Intro
Unlock the secrets of GDP Deflator! Discover how this economic indicator measures inflation, impacts GDP calculations, and affects business decisions. Learn about nominal vs real GDP, price indices, and inflation rates in a simplified explanation. Get a clear understanding of GDP Deflators role in economic analysis and its implications for investors and policymakers.
The concept of the GDP deflator can be quite daunting, especially for those who are not familiar with economic jargon. However, understanding this concept is crucial in grasping the overall health of a country's economy. In this article, we will delve into the world of the GDP deflator, explaining what it is, how it works, and its significance in measuring economic growth.

To begin with, let's define what the GDP deflator is. The GDP deflator, also known as the implicit price deflator, is a measure of the average price level of all goods and services produced within a country. It is a ratio of the nominal GDP to the real GDP, which provides a clearer picture of economic growth by adjusting for inflation. In other words, the GDP deflator helps to differentiate between changes in the quantity of goods and services produced and changes in their prices.
How Does the GDP Deflator Work?
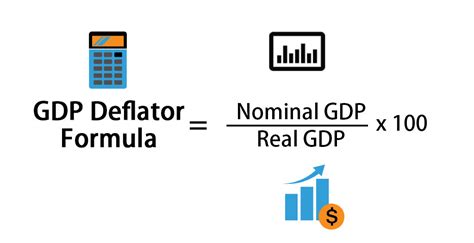
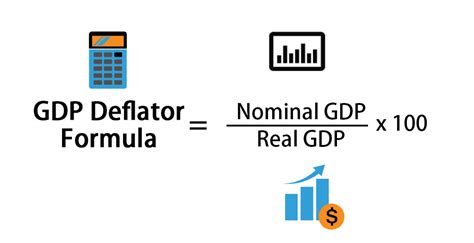
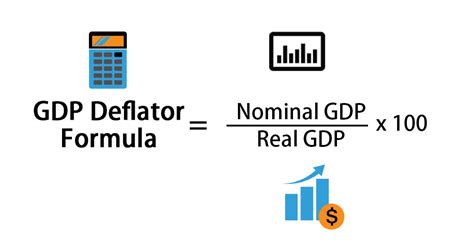
The GDP deflator is calculated by dividing the nominal GDP by the real GDP and then multiplying the result by 100. The formula for this calculation is:
GDP Deflator = (Nominal GDP / Real GDP) x 100
The nominal GDP is the value of goods and services produced within a country, measured in current prices. On the other hand, the real GDP is the value of goods and services produced within a country, measured in constant prices, usually the prices of a base year.
For instance, if the nominal GDP of a country is $100 billion and the real GDP is $80 billion, the GDP deflator would be:
GDP Deflator = ($100 billion / $80 billion) x 100 = 125
This means that the average price level of goods and services has increased by 25% compared to the base year.
Significance of the GDP Deflator
The GDP deflator is a crucial tool in measuring economic growth and inflation. It helps policymakers and economists to:
- Measure inflation: By tracking changes in the GDP deflator, policymakers can gauge the rate of inflation and make informed decisions about monetary policy.
- Evaluate economic growth: The GDP deflator helps to distinguish between real economic growth and growth due to inflation.
- Make international comparisons: The GDP deflator enables economists to compare the economic performance of different countries, taking into account differences in price levels.

Limitations of the GDP Deflator
While the GDP deflator is a valuable tool, it has some limitations:
- Ignores changes in quality: The GDP deflator does not account for changes in the quality of goods and services, which can lead to biased estimates of inflation.
- Assumes constant consumption patterns: The GDP deflator assumes that consumption patterns remain constant over time, which is not always the case.

Real-World Examples of the GDP Deflator
To illustrate the concept of the GDP deflator, let's consider a few examples:
- Country A: Country A experiences a 20% increase in nominal GDP, but the GDP deflator rises by 15%. This means that the real GDP has increased by 5%, indicating a moderate level of economic growth.
- Country B: Country B experiences a 10% decrease in nominal GDP, but the GDP deflator falls by 5%. This means that the real GDP has decreased by 5%, indicating a recession.

FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about the GDP deflator:
- Q: What is the difference between the GDP deflator and the Consumer Price Index (CPI)?
- A: The GDP deflator measures the average price level of all goods and services produced within a country, while the CPI measures the average price level of a basket of goods and services consumed by households.
- Q: How is the GDP deflator used in monetary policy?
- A: Central banks use the GDP deflator to gauge inflation and make decisions about interest rates and other monetary policy tools.
GDP Deflator Image Gallery






Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the GDP deflator is a powerful tool for measuring economic growth and inflation. While it has some limitations, it provides a valuable insight into the overall health of a country's economy. By understanding the GDP deflator, policymakers and economists can make informed decisions about monetary policy and evaluate the effectiveness of economic strategies.
We hope this article has helped you to grasp the concept of the GDP deflator. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
