Intro
Discover 7 expert tips in pharmacology, covering drug interactions, medication management, and pharmacokinetics, to enhance your understanding of pharmaceuticals and improve patient outcomes.
The study of pharmacology is a complex and fascinating field that has led to numerous breakthroughs in the treatment and prevention of diseases. Pharmacology is the branch of medicine concerned with the uses, effects, and modes of action of drugs. Understanding pharmacology is essential for healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients alike, as it helps to ensure the safe and effective use of medications. In this article, we will delve into the world of pharmacology and explore seven key tips that can help individuals navigate this intricate field.
The importance of pharmacology cannot be overstated. With the constant emergence of new diseases and the evolution of existing ones, the development of new medications and treatments is crucial. Pharmacology plays a vital role in this process, as it enables researchers to understand how drugs interact with the body and how they can be used to prevent or treat diseases. Furthermore, pharmacology helps to ensure that medications are used safely and effectively, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions and maximizing their therapeutic benefits.
As we explore the world of pharmacology, it becomes clear that this field is constantly evolving. New discoveries and advancements in technology are continually expanding our understanding of how drugs work and how they can be used to improve human health. From the development of new medications to the discovery of novel therapeutic targets, pharmacology is a field that is always pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a researcher, or simply someone interested in learning more about pharmacology, this article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of this fascinating field and offer seven key tips to help you navigate its complexities.
Understanding Pharmacokinetics
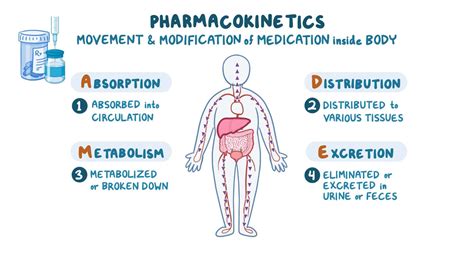
Key Principles of Pharmacokinetics
Some key principles of pharmacokinetics include: * Absorption: The process by which a drug is absorbed into the bloodstream. * Distribution: The process by which a drug is distributed throughout the body. * Metabolism: The process by which a drug is broken down into its active and inactive metabolites. * Excretion: The process by which a drug is eliminated from the body. Understanding these principles is essential for healthcare professionals, as it enables them to optimize drug therapy and minimize the risk of adverse reactions.Drug Interactions and Side Effects
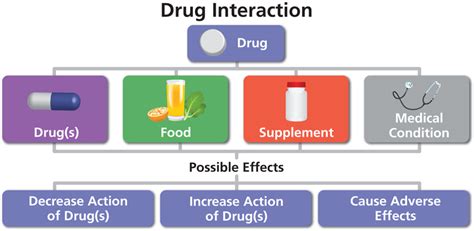
Minimizing the Risk of Adverse Reactions
To minimize the risk of adverse reactions, healthcare professionals should: * Carefully review a patient's medication history before prescribing new medications. * Monitor patients closely for signs of adverse reactions. * Adjust drug dosages and regimens as needed to minimize the risk of interactions. * Educate patients about the potential risks and benefits of their medications.Pharmacodynamics and Therapeutic Effects

Optimizing Therapeutic Effects
To optimize therapeutic effects, healthcare professionals should: * Carefully select medications based on their pharmacodynamic properties. * Adjust drug dosages and regimens as needed to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. * Monitor patients closely for signs of therapeutic effects and adjust treatment as needed.Personalized Medicine and Pharmacogenomics
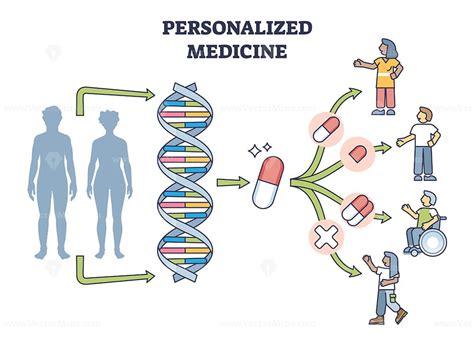
Advantages of Personalized Medicine
The advantages of personalized medicine include: * Improved efficacy: Personalized medicine can help to ensure that medications are used effectively and safely. * Reduced risk of adverse reactions: Personalized medicine can help to minimize the risk of adverse reactions by predicting how an individual will respond to a particular medication. * Increased patient satisfaction: Personalized medicine can help to improve patient satisfaction by tailoring treatment to an individual's unique needs and preferences.Drug Development and Regulatory Affairs
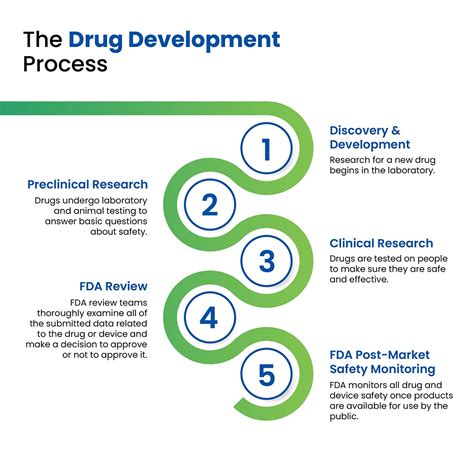
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework for drug development and approval includes: * FDA approval: The process by which the FDA reviews and approves new medications for use in the United States. * EU approval: The process by which the EU reviews and approves new medications for use in Europe. * Other regulatory agencies: The process by which other regulatory agencies, such as the WHO, review and approve new medications for use in other countries.Pharmacology in Clinical Practice

Best Practices in Clinical Practice
Best practices in clinical practice include: * Careful patient assessment: The careful assessment of patients to determine their unique needs and preferences. * Individualized treatment plans: The development of individualized treatment plans that take into account a patient's unique needs and preferences. * Ongoing monitoring: The ongoing monitoring of patients for signs of therapeutic effects and adverse reactions.Future Directions in Pharmacology

Emerging Trends
Emerging trends in pharmacology include: * Increased focus on personalized medicine: The use of genetic information to tailor medication therapy to an individual's unique genetic profile. * Greater emphasis on patient-centered care: The focus on patient-centered care and the development of individualized treatment plans. * Increased use of technology: The use of technology, such as electronic health records and mobile health apps, to improve patient care and outcomes.Pharmacology Image Gallery










In conclusion, the field of pharmacology is complex and multifaceted, and understanding its principles is essential for healthcare professionals, researchers, and patients alike. By following the seven tips outlined in this article, individuals can navigate the intricacies of pharmacology and optimize their use of medications. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a researcher, or simply someone interested in learning more about pharmacology, we hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of this fascinating field. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this article, and to explore the many resources available for learning more about pharmacology. Together, we can work to advance our understanding of pharmacology and to improve patient care and outcomes.
