Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, causing an infection in the bladder, kidneys, or urethra. Women are more prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. However, UTIs can affect anyone, regardless of age or sex. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options for UTIs is crucial for prompt and effective management of the condition.
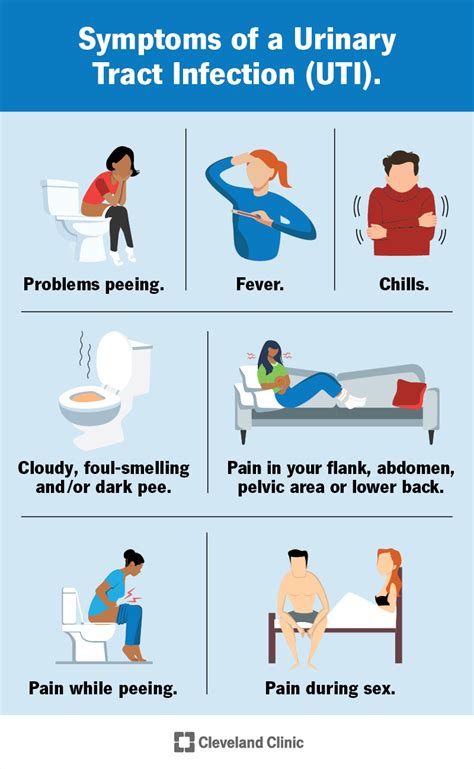
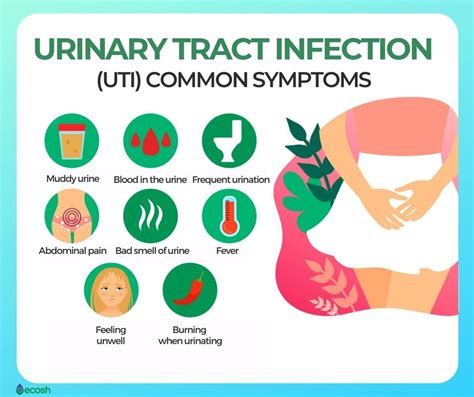
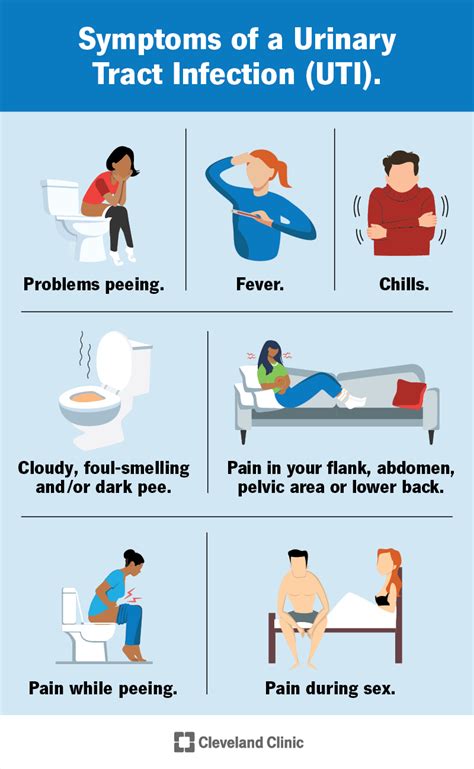
A UTI can be a painful and distressing experience, especially if left untreated. The infection can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain. Common symptoms of a UTI include:
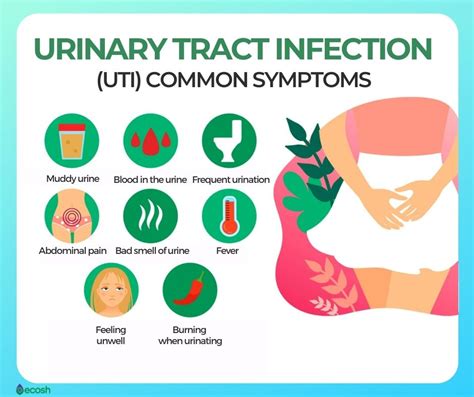
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Frequent urination (urinary frequency)
- Urgent need to urinate (urinary urgency)
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Fever and chills
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Abdominal pain or cramping
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention. Untreated UTIs can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney damage or sepsis.
Causes and Risk Factors of UTIs
UTIs are typically caused by bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Staphylococcus saprophyticus. These bacteria can enter the urinary tract through various means, including:
- Poor hygiene
- Unprotected sex
- Using a catheter or other medical devices
- Abnormalities in the urinary tract
- Weakened immune system
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or kidney stones
Certain individuals are more susceptible to UTIs, including:
- Women, especially those who are pregnant or have a history of UTIs
- Older adults
- People with weakened immune systems
- Those with medical conditions, such as kidney disease or spinal cord injuries
- Individuals with a family history of UTIs
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing a UTI typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Your healthcare provider may:

