Intro
Join the US Naval Reserve and serve part-time while maintaining a civilian career. Discover five ways to enlist, including enlistment incentives, officer commissioning programs, and lateral transfers. Explore the benefits of Naval Reserve recruiting, including drill pay, education assistance, and retirement plans, and start your path to serving your country.
Joining the US Naval Reserve can be a rewarding and challenging experience, offering a unique opportunity to serve your country while also pursuing a civilian career. With various programs and options available, there are several ways to join the Naval Reserve. Here are five ways to get started:
Understanding the Benefits of Joining the Naval Reserve

Before exploring the different ways to join the Naval Reserve, it's essential to understand the benefits of serving in the reserve component. Some of the key advantages include:
- Opportunity to serve your country while maintaining a civilian career
- Competitive pay and benefits
- Education assistance and tuition reimbursement
- Career advancement and leadership opportunities
- Networking and camaraderie with fellow service members
1. Joining the Naval Reserve through the Naval Reserve Officer Training Corps (NROTC)

The NROTC program is a four-year scholarship program that allows students to attend college while training to become a Naval Reserve officer. Students attend college full-time, taking courses in their chosen major, while also participating in Naval Reserve training and activities.
- Requirements:
- Be a US citizen
- Be between the ages of 17 and 27
- Have a minimum GPA of 2.5
- Pass a physical fitness test
- Complete a Naval Reserve officer candidate school
2. Joining the Naval Reserve through the Officer Candidate School (OCS)

The OCS program is a 12-week training course that prepares college graduates to become Naval Reserve officers. Students learn leadership and management skills, as well as military protocol and procedures.
- Requirements:
- Be a US citizen
- Have a bachelor's degree
- Be between the ages of 19 and 29
- Pass a physical fitness test
- Complete a Naval Reserve officer candidate school
3. Joining the Naval Reserve through the Direct Commission Officer (DCO) Program

The DCO program allows professionals with specialized skills, such as lawyers, doctors, and chaplains, to join the Naval Reserve as officers. These individuals receive a direct commission as an officer and attend a short training course to learn about Naval Reserve procedures and protocol.
- Requirements:
- Be a US citizen
- Have a specialized degree or certification
- Be between the ages of 19 and 42
- Pass a physical fitness test
- Complete a short training course
4. Joining the Naval Reserve through the Enlisted Program

The enlisted program allows individuals to join the Naval Reserve as enlisted personnel. Enlistees attend basic training, also known as boot camp, and then attend specialized training in their chosen rating, or job.
- Requirements:
- Be a US citizen
- Be between the ages of 17 and 34
- Pass a physical fitness test
- Complete basic training and specialized training
5. Joining the Naval Reserve through the Nuclear Field Program

The Nuclear Field program allows individuals to join the Naval Reserve and work in nuclear-related fields, such as nuclear engineering or nuclear operations. These individuals receive specialized training and work on nuclear-powered ships and submarines.
- Requirements:
- Be a US citizen
- Be between the ages of 17 and 25
- Pass a physical fitness test
- Complete specialized training in nuclear-related fields
Gallery of Naval Reserve Images
Naval Reserve Image Gallery

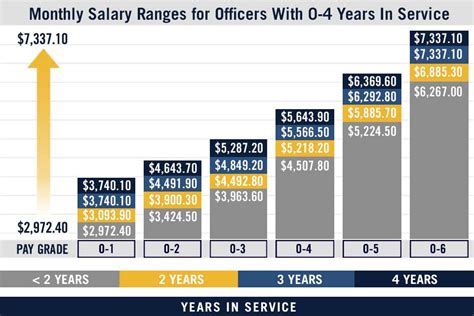








In conclusion, joining the Naval Reserve can be a rewarding and challenging experience, offering a unique opportunity to serve your country while also pursuing a civilian career. Whether you're interested in becoming an officer or enlisted personnel, there are several programs and options available to help you get started. Take the first step today and explore the different ways to join the Naval Reserve.
