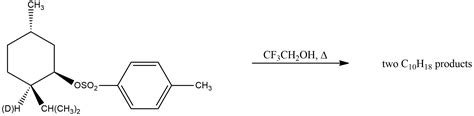
Factors Influencing Solvolysis Reactions
Several factors can influence the rate and outcome of solvolysis reactions, including the nature of the solvent, the temperature, and the presence of catalysts. The solvent can play a crucial role in solvolysis reactions, as it can participate in the reaction mechanism and influence the stability of the reactants and products. For example, polar solvents can facilitate the formation of ions and radicals, while non-polar solvents can stabilize neutral molecules.Types of Solvolysis Reactions
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
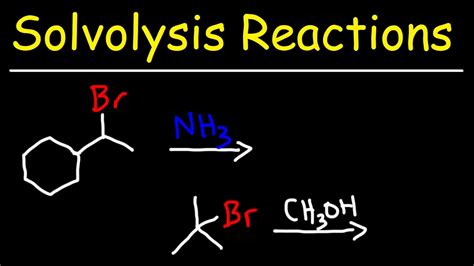
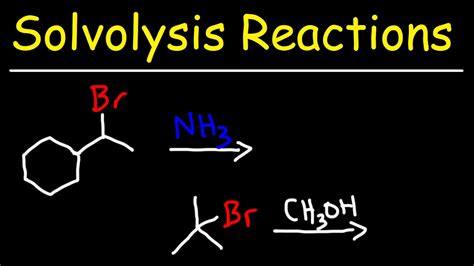
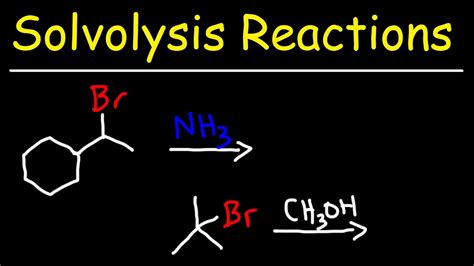
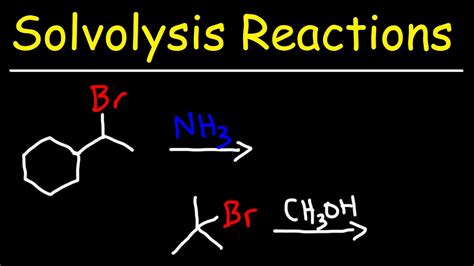
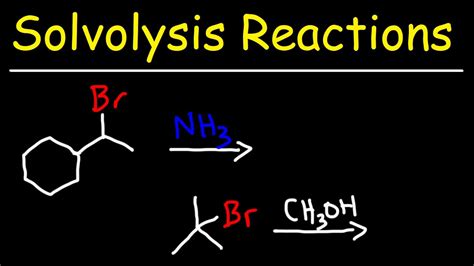
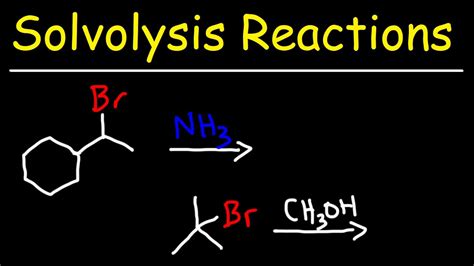
Nucleophilic substitution reactions are a common type of solvolysis reaction, where a nucleophile replaces a leaving group in a molecule. These reactions can occur through various mechanisms, including the SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. The SN1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate, while the SN2 mechanism involves a concerted mechanism with a transition state.Applications of Solvolysis Reactions
Pharmaceutical Applications
Solvolysis reactions are essential in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, as they allow for the formation of complex molecules with specific properties. For instance, solvolysis reactions can be used to introduce functional groups, such as hydroxyl or amino groups, into a molecule. These functional groups can significantly influence the biological activity of a molecule, making solvolysis reactions a crucial step in the development of new drugs.5 Ways Solvolysis Occurs
Nucleophilic Substitution
Nucleophilic substitution reactions involve the replacement of a leaving group by a nucleophile. These reactions can occur through various mechanisms, including the SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. The SN1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate, while the SN2 mechanism involves a concerted mechanism with a transition state.Elimination
Elimination reactions involve the removal of a leaving group and a beta-hydrogen atom, resulting in the formation of a new bond. These reactions can occur through various mechanisms, including the E1 and E2 mechanisms. The E1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate, while the E2 mechanism involves a concerted mechanism with a transition state.Fragmentation
Fragmentation reactions involve the cleavage of a molecule into two or more fragments, often resulting in the formation of radicals or ions. These reactions can occur through various mechanisms, including homolytic and heterolytic cleavage. Homolytic cleavage involves the formation of radicals, while heterolytic cleavage involves the formation of ions.Rearrangement
Rearrangement reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms within a molecule, resulting in the formation of a new compound. These reactions can occur through various mechanisms, including intramolecular and intermolecular rearrangements. Intramolecular rearrangements involve the rearrangement of atoms within a single molecule, while intermolecular rearrangements involve the rearrangement of atoms between two or more molecules.Radical Reactions
Radical reactions involve the formation of radicals, which are highly reactive species that can participate in various reactions. These reactions can occur through various mechanisms, including homolytic and heterolytic cleavage. Homolytic cleavage involves the formation of radicals, while heterolytic cleavage involves the formation of ions.Solvolysis Image Gallery
In conclusion, solvolysis reactions are a crucial aspect of organic chemistry, with numerous applications in various fields. By understanding the mechanisms and factors that control these reactions, chemists can develop new methods for synthesizing complex molecules and materials. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of solvolysis reactions and their importance in modern chemistry. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to share them with us. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with your colleagues and friends who may be interested in learning more about solvolysis reactions.
