Intro
Discover the vital role of vacuoles in cells, exploring their function, structure, and importance in cellular processes like storage, recycling, and maintenance, revealing their significance in plant and animal cells.
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms, and it is composed of various organelles that work together to maintain cellular homeostasis. One of the most fascinating and essential organelles is the vacuole, which plays a crucial role in maintaining the cell's internal environment. The importance of vacuoles cannot be overstated, as they are involved in a wide range of cellular processes, including storage, recycling, and waste management. In this article, we will delve into the world of vacuoles and explore their functions, structure, and importance in cellular biology.
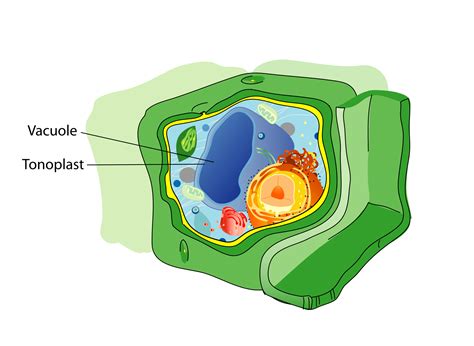
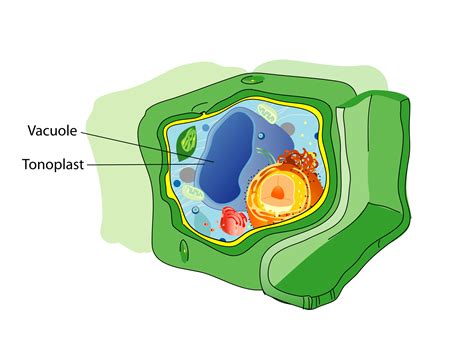
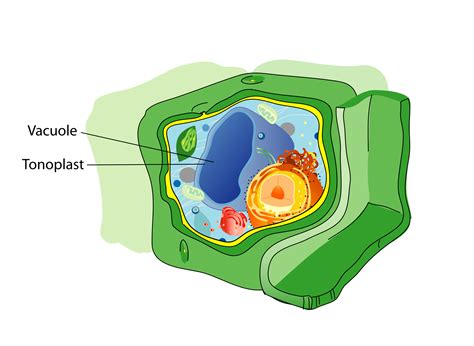
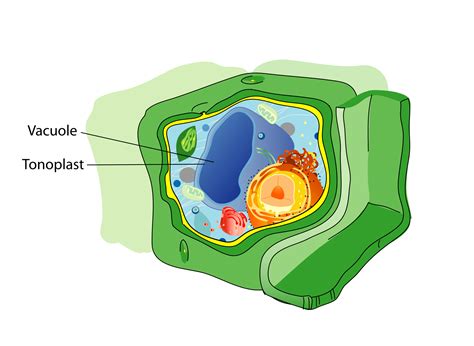
The vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in plant and animal cells, although it is more prominent in plant cells. It is a dynamic structure that can change shape and size depending on the cell's needs. Vacuoles are responsible for storing and recycling various substances, including water, salts, and waste products. They also play a critical role in maintaining the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation. The vacuole's ability to regulate the cell's internal environment makes it an essential component of cellular homeostasis.
The study of vacuoles is a fascinating field that has garnered significant attention in recent years. Researchers have made significant progress in understanding the structure and function of vacuoles, and their findings have shed new light on the importance of these organelles in cellular biology. From the storage of nutrients and waste products to the regulation of cellular pH and osmoregulation, vacuoles play a vital role in maintaining the cell's internal environment. As we explore the world of vacuoles, we will discover the intricate mechanisms that govern their function and the significant impact they have on cellular homeostasis.
