Intro
Explore 6 knee tendon pictures, illustrating tendonitis, ligament injuries, and knee anatomy, to understand knee tendons, tendon strains, and injuries, with detailed images and explanations.
Knee tendon injuries are a common issue for many individuals, particularly athletes and those who engage in regular physical activity. The knee tendons, which connect muscles to bones, play a crucial role in facilitating movement and providing stability to the knee joint. Understanding the different types of knee tendons and the various injuries that can occur is essential for effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the world of knee tendons, exploring their anatomy, functions, and the common injuries that affect them.
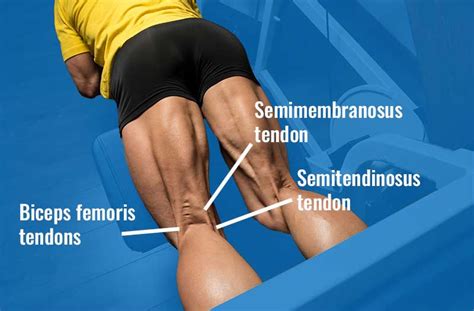
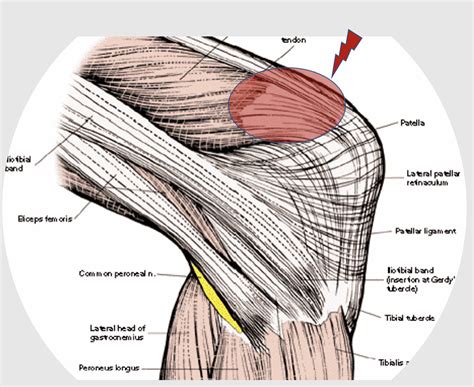
The knee joint is a complex structure comprising bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. The tendons in the knee are responsible for transmitting the forces generated by the muscles to the bones, enabling movement and weight-bearing activities. There are several key tendons in the knee, including the quadriceps tendon, patellar tendon, and hamstring tendons. Each of these tendons has a unique function and is susceptible to different types of injuries.
The importance of knee tendons cannot be overstated. They are vital for maintaining knee stability, facilitating movement, and enabling individuals to perform daily activities without discomfort or pain. Knee tendon injuries can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, making it essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for knee tendon injuries, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent these injuries and maintain optimal knee health.
Knee Tendon Anatomy
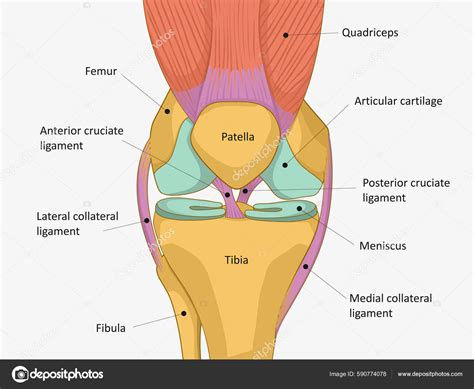
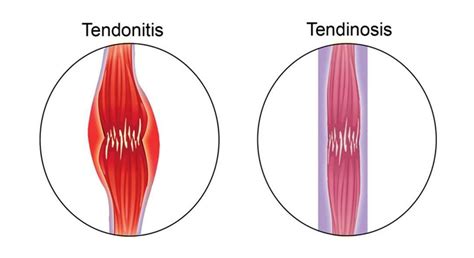
Types of Knee Tendon Injuries
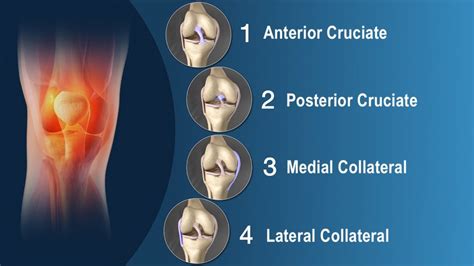
Causes and Risk Factors

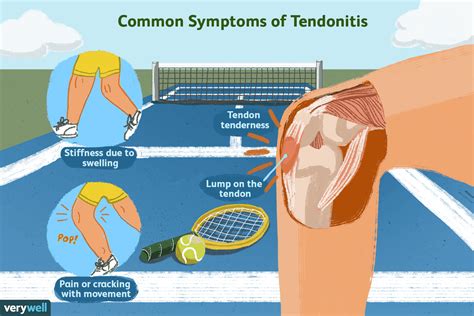
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Treatment and Prevention

Recovery and Rehabilitation

Gallery of Knee Tendon Images
Knee Tendon Image Gallery
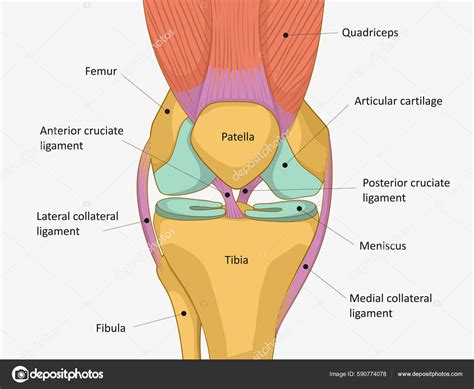
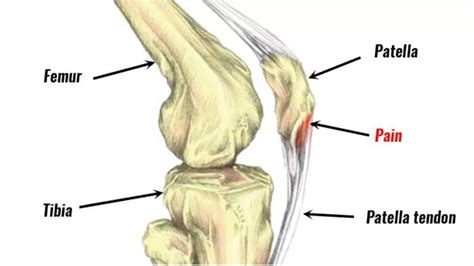
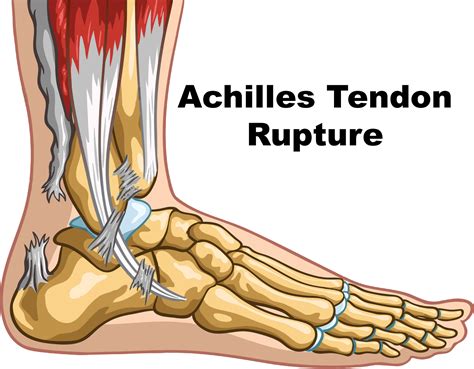
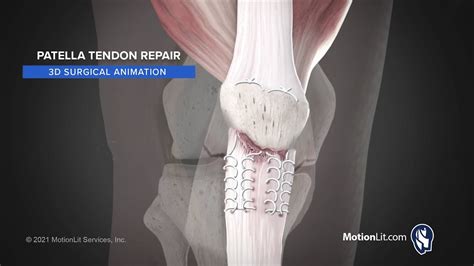
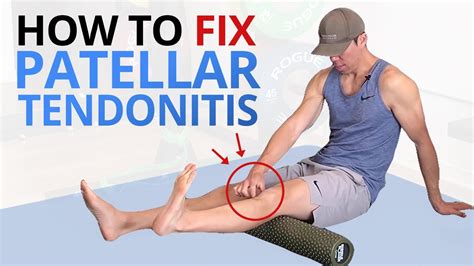

In conclusion, knee tendon injuries are a significant concern for individuals who engage in regular physical activity or have underlying medical conditions. Understanding the anatomy, functions, and common injuries affecting the knee tendons is essential for effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. By adopting a proactive approach to knee health, individuals can reduce the risk of injuries and maintain optimal mobility and function. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with knee tendon injuries in the comments section below. Additionally, please feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and don't hesitate to reach out if you have any further questions or concerns.
