Intro
Explore the evolution of US naval power through 9 historic battleship classes, from the Indiana-class to the Iowa-class. Learn about the design, armament, and service history of each class, and discover how they shaped American military strategy and global conflicts, including World War I and II, and the Cold War.
The United States has a rich naval history, with numerous battleship classes that have played a significant role in shaping the country's military and maritime heritage. From the early 20th century to the mid-20th century, the US Navy commissioned several battleship classes that were designed to serve as the backbone of the fleet. Here, we will explore nine historic United States battleship classes that served during World War I, World War II, and the Cold War era.

1. South Carolina Class
The South Carolina class was a pair of battleships commissioned in 1910, consisting of the USS South Carolina (BB-26) and the USS Michigan (BB-27). These ships were the first dreadnoughts built by the United States, featuring a main armament of eight 12-inch guns. Although they played a minor role in World War I, they served as training ships during World War II.
Design and Construction
The South Carolina class was designed to be more compact and maneuverable than earlier battleships, with a length of 452 feet and a beam of 80 feet. They had a top speed of 18.5 knots and were crewed by approximately 800 officers and men.
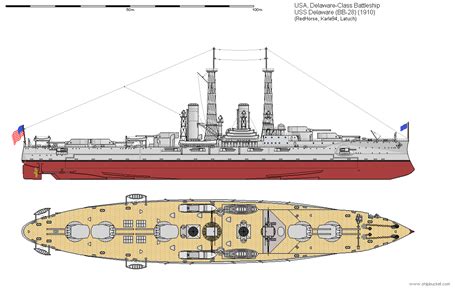
2. Delaware Class
The Delaware class consisted of two battleships, the USS Delaware (BB-28) and the USS North Dakota (BB-29), commissioned in 1910. These ships were the first American battleships to be built with a uniform main armament of 12-inch guns.

Operational History
During World War I, the Delaware class battleships served in the Atlantic Fleet, conducting patrols and escorting convoys. In the interwar period, they underwent modernizations, including the installation of anti-aircraft guns and improved fire control systems.
3. Florida Class
The Florida class consisted of two battleships, the USS Florida (BB-30) and the USS Utah (BB-31), commissioned in 1911. These ships were designed to be more heavily armed than the preceding Delaware class, with a main armament of ten 12-inch guns.
Design Innovations
The Florida class introduced several design innovations, including a more efficient propulsion system and improved armor protection. They also featured a distinctive "cage mast" design, which provided a high platform for spotting and fire control.

4. Wyoming Class
The Wyoming class consisted of two battleships, the USS Wyoming (BB-32) and the USS Arkansas (BB-33), commissioned in 1912. These ships were designed to be more heavily armed than the preceding Florida class, with a main armament of twelve 12-inch guns.
Operational History
During World War I, the Wyoming class battleships served in the Atlantic Fleet, conducting patrols and escorting convoys. In the interwar period, they underwent modernizations, including the installation of anti-aircraft guns and improved fire control systems.
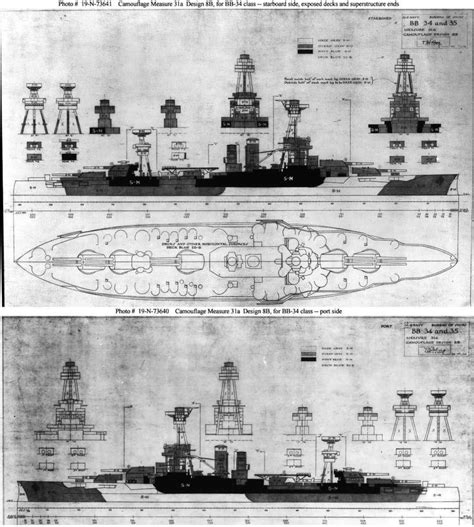
5. New York Class
The New York class consisted of two battleships, the USS New York (BB-34) and the USS Texas (BB-35), commissioned in 1914. These ships were designed to be more heavily armed than the preceding Wyoming class, with a main armament of ten 14-inch guns.
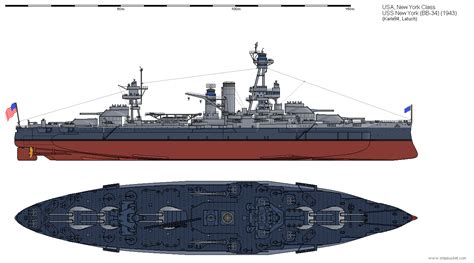
Design Innovations
The New York class introduced several design innovations, including a more efficient propulsion system and improved armor protection. They also featured a distinctive "cage mast" design, which provided a high platform for spotting and fire control.
6. Nevada Class
The Nevada class consisted of two battleships, the USS Nevada (BB-36) and the USS Oklahoma (BB-37), commissioned in 1916. These ships were designed to be more heavily armed than the preceding New York class, with a main armament of ten 14-inch guns.
Operational History
During World War I, the Nevada class battleships served in the Atlantic Fleet, conducting patrols and escorting convoys. In the interwar period, they underwent modernizations, including the installation of anti-aircraft guns and improved fire control systems.