Vacuole Structure and Function
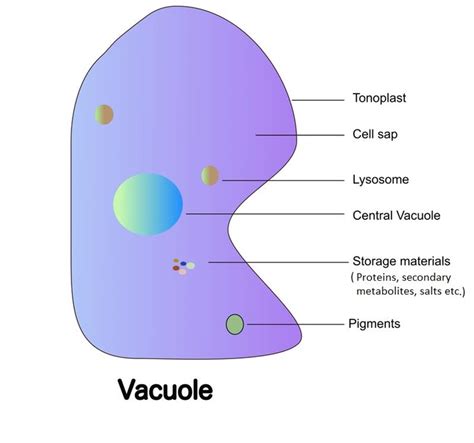
The vacuole is a complex organelle that is composed of a membrane-bound sac filled with a fluid called vacuolar sap. The vacuolar sap is a mixture of water, salts, and various organic compounds, including sugars, amino acids, and waste products. The vacuole membrane, also known as the tonoplast, is a semi-permeable membrane that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The tonoplast is composed of a lipid bilayer embedded with various proteins that facilitate the transport of substances across the membrane.
The vacuole's structure and function are closely linked, and its ability to regulate the cell's internal environment is dependent on its unique structure. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its structure, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.
Vacuole Types and Their Functions
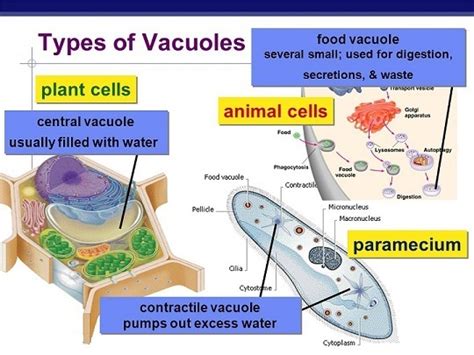
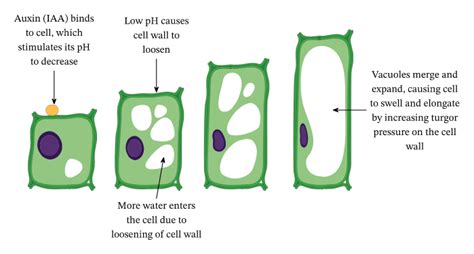
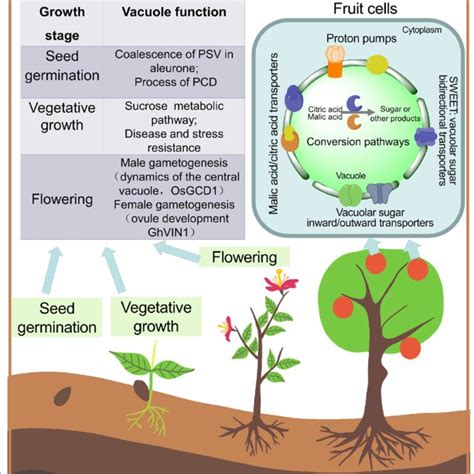
There are several types of vacuoles, each with its unique function and characteristics. The most common types of vacuoles include: * Contractile vacuoles: These vacuoles are found in animal cells and are responsible for regulating the cell's water balance. * Food vacuoles: These vacuoles are found in animal cells and are responsible for storing and digesting food particles. * Sap vacuoles: These vacuoles are found in plant cells and are responsible for storing and recycling various substances, including sugars and amino acids. * Waste vacuoles: These vacuoles are found in both plant and animal cells and are responsible for storing and recycling waste products.Vacuole Formation and Maintenance
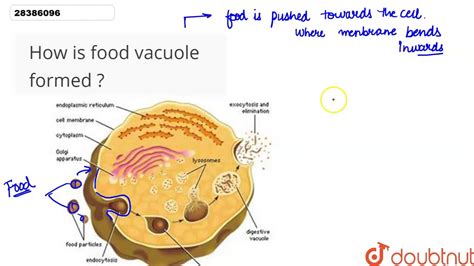
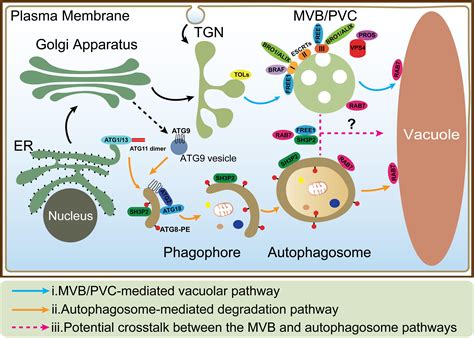
The formation and maintenance of vacuoles are complex processes that involve the coordinated effort of various cellular components. The vacuole is formed through the fusion of smaller vesicles, which are derived from the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. The vacuole's membrane is composed of a lipid bilayer embedded with various proteins that facilitate the transport of substances across the membrane.
