Intro
Discover the 7 plant cell organelles, including chloroplasts, mitochondria, and vacuoles, and learn about their functions in plant cell biology, cellular respiration, and photosynthesis.
The world of plant cell biology is fascinating and complex, with various organelles working together to maintain the cell's overall function and health. Plant cells are the building blocks of plants, and understanding their structure and function is essential for appreciating the beauty and importance of plants in our ecosystem. In this article, we will delve into the world of plant cell organelles, exploring their roles, functions, and importance in plant growth and development. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply a plant enthusiast, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the 7 plant cell organelles that are essential for plant life.
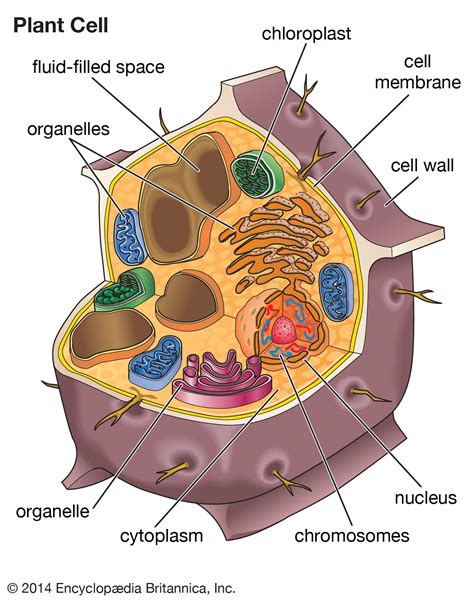
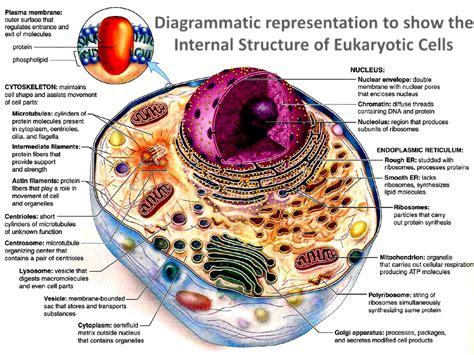
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, meaning they have a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. These organelles work together to perform various functions, such as photosynthesis, respiration, and cell division. The 7 plant cell organelles are the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Each organelle has a unique function, and together they enable plants to grow, thrive, and respond to their environment. In the following sections, we will explore each of these organelles in detail, discussing their structure, function, and importance in plant cell biology.
Introduction to Plant Cell Organelles
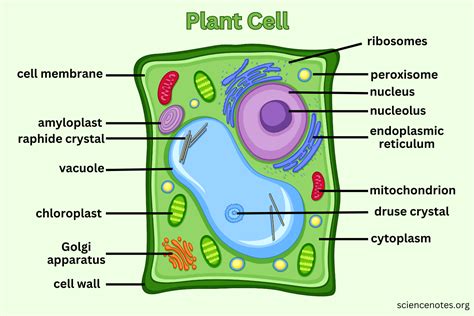
The Nucleus: Control Center of the Cell
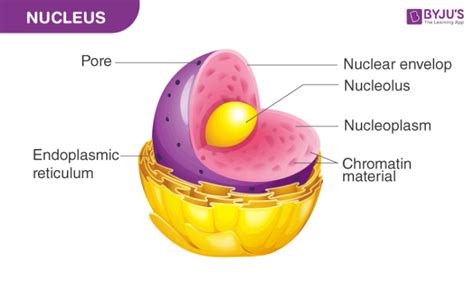
Functions of the Nucleus
The nucleus has several functions, including: * Controlling gene expression and protein synthesis * Regulating cell growth and cell division * Storing and transmitting genetic information * Responding to environmental stimuli and stress The nucleus is essential for plant cell function and development, and any damage to the nucleus can have significant consequences for the cell and the plant as a whole.Mitochondria: Energy Production
