Intro
Learn about Tylenol and Meloxicam interaction, including side effects, dosage, and risks of combining acetaminophen and NSAIDs for pain relief, arthritis treatment, and medication management.
The importance of understanding drug interactions cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to commonly used medications like Tylenol and Meloxicam. Both are widely prescribed and used over-the-counter to manage pain and reduce inflammation. However, combining these medications can have unintended consequences, emphasizing the need for awareness among patients and healthcare providers alike. As we delve into the specifics of the Tylenol and Meloxicam interaction, it's crucial to understand the mechanisms of action, potential risks, and how to mitigate these risks for safe and effective pain management.
Tylenol, known generically as acetaminophen, is a staple in many medicine cabinets due to its effectiveness in relieving fever and pain. It works by influencing the brain's perception of pain and reducing the production of prostaglandins, which are substances in the body that cause pain. On the other hand, Meloxicam, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), operates by directly inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, thereby reducing inflammation and pain. While both drugs are effective on their own, their interaction can lead to increased risks of adverse effects, particularly gastrointestinal issues and liver damage.
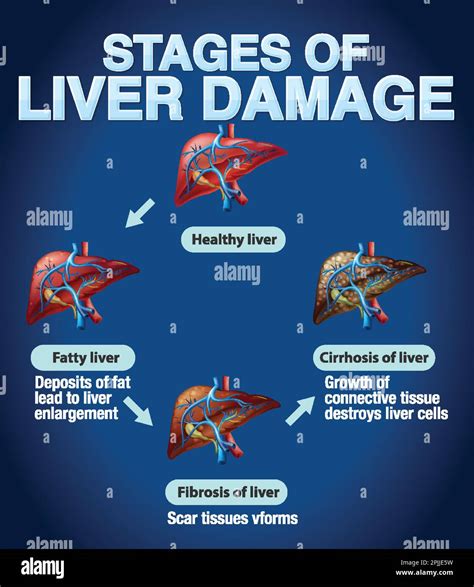
The interaction between Tylenol and Meloxicam is significant because both drugs can affect the liver and the stomach lining. Acetaminophen is known for its potential to cause liver damage when taken in high doses or over an extended period. Similarly, Meloxicam, being an NSAID, can cause stomach ulcers and bleeding due to its effect on the stomach lining. When combined, these risks can be exacerbated, leading to more severe health complications. It's essential for patients to be aware of these potential interactions to avoid unnecessary risks and to discuss their medication regimen with their healthcare provider.
Tylenol Mechanism of Action
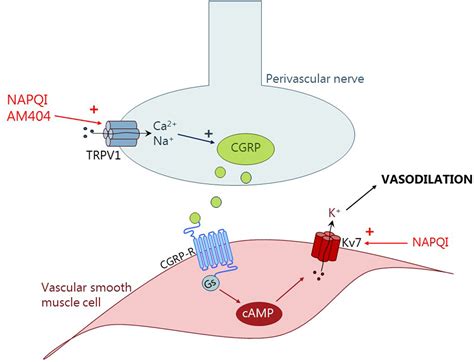
Meloxicam Mechanism of Action
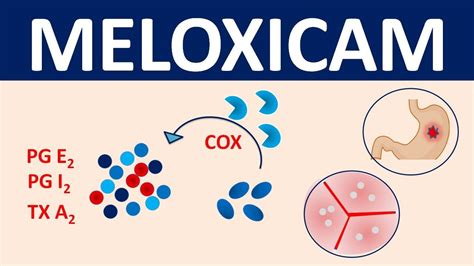
Risks of Interaction
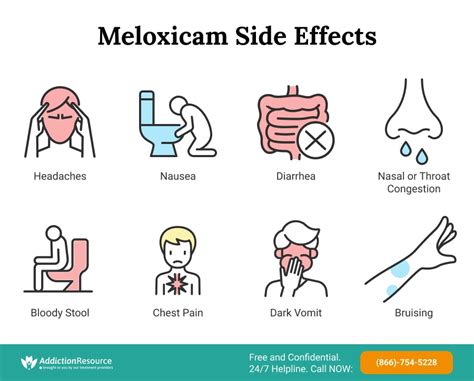
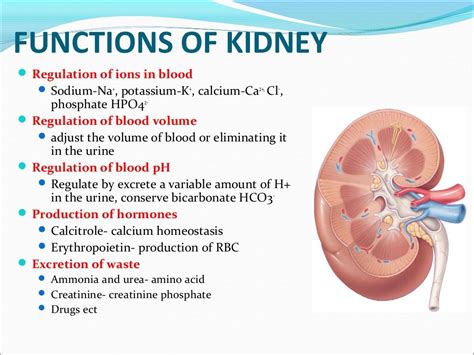
The concurrent use of Tylenol and Meloxicam can increase the risk of several adverse effects. The primary concerns include: - **Liver Damage:** High doses of acetaminophen are well-known for their potential to cause liver injury. The addition of Meloxicam may not directly increase this risk, but the overall burden on the liver could potentially exacerbate any underlying liver conditions. - **Gastrointestinal Issues:** Meloxicam can cause stomach ulcers and bleeding. While acetaminophen is not typically associated with gastrointestinal side effects, the combination may increase the susceptibility to these issues, particularly in patients with a history of stomach problems. - **Kidney Function:** NSAIDs like Meloxicam can affect kidney function, and combining them with other medications that may have renal effects could potentially worsen kidney function in susceptible individuals.Safe Use Guidelines

Alternatives for Pain Management
For patients who require ongoing pain management, there are several alternatives to consider, either in place of or in addition to Tylenol and Meloxicam: - **Topical Pain Relievers:** Creams, gels, or patches applied directly to the skin can provide localized pain relief without the systemic side effects of oral medications. - **Physical Therapy:** Exercise and physical therapy can help improve mobility and reduce pain in conditions like arthritis. - **Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):** CBT and other psychological interventions can help manage chronic pain by changing the way the brain processes pain signals.FAQs

Tylenol and Meloxicam Interaction Image Gallery
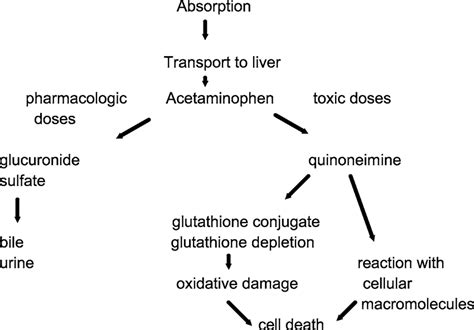




In conclusion, the interaction between Tylenol and Meloxicam, while not necessarily contraindicated, requires careful consideration and monitoring. Patients should be proactive in discussing their medication regimen with healthcare providers and being aware of the potential risks and benefits. By understanding how these medications work and their potential interactions, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and explore alternative strategies for managing pain effectively and safely. We invite readers to share their experiences and questions regarding Tylenol and Meloxicam interaction in the comments below and to consider consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice on pain management.