- Perform a physical examination to check for signs of infection or discomfort
- Ask about your medical history and symptoms
- Conduct a urinalysis to examine the urine for bacteria, blood, or other abnormal substances
- Use a urine culture to identify the type of bacteria causing the infection
- Perform imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, to rule out other conditions or complications
Treatment Options for UTIs
Treatment for UTIs usually involves antibiotics, which can help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. The type and duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection, the type of bacteria, and the individual's overall health.

- Uncomplicated UTIs: Typically treated with a 3- to 5-day course of antibiotics, such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or nitrofurantoin
- Complicated UTIs: May require a longer course of antibiotics (7-14 days) or different types of antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin or ampicillin
- Recurrent UTIs: May involve a longer course of antibiotics or a low-dose antibiotic taken daily for several months to prevent future infections
In addition to antibiotics, your healthcare provider may recommend:
- Pain relief medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to alleviate discomfort and pain
- Urinary tract analgesics, such as phenazopyridine, to help soothe the urinary tract
- Increased fluid intake to help flush out bacteria and promote healing
Prevention and Home Remedies
While UTIs can be effectively treated with antibiotics, there are steps you can take to prevent future infections and alleviate symptoms:

- Practice good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back and avoiding tight-fitting clothing
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Avoid using scented soaps or bubble baths
- Urinate when you feel the need, rather than holding it in
- Avoid consuming foods and drinks that may irritate the bladder, such as spicy or acidic foods
- Consider taking a probiotic supplement to support urinary tract health
Home remedies, such as:
- Drinking cranberry juice or taking cranberry supplements to help prevent UTIs
- Using a heating pad or warm compress to alleviate discomfort and pain
- Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to reduce stress and promote healing
Gallery of UTI Symptoms and Prevention
UTI Symptoms and Prevention Image Gallery
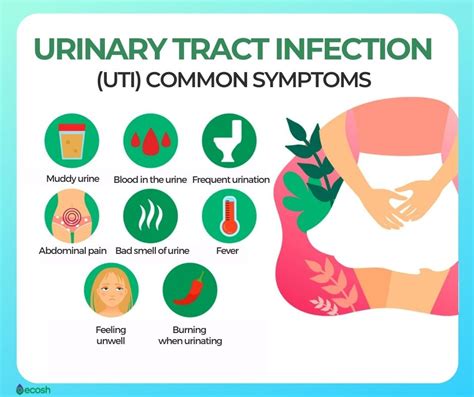



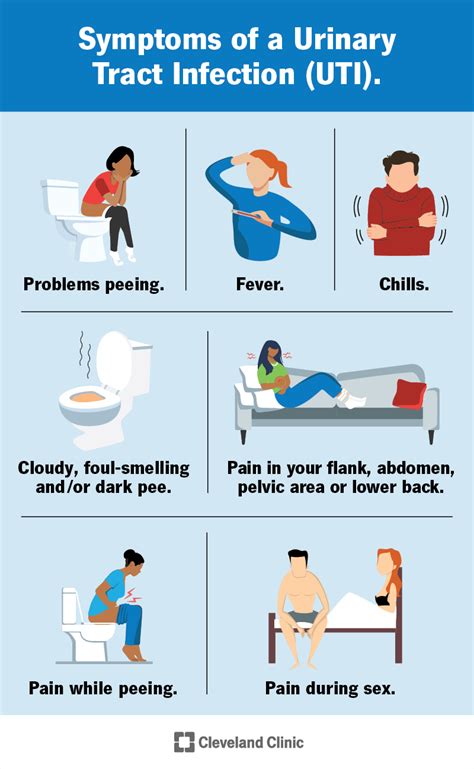


We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of UTI symptoms and treatment options. If you suspect you have a UTI, it is essential to seek medical attention to prevent complications and promote effective treatment. Share your thoughts and experiences with UTIs in the comments below, and don't hesitate to ask any questions or concerns you may have.
