Activating a cell in VBA is a fundamental process that allows you to perform various operations, such as data entry, formatting, and calculations, on a specific cell or range of cells in your Excel worksheet. This article will delve into the different ways to activate a cell in VBA, exploring the syntax, examples, and practical applications of each method.
Why Activate Cells in VBA?
Before we dive into the methods, it's essential to understand why activating cells is necessary in VBA. Activating a cell allows you to:
- Select a specific cell or range of cells for data entry or formatting
- Perform calculations or operations on a specific cell or range
- Use VBA methods and properties that require a specific cell or range to be active
Method 1: Using the Range Object
The Range object is the most common way to activate a cell in VBA. You can use the Range object to select a specific cell or range of cells by specifying the cell address or range address.
Sub ActivateCell()
Range("A1").Activate
End Sub
In this example, the Range object is used to activate cell A1.
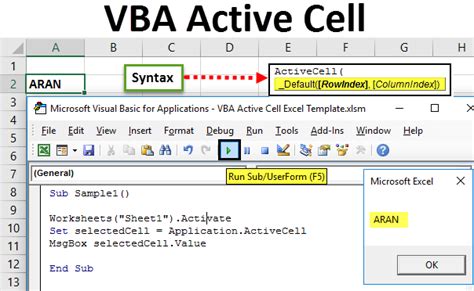
Method 2: Using the Cells Property
The Cells property is another way to activate a cell in VBA. This method allows you to specify the row and column numbers of the cell you want to activate.
Sub ActivateCell()
Cells(1, 1).Activate
End Sub
In this example, the Cells property is used to activate cell A1 by specifying the row number (1) and column number (1).
Method 3: Using the Offset Property
The Offset property allows you to activate a cell that is a specified number of rows and columns from the active cell.
Sub ActivateCell()
ActiveCell.Offset(1, 1).Activate
End Sub
In this example, the Offset property is used to activate a cell that is one row and one column from the active cell.
Method 4: Using the End Property
The End property allows you to activate a cell that is at the end of a row or column.
Sub ActivateCell()
ActiveCell.End(xlDown).Activate
End Sub
In this example, the End property is used to activate the cell at the end of the column that contains the active cell.
Method 5: Using the Find Method
The Find method allows you to activate a cell that contains a specific value.
Sub ActivateCell()
Range("A1:A100").Find("SearchValue").Activate
End Sub
In this example, the Find method is used to activate the cell that contains the value "SearchValue" in the range A1:A100.
Gallery of Activate Cell VBA Images
Activate Cell VBA Image Gallery
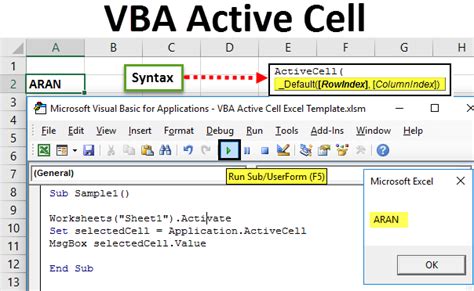
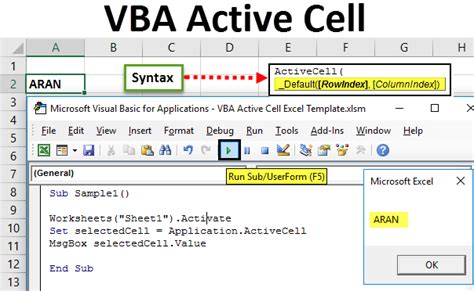
Conclusion
In this article, we explored five different ways to activate a cell in VBA, including using the Range object, Cells property, Offset property, End property, and Find method. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which method to use depends on the specific requirements of your VBA project. By mastering these methods, you can take your VBA skills to the next level and become more efficient in your work. We hope this article has been informative and helpful. Please leave a comment below if you have any questions or need further clarification on any of the methods discussed.
