Intro
Working with large datasets in Excel can be a daunting task, especially when you need to perform repetitive actions on each cell in a range. This is where VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) comes to the rescue. VBA is a powerful programming language that allows you to automate tasks in Excel by writing code. In this article, we'll explore five ways to use VBA to perform actions on each cell in a range.
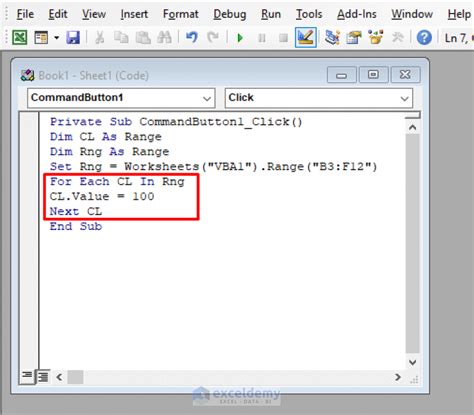
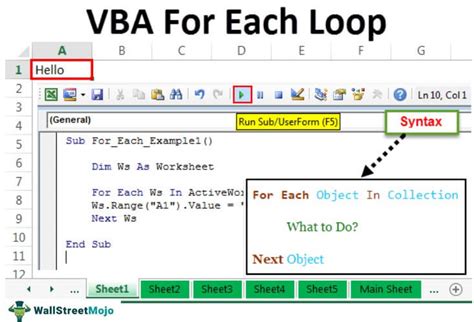
1. Looping Through Cells with a For-Each Loop
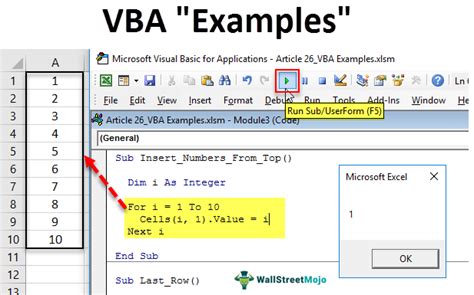
One of the most common ways to perform actions on each cell in a range is by using a For-Each loop. This loop allows you to iterate through each cell in a range and perform a specific action.
Sub LoopThroughCells()
Dim cell As Range
For Each cell In Range("A1:A10")
' Perform action on each cell
cell.Value = cell.Value * 2
Next cell
End Sub
In this example, the code loops through each cell in the range A1:A10 and multiplies the value by 2.
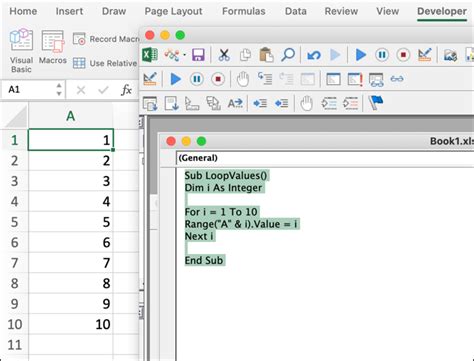
2. Using the For Loop with a Cell Counter
Another way to perform actions on each cell in a range is by using a For loop with a cell counter. This method is similar to the For-Each loop, but it uses a counter to keep track of the current cell.
Sub LoopThroughCellsUsingCounter()
Dim i As Long
For i = 1 To 10
' Perform action on each cell
Cells(i, 1).Value = Cells(i, 1).Value * 2
Next i
End Sub
In this example, the code loops through each cell in the range A1:A10 and multiplies the value by 2.
3. Using the Range Object's Cells Property
You can also use the Range object's Cells property to perform actions on each cell in a range. This method is similar to the For-Each loop, but it uses the Cells property to access each cell.
Sub LoopThroughCellsUsingCellsProperty()
Dim cell As Range
For i = 1 To 10
Set cell = Range("A1:A10").Cells(i)
' Perform action on each cell
cell.Value = cell.Value * 2
Next i
End Sub
In this example, the code loops through each cell in the range A1:A10 and multiplies the value by 2.
4. Using the Application Index Property
You can also use the Application Index property to perform actions on each cell in a range. This method is similar to the For-Each loop, but it uses the Index property to access each cell.
Sub LoopThroughCellsUsingIndexProperty()
Dim cell As Range
For i = 1 To 10
Set cell = Application.Index(Range("A1:A10"), i)
' Perform action on each cell
cell.Value = cell.Value * 2
Next i
End Sub
In this example, the code loops through each cell in the range A1:A10 and multiplies the value by 2.

5. Using the Evaluate Method
Finally, you can use the Evaluate method to perform actions on each cell in a range. This method is similar to the For-Each loop, but it uses the Evaluate method to access each cell.
Sub LoopThroughCellsUsingEvaluateMethod()
Dim cell As Range
For i = 1 To 10
Set cell = Range("A1:A10").Evaluate("A" & i)
' Perform action on each cell
cell.Value = cell.Value * 2
Next i
End Sub
In this example, the code loops through each cell in the range A1:A10 and multiplies the value by 2.
In conclusion, there are several ways to use VBA to perform actions on each cell in a range. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific requirements of the task.
Gallery of VBA For Each Cell In Range Examples
VBA For Each Cell In Range Image Gallery
We hope this article has helped you learn how to use VBA to perform actions on each cell in a range. If you have any questions or need further assistance, please don't hesitate to ask.
