Saving a file as an Excel spreadsheet (XLS) using VBA can be a useful skill for automating tasks and streamlining workflows. VBA, or Visual Basic for Applications, is a programming language used to create and automate tasks in Microsoft Office applications, including Excel. Here are five ways to save a file as XLS using VBA:
Method 1: Using the SaveAs Method
The SaveAs method is a straightforward way to save a file as XLS using VBA. This method allows you to specify the file name, file format, and other options.
Sub SaveAsXLS()
ThisWorkbook.SaveAs "example.xls", xlExcel8
End Sub
In this example, ThisWorkbook refers to the active workbook, and SaveAs is used to save the file as "example.xls" in the Excel 97-2003 format (xlExcel8).
Method 2: Using the FileDialog Object
The FileDialog object allows you to prompt the user to select a location and file name for saving the file.
Sub SaveAsXLSFileDialog()
Dim fDialog As FileDialog
Set fDialog = Application.FileDialog(msoFileDialogSaveAs)
fDialog.InitialFileName = "example.xls"
fDialog.DefaultName = "example.xls"
fDialog.DefaultExtension = "xls"
fDialog.FilterIndex = 2
If fDialog.Show = -1 Then
ThisWorkbook.SaveAs fDialog.SelectedItems(1), xlExcel8
End If
End Sub
In this example, the FileDialog object is used to prompt the user to select a location and file name for saving the file. The SaveAs method is then used to save the file in the selected location and format.
Method 3: Using the Workbook.SaveAs Method with FileFormat Parameter
This method allows you to specify the file format using the FileFormat parameter.
Sub SaveAsXLSFileFormat()
ThisWorkbook.SaveAs "example.xls", FileFormat:=xlExcel8
End Sub
In this example, the SaveAs method is used to save the file as "example.xls" in the Excel 97-2003 format (xlExcel8).
Method 4: Using the Application.GetSaveAsFilename Method
This method allows you to prompt the user to select a location and file name for saving the file, and then returns the file name and path.
Sub SaveAsXLSGetSaveAsFilename()
Dim fileName As Variant
fileName = Application.GetSaveAsFilename("example.xls", "Excel Files (*.xls), *.xls")
If fileName <> False Then
ThisWorkbook.SaveAs fileName, xlExcel8
End If
End Sub
In this example, the GetSaveAsFilename method is used to prompt the user to select a location and file name for saving the file. The SaveAs method is then used to save the file in the selected location and format.
Method 5: Using the Workbook.SaveCopyAs Method
This method allows you to save a copy of the workbook in a different format.
Sub SaveAsXLSaveCopyAs()
ThisWorkbook.SaveCopyAs "example.xls"
End Sub
In this example, the SaveCopyAs method is used to save a copy of the workbook as "example.xls".
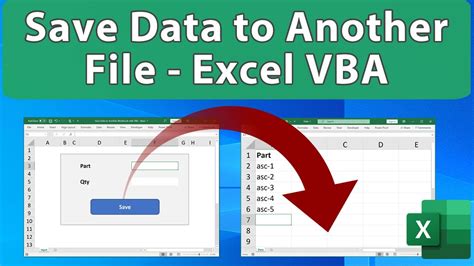
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which one to use will depend on the specific requirements of your project.
Gallery of VBA Excel Save as XLS Images
VBA Excel Save as XLS Image Gallery
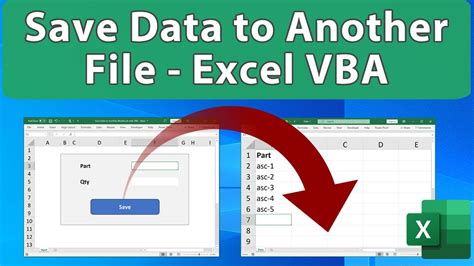
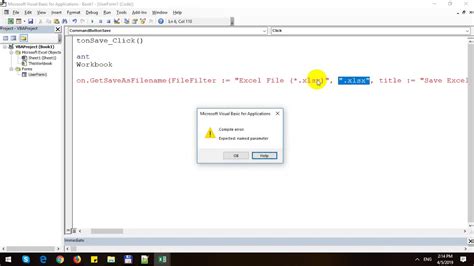
We hope this article has been helpful in providing you with five different methods for saving a file as XLS using VBA. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced programmer, these methods can be used to automate tasks and streamline workflows in Excel. Don't forget to leave a comment below and share this article with your friends and colleagues!
