Intro
Master VBA sheet management with our expert guide. Discover 3 efficient ways to check if a sheet exists in VBA, including using the WorksheetExists function, iterating through worksheets, and leveraging the On Error Resume Next statement. Optimize your macros with these practical tips and improve your Excel automation skills.
Working with Excel sheets in VBA can be a powerful way to automate tasks and manipulate data. However, one common challenge that developers face is checking if a specific sheet exists in a workbook before attempting to access or manipulate it. In this article, we will explore three different methods to check if a sheet exists in VBA.
The Importance of Checking Sheet Existence
Before we dive into the methods, it's essential to understand why checking sheet existence is crucial. If you try to access or manipulate a sheet that doesn't exist, VBA will throw an error, which can be frustrating and time-consuming to debug. By checking if a sheet exists, you can avoid errors and ensure that your code runs smoothly.
Method 1: Using the On Error Resume Next Statement
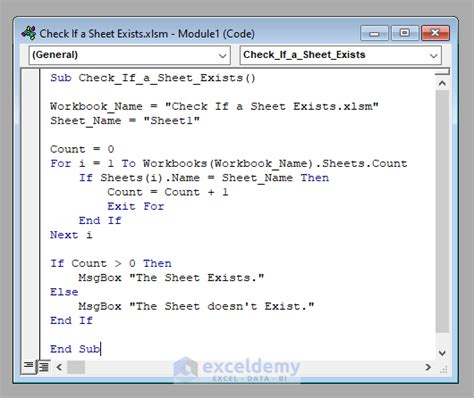
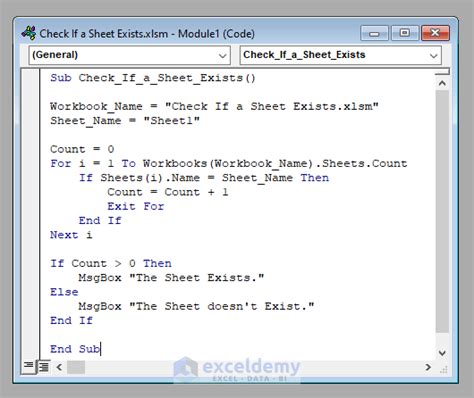
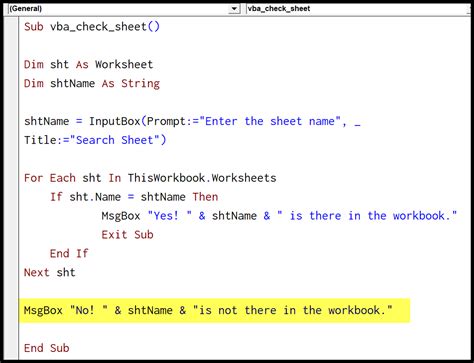
One way to check if a sheet exists is by using the On Error Resume Next statement. This statement allows you to execute a block of code that might throw an error, and if an error occurs, the code will continue executing the next line.
Sub CheckSheetExistence()
Dim ws As Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Set ws = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets("Sheet1")
If ws Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Sheet does not exist"
Else
MsgBox "Sheet exists"
End If
On Error GoTo 0
End Sub
In this example, we're trying to set a worksheet object ws to a sheet named "Sheet1". If the sheet doesn't exist, the ws object will be Nothing, and we can display a message box indicating that the sheet doesn't exist.
Image:
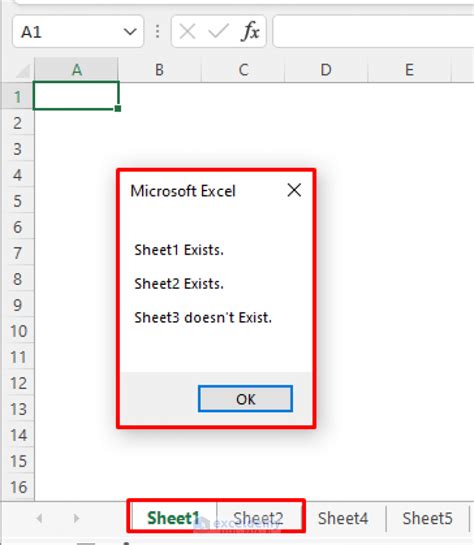
Method 2: Using the Worksheets Collection
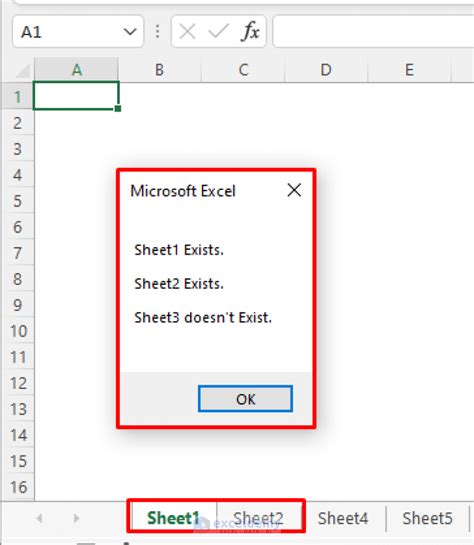
Another way to check if a sheet exists is by iterating through the Worksheets collection and checking if the sheet name matches the one you're looking for.
Sub CheckSheetExistence()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
If ws.Name = "Sheet1" Then
MsgBox "Sheet exists"
Exit For
End If
Next ws
If ws Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Sheet does not exist"
End If
End Sub
In this example, we're iterating through the Worksheets collection and checking if the sheet name matches "Sheet1". If we find a match, we display a message box indicating that the sheet exists. If we don't find a match after iterating through all the sheets, we display a message box indicating that the sheet doesn't exist.
Image:
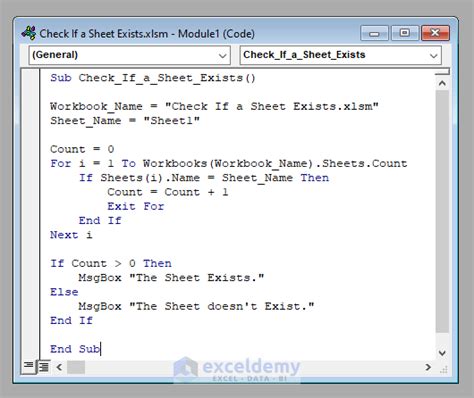
Method 3: Using the Evaluate Function
A third way to check if a sheet exists is by using the Evaluate function, which allows you to execute a worksheet formula and return the result.
Sub CheckSheetExistence()
If Evaluate("ISREF('Sheet1'!A1)") Then
MsgBox "Sheet exists"
Else
MsgBox "Sheet does not exist"
End If
End Sub
In this example, we're using the Evaluate function to execute the ISREF formula, which checks if a reference to a cell on the sheet exists. If the reference exists, the sheet exists, and we display a message box indicating that the sheet exists. If the reference doesn't exist, the sheet doesn't exist, and we display a message box indicating that the sheet doesn't exist.
Image:
Gallery of VBA Sheet Existence Methods
VBA Sheet Existence Methods Gallery


Conclusion
In this article, we explored three different methods to check if a sheet exists in VBA. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on your specific needs and preferences. By using these methods, you can ensure that your VBA code runs smoothly and avoids errors caused by attempting to access or manipulate non-existent sheets.
