Intro
Unlock the hierarchy of elite warriors with our detailed explanation of the Special Forces ranking system. Discover the rigorous structure, from initial training to highest honors, and understand the significance of each rank, including Lieutenant, Captain, and Sergeant, in the secretive world of special operations forces, Green Berets, and counterterrorism units.
The special forces ranking system is a complex and multifaceted hierarchy that governs the career progression of special forces operatives in the United States military. This ranking system is designed to recognize and reward the unique skills, training, and experience that special forces operatives bring to their roles. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the special forces ranking system, exploring the different ranks, their responsibilities, and the requirements for advancement.
The Importance of Rank in Special Forces
Rank is a crucial aspect of the special forces, as it not only reflects an operative's level of experience and expertise but also their leadership potential and ability to take on increasingly complex missions. The special forces ranking system is designed to identify and promote the most capable and dedicated operatives, ensuring that the most critical missions are led by the most qualified individuals.

The Enlisted Ranks
The enlisted ranks in the special forces are the backbone of the organization, comprising the majority of operatives. These ranks are responsible for executing the day-to-day missions and operations of the special forces.
Enlisted Ranks in Special Forces
- Private (PVT): The entry-level rank in the special forces, privates are new recruits who have just completed Basic Underwater Demolition/SEAL (BUD/S) training or the Special Forces Qualification Course (SFQC).
- Private First Class (PFC): A junior enlisted rank, private first class operatives have completed their initial training and are beginning to gain experience in the special forces.
- Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL): A senior enlisted rank, specialists/corporals have demonstrated leadership potential and are responsible for leading small teams and executing complex missions.
- Sergeant (SGT): A mid-level enlisted rank, sergeants are experienced operatives who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and tactical skills.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): A senior enlisted rank, staff sergeants are responsible for leading large teams and executing high-level missions.

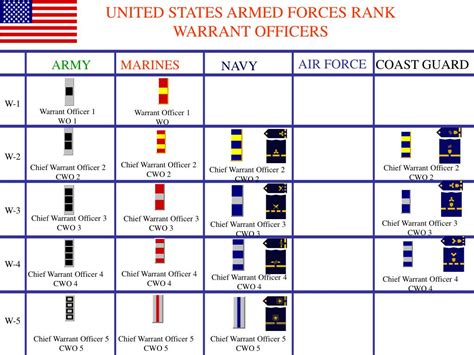
The Warrant Officer Ranks
The warrant officer ranks in the special forces are technical experts who have specialized skills and knowledge. These ranks are responsible for providing technical expertise and support to the enlisted ranks.
Warrant Officer Ranks in Special Forces
- Warrant Officer 1 (WO1): The entry-level warrant officer rank, WO1s are technical experts who have completed the Warrant Officer Candidate School (WOCS) and have specialized skills in areas such as communications or intelligence.
- Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2): A mid-level warrant officer rank, CW2s are experienced technical experts who have demonstrated exceptional skills and knowledge in their area of expertise.
- Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3): A senior warrant officer rank, CW3s are highly experienced technical experts who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and technical skills.
- Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4): The highest warrant officer rank, CW4s are master technical experts who have demonstrated exceptional skills and knowledge in their area of expertise.
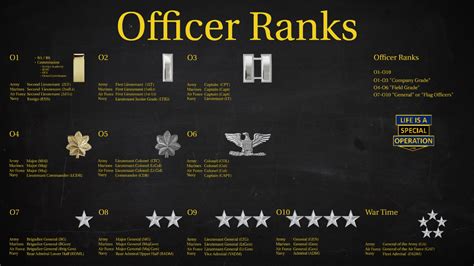
The Officer Ranks
The officer ranks in the special forces are leaders who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and tactical skills. These ranks are responsible for leading large teams and executing high-level missions.
Officer Ranks in Special Forces
- Second Lieutenant (2LT): The entry-level officer rank, 2LTs are new officers who have completed the Special Forces Qualification Course (SFQC) and have demonstrated leadership potential.
- First Lieutenant (1LT): A junior officer rank, 1LTs are experienced officers who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and tactical skills.
- Captain (CPT): A mid-level officer rank, captains are experienced leaders who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and tactical skills.
- Major (MAJ): A senior officer rank, majors are highly experienced leaders who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and tactical skills.
- Lieutenant Colonel (LTC): The highest officer rank, lieutenant colonels are master leaders who have demonstrated exceptional leadership and tactical skills.
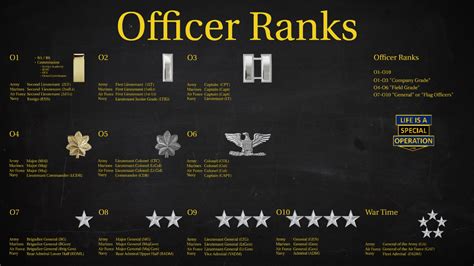
Gallery of Special Forces Ranks
Special Forces Rank Gallery








Conclusion
The special forces ranking system is a complex and multifaceted hierarchy that recognizes and rewards the unique skills, training, and experience of special forces operatives. Understanding this ranking system is essential for anyone interested in pursuing a career in the special forces. Whether you're an enlisted operative, a warrant officer, or an officer, the special forces ranking system provides a clear path for career progression and advancement. We hope this article has provided valuable insights into the special forces ranking system and has inspired you to learn more about this elite organization.
We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this article. Have you served in the special forces or are you interested in learning more about this elite organization? Share your experiences and questions in the comments below!
