Intro
Discover how to sort a Listbox in descending order using VBA with ease. Learn the simple code and techniques to organize your data in a Listbox control. Master VBA Listbox sorting, filtering, and manipulation with expert tips and examples. Take control of your data and improve your VBA skills today!
When working with ListBoxes in VBA, sorting the data in descending order can be a bit tricky, but don't worry, I've got you covered. In this article, we'll explore the easiest ways to sort your ListBox data in descending order.
Why Sort ListBox Data?
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty, let's quickly discuss why sorting ListBox data is important. Sorting data makes it easier to analyze and understand, especially when working with large datasets. In VBA, sorting ListBox data can help you:
- Identify trends and patterns
- Quickly find specific data points
- Create more informative and readable reports
The Easy Way: Using the List Property
The simplest way to sort ListBox data in descending order is to use the List property. Here's an example:
Dim i As Long
Dim j As Long
Dim temp As Variant
With Me.ListBox1
For i = 0 To.ListCount - 2
For j = i + 1 To.ListCount - 1
If.List(i) <.List(j) Then
temp =.List(i)
.List(i) =.List(j)
.List(j) = temp
End If
Next j
Next i
End With
This code uses a simple bubble sort algorithm to sort the ListBox data in descending order. It works by iterating through the list and swapping adjacent items if they are in the wrong order.
The Efficient Way: Using an Array
While the previous method is easy to implement, it's not the most efficient way to sort large datasets. A better approach is to use an array to store the ListBox data and then sort the array using the QuickSort algorithm.
Dim arr As Variant
Dim i As Long
With Me.ListBox1
ReDim arr(.ListCount - 1)
For i = 0 To.ListCount - 1
arr(i) =.List(i)
Next i
QuickSort arr, 0, UBound(arr)
.Clear
.List = arr
End With
Sub QuickSort(arr As Variant, ByVal low As Long, ByVal high As Long)
Dim pivot As Variant
Dim i As Long
Dim j As Long
Dim temp As Variant
If low < high Then
pivot = arr(low)
i = low + 1
j = high
While i <= j
While i <= high And arr(i) > pivot
i = i + 1
Wend
While j >= low And arr(j) < pivot
j = j - 1
Wend
If i <= j Then
temp = arr(i)
arr(i) = arr(j)
arr(j) = temp
i = i + 1
j = j - 1
End If
Wend
temp = arr(low)
arr(low) = arr(j)
arr(j) = temp
QuickSort arr, low, j - 1
QuickSort arr, j + 1, high
End If
End Sub
This code uses the QuickSort algorithm to sort the array in descending order. It's much faster than the previous method, especially for large datasets.
The Advanced Way: Using a Class Module
If you need to sort ListBox data in a more complex way, you can create a class module to encapsulate the sorting logic. Here's an example:
'ClsListBoxSorter.cls
Option Explicit
Private m_lb As MSForms.ListBox
Public Sub SortDescending()
Dim arr As Variant
Dim i As Long
With m_lb
ReDim arr(.ListCount - 1)
For i = 0 To.ListCount - 1
arr(i) =.List(i)
Next i
QuickSort arr, 0, UBound(arr)
.Clear
.List = arr
End With
End Sub
Private Sub QuickSort(arr As Variant, ByVal low As Long, ByVal high As Long)
'Implementation of QuickSort algorithm
End Sub
Public Property Set ListBox(value As MSForms.ListBox)
Set m_lb = value
End Property
You can then use this class module in your code like this:
Dim sorter As New ClsListBoxSorter
Set sorter.ListBox = Me.ListBox1
sorter.SortDescending
This approach is more advanced, but it allows you to encapsulate the sorting logic and reuse it throughout your project.
Conclusion
Sorting ListBox data in descending order can be achieved using various methods, ranging from simple to advanced. The choice of method depends on the size and complexity of your dataset, as well as your personal preference. By following these examples, you can easily sort your ListBox data in descending order and improve the readability and analysis of your data.

VBA ListBox Sort Descending Gallery


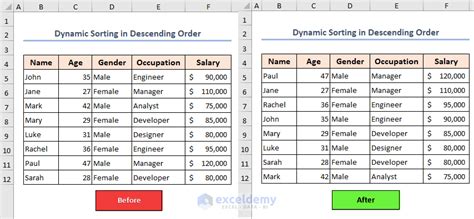
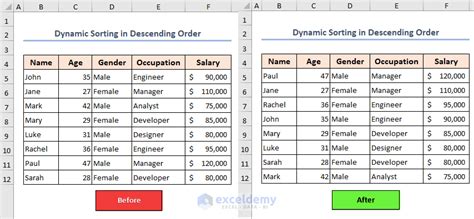

FAQ
Q: How do I sort ListBox data in ascending order?
A: To sort ListBox data in ascending order, you can use the same methods described in this article, but with a few modifications. For example, in the QuickSort algorithm, you can change the comparison operator from < to >.
Q: Can I use this code to sort other types of data, such as arrays or collections?
A: Yes, the QuickSort algorithm can be modified to sort other types of data, such as arrays or collections. You'll need to modify the comparison operator and the swap logic accordingly.
Q: How do I handle errors and exceptions when sorting ListBox data?
A: You can use error handling statements, such as On Error GoTo or Try-Catch, to handle errors and exceptions when sorting ListBox data. Additionally, you can add checks to ensure that the data is valid and can be sorted correctly.
