Intro
Discover the crucial difference between Template and Non-Template Strand in DNA replication. Understand how each strand plays a unique role in transcription and replication, and learn how Template-Dependent DNA Synthesis and Leading Strand Synthesis differ from Lagging Strand Synthesis. Get clarity on DNA synthesis and transcription processes.
Strand displacement is a fundamental concept in molecular biology, and understanding the difference between template and nontemplate strands is crucial for comprehending various biological processes. In this article, we will delve into the world of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, exploring the distinct roles of the template and nontemplate strands.
What are Template and Nontemplate Strands?
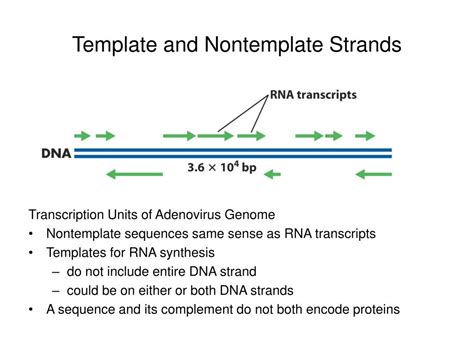
During DNA replication, the double helix is unwound, and the genetic material is duplicated. The two strands of DNA are complementary, with each base pairing with its specific partner (adenine with thymine and guanine with cytosine). The template strand is the parental DNA strand that serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. The nontemplate strand, on the other hand, is the newly synthesized strand that is complementary to the template strand.
Role of Template Strand in DNA Replication
The template strand plays a crucial role in DNA replication, as it provides the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. The template strand is read by DNA polymerase, an enzyme that matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules. The template strand determines the sequence of nucleotides in the newly synthesized strand, ensuring that the genetic information is accurately replicated.
Role of Nontemplate Strand in DNA Replication
The nontemplate strand, although not directly involved in the synthesis of the new strand, is essential for the completion of DNA replication. The nontemplate strand is used as a scaffold for the assembly of the replication machinery, including the primosome and the replication fork. The nontemplate strand also provides a binding site for proteins that help to stabilize the replication fork and facilitate the unwinding of the DNA double helix.
Transcription and the Template Strand
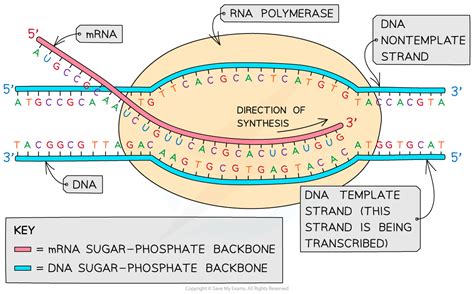
During transcription, the template strand is used as a template for the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule. The template strand is read by RNA polymerase, an enzyme that matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules. The template strand determines the sequence of nucleotides in the newly synthesized RNA molecule, ensuring that the genetic information is accurately transcribed.
Translation and the Nontemplate Strand
The nontemplate strand is not directly involved in translation, as the genetic information is stored in the RNA molecule synthesized during transcription. However, the nontemplate strand plays an indirect role in translation, as the RNA molecule synthesized during transcription is complementary to the nontemplate strand. The sequence of nucleotides in the RNA molecule determines the sequence of amino acids in the protein, ensuring that the genetic information is accurately translated.
Importance of Template and Nontemplate Strands
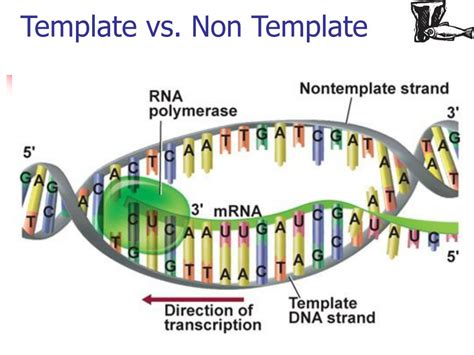
The template and nontemplate strands play crucial roles in various biological processes, including DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Understanding the difference between these two strands is essential for comprehending the mechanisms of genetic inheritance and the transmission of genetic information.
- Template strand: provides the genetic information necessary for the synthesis of a new complementary strand during DNA replication and transcription.
- Nontemplate strand: provides a scaffold for the assembly of the replication machinery and helps to stabilize the replication fork during DNA replication.