7. Pennsylvania Class
The Pennsylvania class consisted of two battleships, the USS Pennsylvania (BB-38) and the USS Arizona (BB-39), commissioned in 1916. These ships were designed to be more heavily armed than the preceding Nevada class, with a main armament of twelve 14-inch guns.
Design Innovations
The Pennsylvania class introduced several design innovations, including a more efficient propulsion system and improved armor protection. They also featured a distinctive "cage mast" design, which provided a high platform for spotting and fire control.
8. New Mexico Class
The New Mexico class consisted of three battleships, the USS New Mexico (BB-40), the USS Mississippi (BB-41), and the USS Idaho (BB-42), commissioned in 1918. These ships were designed to be more heavily armed than the preceding Pennsylvania class, with a main armament of twelve 14-inch guns.

Operational History
During World War II, the New Mexico class battleships served in the Pacific Fleet, conducting bombardments and supporting amphibious landings. They played a significant role in several major battles, including the Battle of Midway and the Battle of Guadalcanal.
9. Colorado Class
The Colorado class consisted of three battleships, the USS Colorado (BB-45), the USS Maryland (BB-46), and the USS West Virginia (BB-48), commissioned in 1923. These ships were designed to be more heavily armed than the preceding New Mexico class, with a main armament of eight 16-inch guns.
Design Innovations
The Colorado class introduced several design innovations, including a more efficient propulsion system and improved armor protection. They also featured a distinctive "pagoda mast" design, which provided a high platform for spotting and fire control.

US Battleship Classes Image Gallery




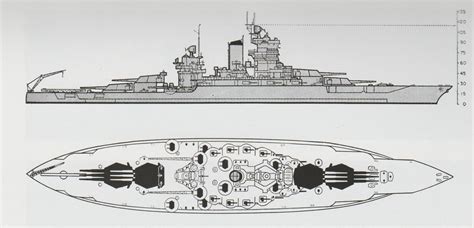

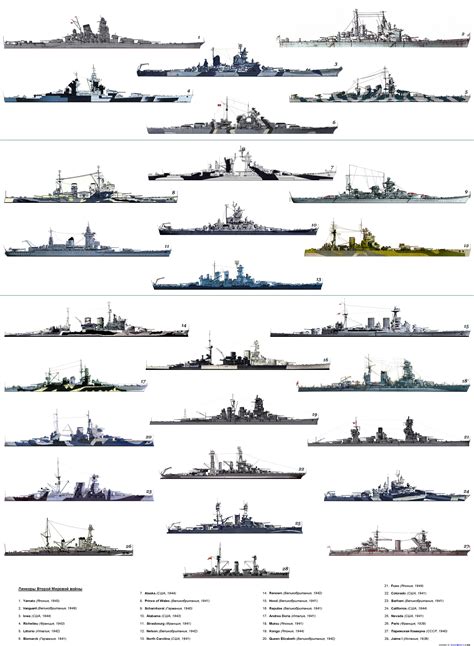
These nine historic United States battleship classes played a significant role in shaping the country's naval history. From the early 20th century to the mid-20th century, these ships served as the backbone of the US Navy, participating in several major conflicts, including World War I and World War II. Their design innovations, operational histories, and contributions to American naval power continue to fascinate historians and naval enthusiasts alike.
