Intro
Unlock the full potential of C++ variadic templates with our expert guide. Discover 5 powerful ways to master variadic templates, from recursive expansion to SFINAE techniques. Improve your codes flexibility and efficiency. Learn how to write more expressive and reusable functions with C++ variadic templates and metaprogramming concepts.
Mastering variadic templates in C++ is an essential skill for any programmer looking to take their coding skills to the next level. Variadic templates are a powerful feature in C++ that allows for the creation of functions and classes that can handle a variable number of arguments. This flexibility makes them extremely useful in a wide range of programming applications. In this article, we will explore five ways to master variadic templates in C++, including understanding the basics, using parameter packs, and applying them to real-world problems.
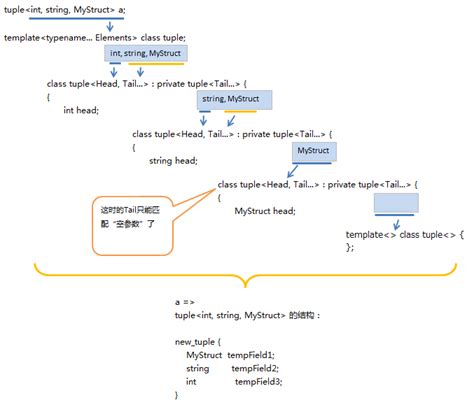
Understanding the Basics of Variadic Templates
Before diving into the more advanced topics, it's essential to understand the basics of variadic templates. A variadic template is a template that can take a variable number of arguments. This is achieved using the ... operator, which is used to declare a parameter pack. A parameter pack is a sequence of template parameters that can be expanded into a comma-separated list of parameters.
For example, the following code declares a variadic template function that takes a variable number of arguments:
template
void print(Args... args) {
// do something with args
}
In this example, Args is a parameter pack that represents the variable number of arguments. The ... operator is used to expand the parameter pack into a comma-separated list of parameters.
Using Parameter Packs
Parameter packs are a fundamental concept in variadic templates. They allow you to declare a variable number of parameters and then expand them into a comma-separated list. There are several ways to use parameter packs, including:
- Expanding the parameter pack into a comma-separated list of parameters using the
...operator. - Using the
sizeof...operator to get the number of parameters in the parameter pack. - Using the
std::tupleclass to store the parameters in a tuple.
For example, the following code uses the ... operator to expand the parameter pack into a comma-separated list of parameters:
template
void print(Args... args) {
std::cout << (std::string(", ") +... + std::to_string(args));
}
In this example, the ... operator is used to expand the parameter pack into a comma-separated list of parameters. The std::string and std::to_string functions are used to convert the parameters to strings.
Using Variadic Templates with Recursion
One way to master variadic templates is to use them with recursion. Recursion is a programming technique where a function calls itself repeatedly until a base case is reached. Variadic templates can be used with recursion to create functions that can handle a variable number of arguments.
For example, the following code uses variadic templates with recursion to create a function that calculates the sum of a variable number of arguments:
template
T sum(T t) {
return t;
}
template
auto sum(T t, Args... args) {
return t + sum(args...);
}
In this example, the sum function is defined recursively using variadic templates. The base case is the function that takes a single argument, and the recursive case is the function that takes a variable number of arguments.
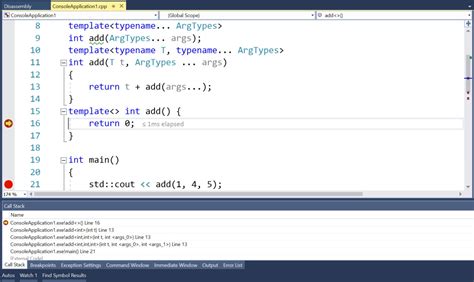
Using Variadic Templates with Folding Expressions
Folding expressions are a feature in C++17 that allows you to apply a binary operation to a parameter pack. They are a concise way to perform operations on a variable number of arguments. Variadic templates can be used with folding expressions to create functions that can handle a variable number of arguments.
For example, the following code uses variadic templates with folding expressions to create a function that calculates the sum of a variable number of arguments:
template
auto sum(Args... args) {
return (... + args);
}
In this example, the ... operator is used to expand the parameter pack into a comma-separated list of parameters. The + operator is used to calculate the sum of the parameters.
Applying Variadic Templates to Real-World Problems
Variadic templates have many real-world applications, including:
- Creating functions that can handle a variable number of arguments.
- Creating classes that can store a variable number of objects.
- Creating generic algorithms that can work with a variable number of types.
For example, the following code uses variadic templates to create a function that prints the values of a variable number of arguments:
template
void print(Args... args) {
std::cout << (std::string(", ") +... + std::to_string(args));
}
int main() {
print(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
return 0;
}
In this example, the print function is used to print the values of a variable number of arguments.
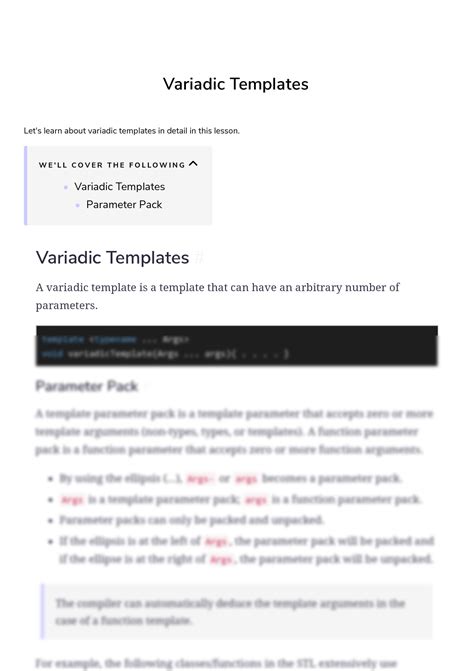
Best Practices for Using Variadic Templates
Here are some best practices for using variadic templates:
- Use meaningful names for your parameter packs and template parameters.
- Use the
...operator to expand parameter packs into comma-separated lists. - Use the
sizeof...operator to get the number of parameters in a parameter pack. - Use folding expressions to perform operations on parameter packs.
By following these best practices, you can write more effective and readable variadic template code.
Variadic Templates in C++ Image Gallery


