Intro
Compare the capabilities of the Su-35 and F-16 in air superiority, exploring five key differences in design, avionics, maneuverability, and armament. Discover how these fighters stack up in terms of beyond-visual-range combat, within-visual-range combat, and ground attack capabilities, shedding light on the strengths and weaknesses of each aircraft.
The world of military aviation is a complex and ever-evolving field, with various countries developing and deploying advanced fighter jets to gain an edge in air superiority. Two of the most notable fighter jets in the world today are the Russian Su-35 and the American F-16. While both aircraft have their own strengths and weaknesses, they have distinct differences that set them apart from each other. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between the Su-35 and the F-16 in terms of air superiority.

Design and Aerodynamics
The Su-35 and F-16 have different design philosophies that impact their aerodynamic performance. The Su-35 is a twin-engine, multirole fighter with a large wing area, which provides excellent maneuverability and stability at high angles of attack. Its canards and thrust-vectoring nozzles enable the Su-35 to achieve exceptional roll rates and maintain control during high-G maneuvers.
On the other hand, the F-16 is a single-engine, multirole fighter with a smaller wing area, which results in lower maneuverability compared to the Su-35. However, the F-16's design focuses on achieving high speeds and acceleration, making it an excellent platform for air-to-air combat.
Key Differences in Design
- Su-35: Twin-engine, multirole fighter with canards and thrust-vectoring nozzles
- F-16: Single-engine, multirole fighter with a smaller wing area
Avionics and Radar Systems
The Su-35 and F-16 have advanced avionics and radar systems that provide them with exceptional situational awareness and targeting capabilities. The Su-35 is equipped with the Phased Array Radar (PAR) system, which can detect and track multiple targets simultaneously at ranges of up to 400 km.
The F-16, on the other hand, uses the AN/APG-66 or AN/APG-68 radar system, depending on the variant. These radar systems provide excellent air-to-air and air-to-ground capabilities, but have a shorter detection range compared to the Su-35's PAR system.
Key Differences in Avionics
- Su-35: Phased Array Radar (PAR) system with a detection range of up to 400 km
- F-16: AN/APG-66 or AN/APG-68 radar system with a shorter detection range

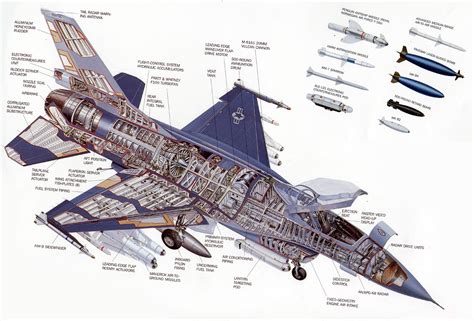
Armament and Payload Capacity
The Su-35 and F-16 have different armament and payload capacities that affect their air superiority capabilities. The Su-35 can carry a maximum payload of 8,000 kg, including a range of air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles, such as the R-77 and R-73.
The F-16, on the other hand, has a lower payload capacity of up to 5,000 kg, but can still carry a range of air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles, such as the AIM-120 and AIM-9.
Key Differences in Armament
- Su-35: Maximum payload capacity of 8,000 kg
- F-16: Maximum payload capacity of up to 5,000 kg

Engine Performance and Range
The Su-35 and F-16 have different engine performance and range capabilities that impact their air superiority capabilities. The Su-35 is powered by two Saturn AL-41F1S engines, which provide a combined thrust of 25,000 kgf.
The F-16, on the other hand, is powered by a single General Electric F110-GE-129 or Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-229 engine, which provides a thrust of up to 13,000 kgf.
Key Differences in Engine Performance
- Su-35: Combined thrust of 25,000 kgf from two Saturn AL-41F1S engines
- F-16: Thrust of up to 13,000 kgf from a single General Electric F110-GE-129 or Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-229 engine

Crew Training and Operations
The Su-35 and F-16 have different crew training and operations requirements that affect their air superiority capabilities. The Su-35 has a more complex avionics system, which requires more extensive training for pilots.
The F-16, on the other hand, has a more user-friendly avionics system, which requires less training for pilots.
Key Differences in Crew Training
- Su-35: More extensive training required for pilots due to complex avionics system
- F-16: Less training required for pilots due to user-friendly avionics system

Su-35 vs F-16 Image Gallery









In conclusion, the Su-35 and F-16 have distinct differences in terms of design, avionics, armament, engine performance, and crew training. While the Su-35 has a more advanced radar system and better maneuverability, the F-16 has a more user-friendly avionics system and better acceleration. Ultimately, the choice between the Su-35 and F-16 depends on the specific needs and requirements of the military.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the Su-35 vs F-16 comparison in the comments section below. Which fighter jet do you think has the edge in air superiority?
