Intro
Unlock the secrets of sound propagation! Discover the speed of sound in kilometers per second, how it varies with temperature, humidity, and air pressure. Learn about the science behind sonic booms, shockwaves, and supersonic flight. Get the facts on acoustic physics and the speed of sound in different environments.
The speed of sound is a fundamental concept in physics that has fascinated humans for centuries. It's a measure of how fast sound waves propagate through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. In this article, we'll delve into the speed of sound in kilometers per second, exploring its definition, significance, and practical applications.
What is the Speed of Sound?

The speed of sound is the distance traveled by a sound wave per unit time. In other words, it's the rate at which sound waves propagate through a medium. The speed of sound is typically denoted by the symbol "c" and is measured in units of distance per unit time, such as meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per second (km/s).
Factors Affecting the Speed of Sound

The speed of sound is influenced by several factors, including:
- Temperature: The speed of sound increases with temperature. In air, the speed of sound is approximately 331 meters per second at 0°C and increases by about 0.6 meters per second per degree Celsius.
- Pressure: The speed of sound is affected by pressure, but only at very high pressures.
- Humidity: The speed of sound is slightly affected by humidity, but only at very high frequencies.
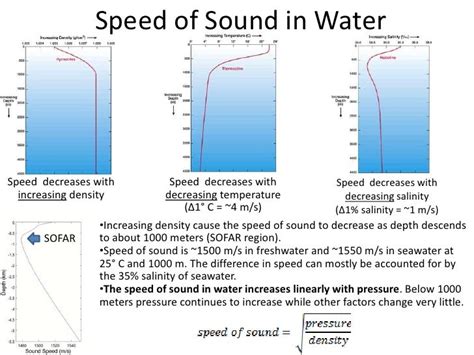
- Medium: The speed of sound varies significantly depending on the medium it's traveling through. For example, the speed of sound in water is approximately 1,482 meters per second, while in steel it's around 5,960 meters per second.
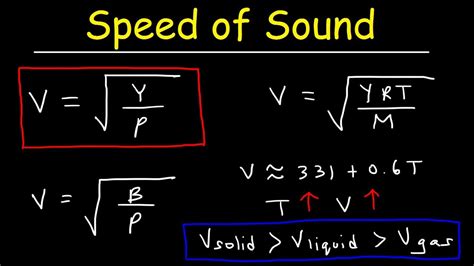
Calculating the Speed of Sound
The speed of sound can be calculated using the following formula:
c = √(B/ρ)
where:
- c is the speed of sound
- B is the bulk modulus of the medium
- ρ is the density of the medium
Speed of Sound in Kilometers Per Second
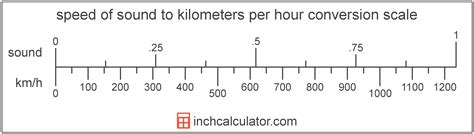
In kilometers per second, the speed of sound is approximately:
- In air at 20°C: 0.343 km/s
- In water: 1.482 km/s
- In steel: 5.960 km/s
Practical Applications of the Speed of Sound
The speed of sound has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Acoustics: Understanding the speed of sound is crucial for designing acoustic systems, such as concert halls and recording studios.
- Aviation: The speed of sound is critical for supersonic flight, as it determines the speed at which an aircraft can break the sound barrier.
- Medical Imaging: The speed of sound is used in medical imaging techniques, such as ultrasound and sonography.
- Seismology: The speed of sound is used to study seismic waves and understand earthquakes.
Real-World Examples of the Speed of Sound

- Thunder and Lightning: When a lightning bolt strikes, it creates a shockwave that travels at the speed of sound, producing the sound we know as thunder.
- Sonic Booms: When an aircraft breaks the sound barrier, it produces a sonic boom, which is a shockwave that travels at the speed of sound.
- Ultrasound: Medical ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues.
Speed of Sound Image Gallery


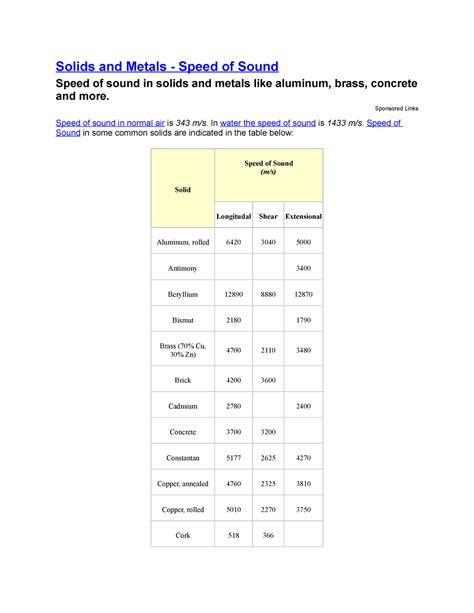


In conclusion, the speed of sound is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in various fields, from acoustics to seismology. Understanding the speed of sound in kilometers per second can help us appreciate the intricacies of sound wave propagation and its practical applications. Whether you're an engineer designing acoustic systems or a medical professional using ultrasound, the speed of sound is an essential concept to grasp.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the speed of sound in kilometers per second. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