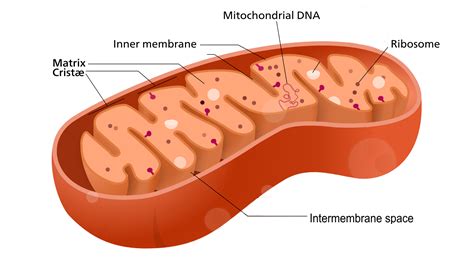
Functions of Mitochondria
Mitochondria have several functions, including: * Generating energy in the form of ATP * Regulating cellular respiration and metabolism * Responding to environmental stimuli and stress * Maintaining cellular homeostasis Mitochondria are essential for plant cell function, as they provide the energy necessary for growth, development, and maintenance of cellular processes.Chloroplasts: Photosynthesis
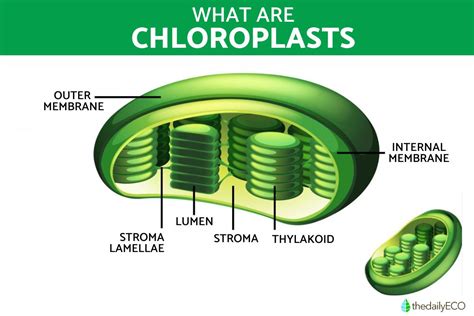
Functions of Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts have several functions, including: * Photosynthesis: converting light energy into chemical energy * Regulating carbohydrate synthesis and metabolism * Responding to environmental stimuli and stress * Maintaining cellular homeostasis Chloroplasts are essential for plant growth and development, as they provide the energy and organic compounds necessary for plant survival.Endoplasmic Reticulum: Protein Synthesis and Transport
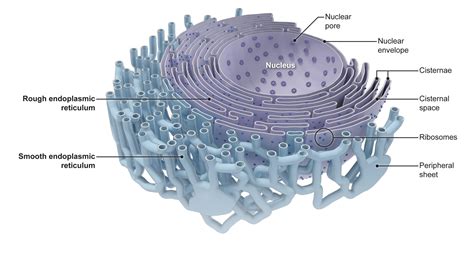
Functions of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
The ER has several functions, including: * Protein synthesis and folding * Protein transport and secretion * Lipid synthesis and metabolism * Responding to environmental stimuli and stress The ER is essential for plant cell function, as it provides the proteins and lipids necessary for growth, development, and maintenance of cellular processes.Golgi Apparatus: Protein Modification and Sorting
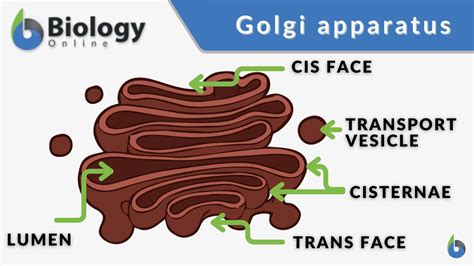
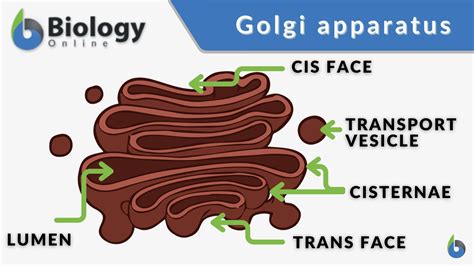
Functions of the Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus has several functions, including: * Protein modification and sorting * Lipid synthesis and metabolism * Responding to environmental stimuli and stress * Maintaining cellular homeostasis The Golgi apparatus is essential for plant cell function, as it provides the modified proteins and lipids necessary for growth, development, and maintenance of cellular processes.Lysosomes: Cellular Digestion and Recycling
