Intro
Discover 7 Hawaii tax tips to minimize liability, including deductions, credits, and exemptions, optimizing tax strategy for residents and non-residents, with insights on state income tax, property tax, and sales tax.
Living in Hawaii can be a dream come true, with its beautiful beaches, lush greenery, and active volcanoes. However, when it comes to taxes, Hawaii can be a challenging place to navigate. The state has a unique tax system that can be complex and overwhelming, especially for those who are new to the islands. In this article, we will explore seven Hawaii tax tips that can help you save money and reduce your tax liability.
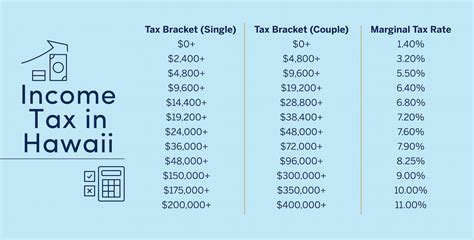
Hawaii is known for its high cost of living, and taxes are a significant contributor to this expense. The state has a general excise tax, which is a tax on the gross income of businesses, as well as a state income tax, which ranges from 1.4% to 11%. Understanding how these taxes work and how to minimize them can make a big difference in your overall tax bill. Whether you are a resident, non-resident, or business owner, it's essential to stay informed about Hawaii's tax laws and regulations to avoid any potential pitfalls.
From tax credits and deductions to exemptions and allowances, there are several ways to reduce your tax liability in Hawaii. For example, the state offers a tax credit for low-income individuals and families, as well as a deduction for mortgage interest and property taxes. Additionally, Hawaii has a unique tax exemption for certain types of income, such as income from a 401(k) or IRA. By taking advantage of these tax breaks, you can lower your tax bill and keep more of your hard-earned money.
Understanding Hawaii's Tax System

General Excise Tax
The general excise tax is a tax on the gross income of businesses, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. The tax rate is 0.5% for most businesses, but can be higher for certain types of businesses, such as hotels and restaurants. The general excise tax is a significant contributor to the state's revenue, and businesses must file a tax return and pay the tax on a quarterly basis.State Income Tax
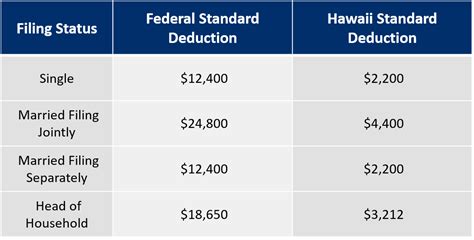
Hawaii's state income tax ranges from 1.4% to 11%, depending on the taxpayer's income level. The tax is progressive, meaning that higher income earners pay a higher tax rate. The state income tax is also subject to a standard deduction, which reduces the amount of income that is subject to tax.Tax Credits and Deductions
Tax Credit for Low-Income Individuals and Families
The tax credit for low-income individuals and families is a refundable credit that can help reduce the tax liability of eligible taxpayers. The credit is based on the taxpayer's income level and family size, and can be claimed on the taxpayer's state income tax return.Tax Deduction for Mortgage Interest and Property Taxes
The tax deduction for mortgage interest and property taxes can help reduce the tax liability of homeowners. The deduction is based on the amount of mortgage interest and property taxes paid during the tax year, and can be claimed on the taxpayer's state income tax return.Exemptions and Allowances

Exemption for Certain Types of Income
The exemption for certain types of income can help reduce the tax liability of taxpayers who receive income from a 401(k) or IRA. The exemption is based on the amount of income received, and can be claimed on the taxpayer's state income tax return.Allowance for Dependents
The allowance for dependents can help reduce the tax liability of taxpayers who have dependents, such as children or elderly parents. The allowance is based on the number of dependents and their relationship to the taxpayer, and can be claimed on the taxpayer's state income tax return.Business Tax Tips

Tax Credit for Research and Development Expenses
The tax credit for research and development expenses can help reduce the tax liability of businesses that invest in research and development. The credit is based on the amount of research and development expenses incurred during the tax year, and can be claimed on the business's state income tax return.Tax Deduction for Business Expenses
The tax deduction for business expenses can help reduce the tax liability of businesses that incur expenses related to their operations. The deduction is based on the amount of business expenses incurred during the tax year, and can be claimed on the business's state income tax return.Individual Tax Tips

Tax Credit for Charitable Contributions
The tax credit for charitable contributions can help reduce the tax liability of individuals who make charitable contributions. The credit is based on the amount of charitable contributions made during the tax year, and can be claimed on the individual's state income tax return.Tax Deduction for Medical Expenses
The tax deduction for medical expenses can help reduce the tax liability of individuals who incur medical expenses. The deduction is based on the amount of medical expenses incurred during the tax year, and can be claimed on the individual's state income tax return.Gallery of Hawaii Tax Images
Hawaii Tax Image Gallery






In conclusion, navigating Hawaii's tax system can be complex, but by understanding the state's tax laws and regulations, individuals and businesses can minimize their tax liability and keep more of their hard-earned money. By taking advantage of tax credits, deductions, exemptions, and allowances, taxpayers can reduce their tax bill and enjoy the beautiful islands of Hawaii without breaking the bank. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Hawaii's tax system in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and family who may benefit from these valuable tax tips.