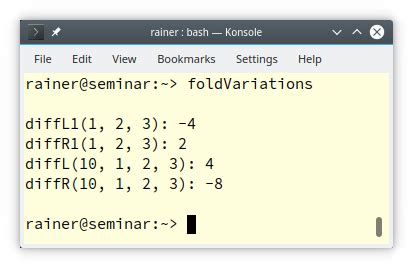

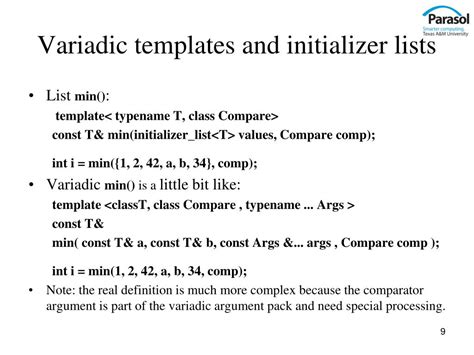

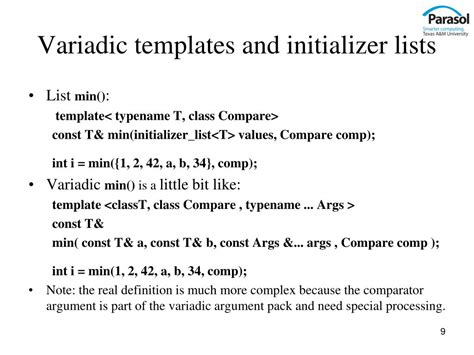
Conclusion: Mastering variadic templates in C++ is an essential skill for any programmer looking to take their coding skills to the next level. By understanding the basics, using parameter packs, and applying them to real-world problems, you can write more effective and readable code. Additionally, following best practices and avoiding common pitfalls can help you to become a proficient variadic template user.
Share your thoughts on variadic templates in C++ in the comments below! Have you used variadic templates in your projects? What challenges have you faced, and how did you overcome them? Let's discuss!