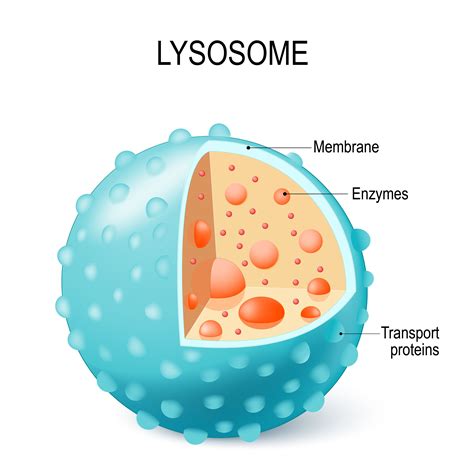
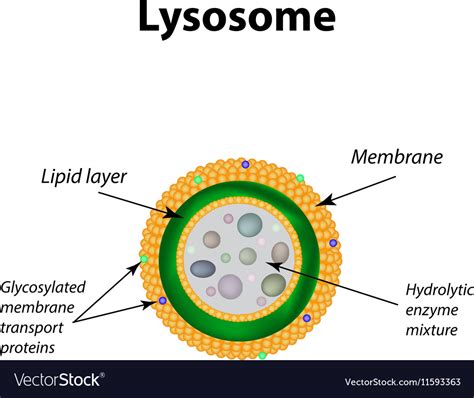
Functions of Lysosomes
Lysosomes have several functions, including: * Cellular digestion and recycling * Protein degradation and metabolism * Lipid metabolism and recycling * Responding to environmental stimuli and stress Lysosomes are essential for plant cell function, as they provide the necessary digestive enzymes for cellular recycling and maintenance of cellular homeostasis.Vacuoles: Storage and Maintenance
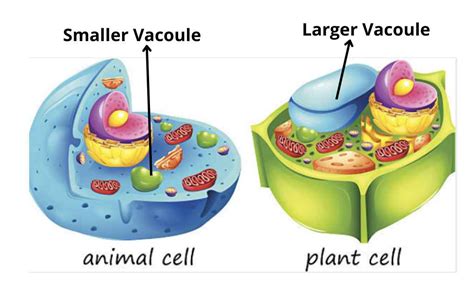
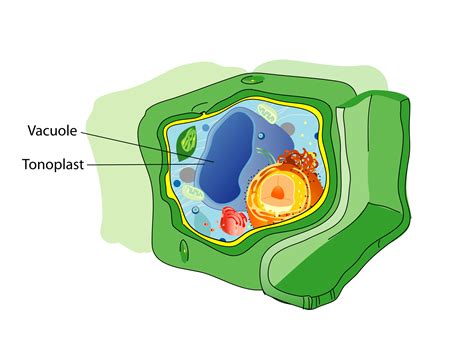
Functions of Vacuoles
Vacuoles have several functions, including: * Storage and maintenance of cellular substances * Water and ion balance * Waste removal and recycling * Responding to environmental stimuli and stress Vacuoles are essential for plant cell function, as they provide the necessary storage and maintenance of cellular substances for growth, development, and maintenance of cellular processes.Plant Cell Organelles Image Gallery
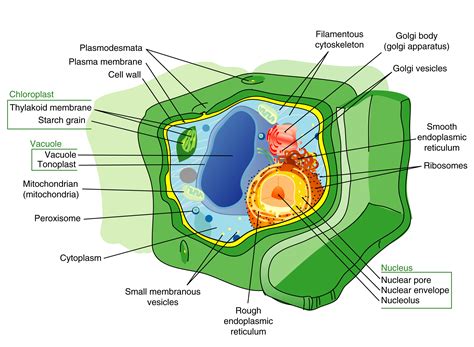
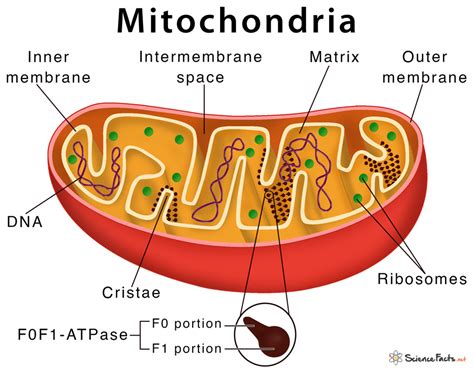
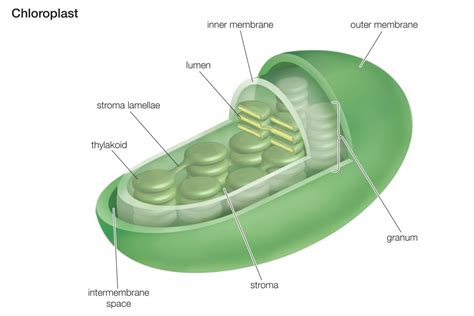
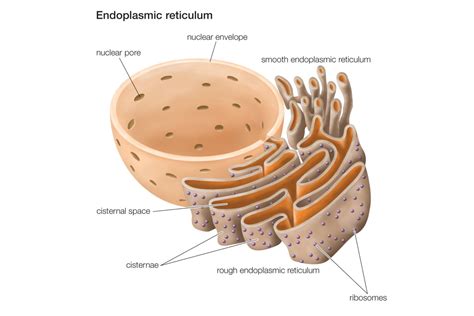
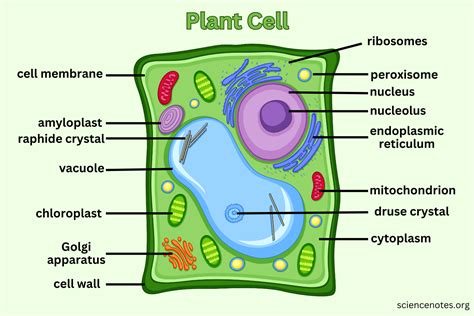
In conclusion, the 7 plant cell organelles are essential for plant growth, development, and maintenance of cellular processes. Each organelle has a unique function, and together they enable plants to respond to environmental stimuli, maintain cellular homeostasis, and thrive in a variety of environments. Understanding the structure and function of plant cell organelles is essential for appreciating the beauty and importance of plants in our ecosystem. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the 7 plant cell organelles and has inspired you to learn more about the fascinating world of plant cell biology. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may be interested in learning more about plant cell organelles.
