Intro
Unlock the power of VBA with our expert guide on selecting workbooks. Learn the top 5 ways to choose the right workbook in VBA, including activating worksheets, using workbook objects, and more. Master workbook selection techniques to streamline your VBA code and boost productivity.
Understanding the Importance of Workbook Selection in VBA
When working with VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) in Microsoft Excel, selecting the correct workbook is crucial for performing various tasks, such as data manipulation, automation, and reporting. With multiple workbooks open, it's essential to identify the desired workbook to avoid errors and ensure accurate results. In this article, we'll explore five ways to select a workbook in VBA, highlighting their benefits and use cases.
The Consequences of Incorrect Workbook Selection
Incorrect workbook selection can lead to a range of issues, including:
- Data corruption or loss
- Inaccurate results
- Errors and crashes
- Inefficient code execution
To avoid these problems, it's vital to understand the different methods for selecting a workbook in VBA.
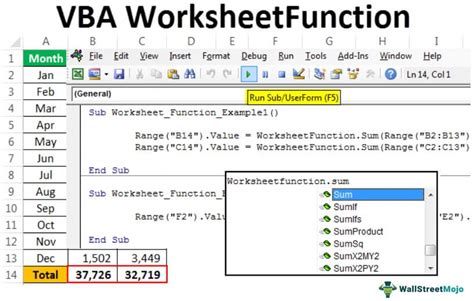
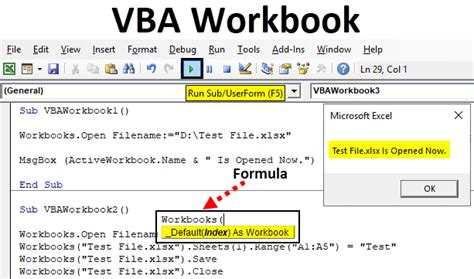
Method 1: Using the `Workbooks` Collection

The Workbooks collection is a built-in VBA object that contains all open workbooks. You can access a specific workbook by its index or name.
Sub SelectWorkbookByIndex()
Workbooks(1).Activate
End Sub
Sub SelectWorkbookByName()
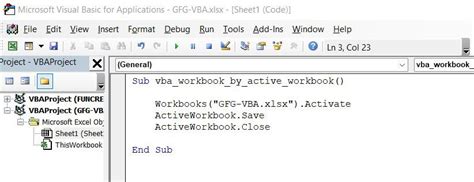
Workbooks("MyWorkbook.xlsx").Activate
End Sub
Benefits and Use Cases
- Easy to use and understand
- Suitable for small-scale projects with a limited number of workbooks
- Useful when working with a specific workbook that is always open
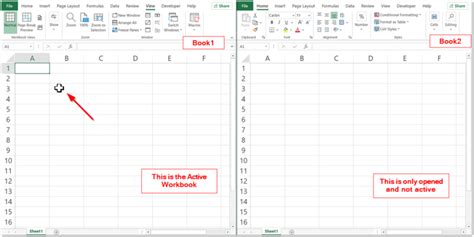
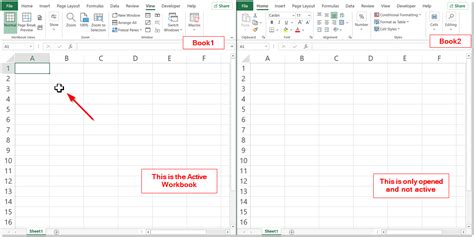
Method 2: Using the `ActiveWorkbook` Object
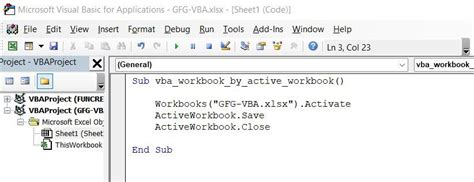
The ActiveWorkbook object refers to the currently active workbook. You can use this object to select the active workbook.
Sub SelectActiveWorkbook()
ActiveWorkbook.Activate
End Sub
Benefits and Use Cases
- Convenient when working with a single workbook
- Useful when the active workbook is the one that needs to be selected
- Simplifies code by eliminating the need to specify a workbook name or index
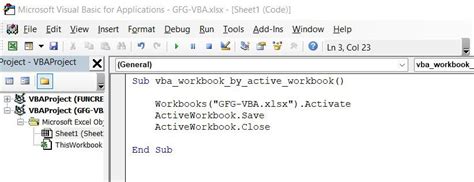
Method 3: Using the `ThisWorkbook` Object
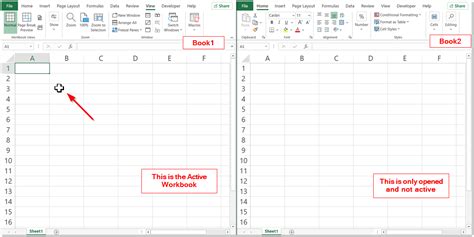
The ThisWorkbook object refers to the workbook that contains the VBA code. You can use this object to select the workbook that contains the code.
Sub SelectThisWorkbook()
ThisWorkbook.Activate
End Sub
Benefits and Use Cases
- Useful when working with a workbook that contains the VBA code
- Convenient when the workbook that contains the code needs to be selected
- Simplifies code by eliminating the need to specify a workbook name or index
Method 4: Using the `GetWorkbook` Function
The GetWorkbook function returns a workbook object based on a specified name or index.
Function GetWorkbook(name As String) As Workbook
Set GetWorkbook = Workbooks(name)
End Function
Sub SelectWorkbookUsingGetWorkbook()
Dim wb As Workbook
Set wb = GetWorkbook("MyWorkbook.xlsx")
wb.Activate
End Sub
Benefits and Use Cases
- Useful when working with a large number of workbooks
- Convenient when the workbook name or index is unknown
- Simplifies code by providing a flexible way to select a workbook
Method 5: Using the `Application.Workbooks` Collection
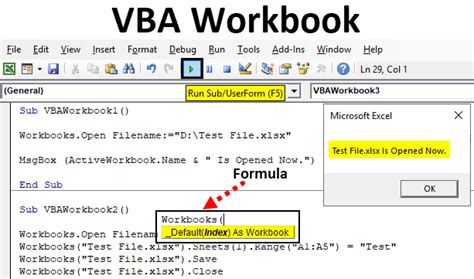
The Application.Workbooks collection is similar to the Workbooks collection, but it provides additional functionality.
Sub SelectWorkbookUsingApplicationWorkbooks()
Application.Workbooks("MyWorkbook.xlsx").Activate
End Sub
Benefits and Use Cases
- Useful when working with a large number of workbooks
- Convenient when the workbook name or index is unknown
- Simplifies code by providing a flexible way to select a workbook
VBA Workbook Selection Image Gallery


We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the different methods for selecting a workbook in VBA. By mastering these techniques, you'll be able to write more efficient and effective code, and avoid common errors. Share your thoughts and experiences with workbook selection in VBA in the comments below!