Gallery of Template and Nontemplate Strands
Template and Nontemplate Strands Image Gallery
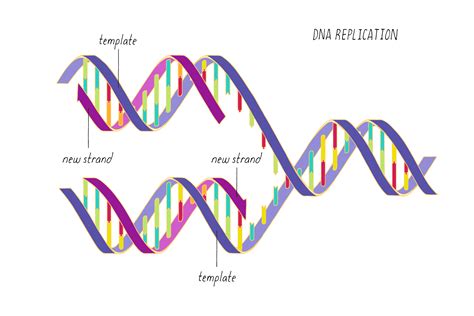
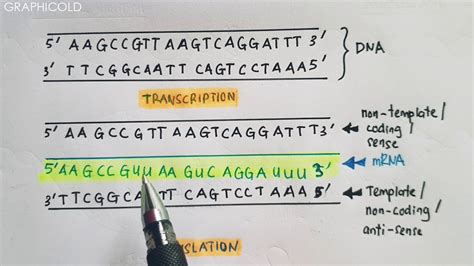
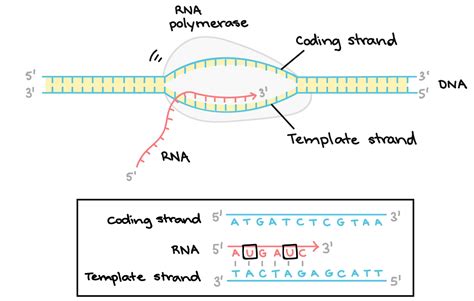
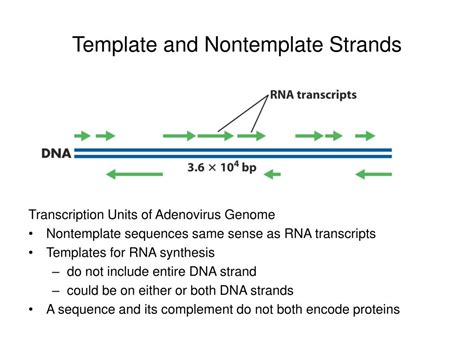
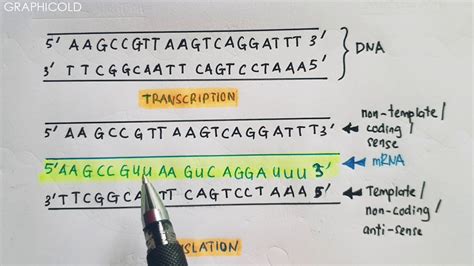
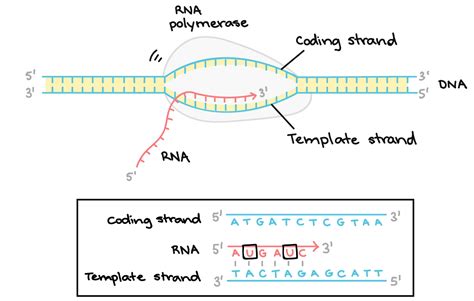
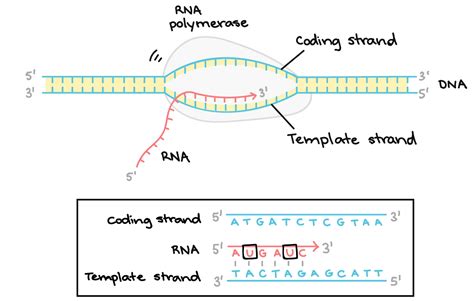
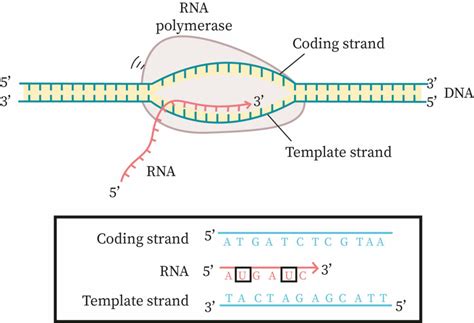
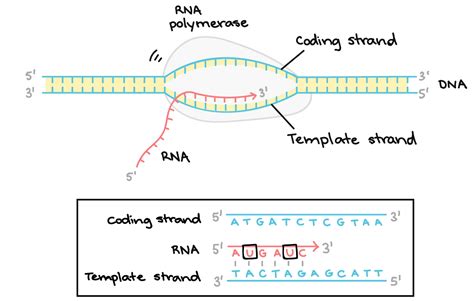
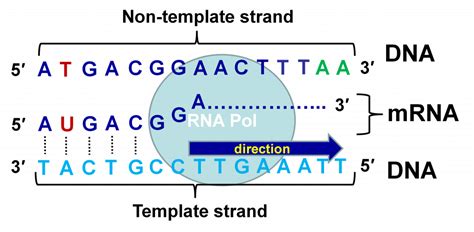
In conclusion, the template and nontemplate strands play vital roles in various biological processes, including DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Understanding the difference between these two strands is essential for comprehending the mechanisms of genetic inheritance and the transmission of genetic information. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the template and nontemplate strands and their importance in molecular biology.
Please share your thoughts and comments on this article. We would love to hear your feedback and engage in a discussion on the topic of template and nontemplate strands.