The maintenance of the vacuole is dependent on the cell's ability to regulate its internal environment. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its maintenance, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.
Vacuole Regulation and Signaling
The regulation and signaling of vacuoles are complex processes that involve the coordinated effort of various cellular components. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its regulation, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.The signaling pathways that regulate vacuole function are complex and involve the coordinated effort of various cellular components. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its signaling, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.
Vacuole and Cellular Homeostasis
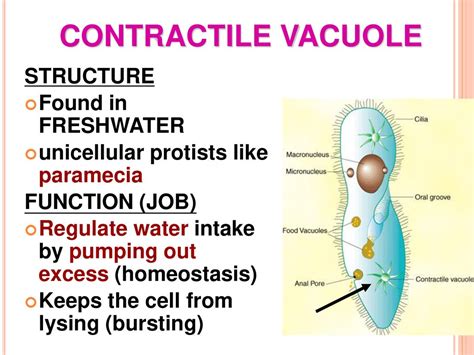
The vacuole plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, as it is able to regulate the cell's internal environment. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its function, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.
The vacuole's role in cellular homeostasis is closely linked to its ability to regulate the cell's internal environment. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its function, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.
Vacuole and Cell Signaling
The vacuole plays a critical role in cell signaling, as it is able to regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its signaling, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.The signaling pathways that regulate vacuole function are complex and involve the coordinated effort of various cellular components. The vacuole's membrane-bound sac allows it to store and recycle various substances, while its semi-permeable membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the vacuole. The vacuole's ability to maintain the cell's internal pH and osmoregulation is also dependent on its signaling, as it is able to regulate the movement of ions and water across its membrane.
Vacuole and Disease
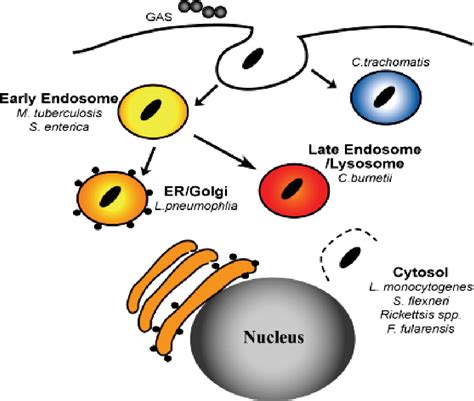
The vacuole plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis, and its dysfunction has been implicated in various diseases. The vacuole's ability to regulate the cell's internal environment is dependent on its function, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities. The vacuole's role in disease is closely linked to its ability to regulate the cell's internal environment, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities.
The vacuole's dysfunction has been implicated in various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders. The vacuole's ability to regulate the cell's internal environment is dependent on its function, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities. The vacuole's role in disease is closely linked to its ability to regulate the cell's internal environment, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities.
Vacuole and Therapeutic Targets
The vacuole's dysfunction has been implicated in various diseases, and its therapeutic targeting has been proposed as a potential treatment strategy. The vacuole's ability to regulate the cell's internal environment is dependent on its function, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities. The vacuole's role in disease is closely linked to its ability to regulate the cell's internal environment, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities.The therapeutic targeting of the vacuole has been proposed as a potential treatment strategy for various diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders. The vacuole's ability to regulate the cell's internal environment is dependent on its function, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities. The vacuole's role in disease is closely linked to its ability to regulate the cell's internal environment, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities.
Vacuole Image Gallery

Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the vacuole is a complex and essential organelle that plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Its ability to regulate the cell's internal environment is dependent on its function, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of cellular abnormalities. The therapeutic targeting of the vacuole has been proposed as a potential treatment strategy for various diseases, and further research is needed to fully understand its role in cellular biology.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the vacuole's function and importance in cellular biology. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We would love to hear from you and engage in a discussion about the fascinating world of vacuoles. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and colleagues. Together, we can continue to explore and understand the complex and fascinating world of cellular biology.
