When working with multiple sheets in Excel, it's common to need to reference data from one sheet in another. One of the most powerful tools for doing this is the VLOOKUP function. VLOOKUP allows you to search for a value in a table and return a corresponding value from another column. In this article, we'll explore five ways to use VLOOKUP to reference another sheet in Excel.
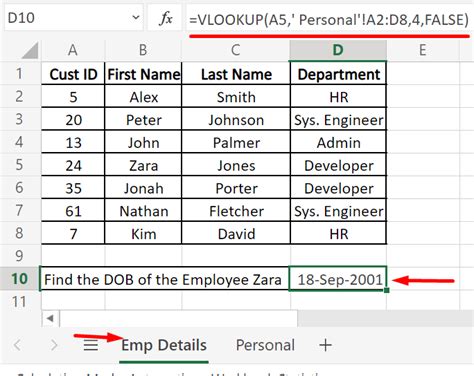
Why Use VLOOKUP?
Before we dive into the different ways to use VLOOKUP, let's quickly discuss why it's such a powerful tool. VLOOKUP allows you to perform lookups in a table and return a corresponding value from another column. This is particularly useful when working with large datasets or when you need to reference data from one sheet in another. With VLOOKUP, you can easily perform lookups and return the data you need without having to manually search for it.
Method 1: Basic VLOOKUP
The basic VLOOKUP formula is as follows:
=VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
lookup_valueis the value you want to search fortable_arrayis the range of cells that contains the data you want to searchcol_index_numis the column number that contains the value you want to return[range_lookup]is an optional argument that specifies whether you want an exact match or an approximate match
For example, suppose you have a sheet called "Sheet1" with the following data:
| Employee ID | Name | Department |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | John Smith | Sales |
| 102 | Jane Doe | Marketing |
| 103 | Bob Johnson | IT |
And you have another sheet called "Sheet2" with the following data:
| Employee ID | Job Title |
|---|---|
| 101 | Sales Manager |
| 102 | Marketing Manager |
| 103 | IT Manager |
You can use the following VLOOKUP formula to return the job title for an employee based on their employee ID:
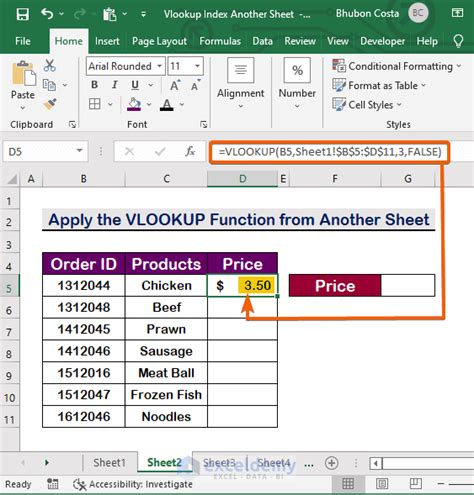
=VLOOKUP(A2, Sheet1!A:C, 2, FALSE)
Assuming the employee ID is in cell A2, this formula will return the job title for that employee.
Method 2: VLOOKUP with Multiple Criteria
Sometimes you may need to search for a value based on multiple criteria. For example, suppose you have a sheet with the following data:
| Employee ID | Name | Department | Job Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | John Smith | Sales | Sales Manager |
| 102 | Jane Doe | Marketing | Marketing Manager |
| 103 | Bob Johnson | IT | IT Manager |
| 104 | John Smith | Marketing | Marketing Manager |
And you want to return the job title for an employee based on their employee ID and department. You can use the following VLOOKUP formula:
=VLOOKUP(A2&B2, Sheet1!A:D, 4, FALSE)
Assuming the employee ID is in cell A2 and the department is in cell B2, this formula will return the job title for that employee.
Method 3: VLOOKUP with Dynamic Range
Sometimes you may need to search for a value in a range that changes dynamically. For example, suppose you have a sheet with the following data:
| Employee ID | Name | Department |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | John Smith | Sales |
| 102 | Jane Doe | Marketing |
| 103 | Bob Johnson | IT |
| 104 | John Smith | Marketing |
And you want to return the department for an employee based on their employee ID. You can use the following VLOOKUP formula:
=VLOOKUP(A2, OFFSET(Sheet1!A:A, 0, 0, COUNTA(Sheet1!A:A), 1), 2, FALSE)
This formula uses the OFFSET function to create a dynamic range that changes based on the number of rows in the data.
Method 4: VLOOKUP with Index and Match
The INDEX and MATCH functions can be used together to perform a lookup similar to VLOOKUP. The syntax for the INDEX and MATCH functions is as follows:
=INDEX(range, MATCH(lookup_value, range, [match_type])
rangeis the range of cells that contains the data you want to returnlookup_valueis the value you want to search forrangeis the range of cells that contains the values you want to search[match_type]is an optional argument that specifies the type of match you want to perform
For example, suppose you have a sheet with the following data:
| Employee ID | Name | Department |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | John Smith | Sales |
| 102 | Jane Doe | Marketing |
| 103 | Bob Johnson | IT |
And you want to return the department for an employee based on their employee ID. You can use the following INDEX and MATCH formula:
=INDEX(Sheet1!C:C, MATCH(A2, Sheet1!A:A, 0))
Assuming the employee ID is in cell A2, this formula will return the department for that employee.
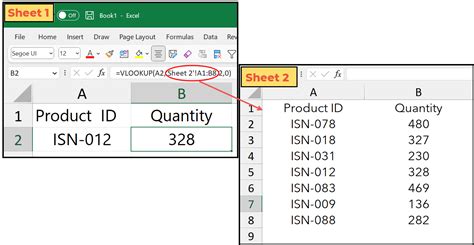
Method 5: VLOOKUP with Multiple Sheets
Sometimes you may need to search for a value in multiple sheets. For example, suppose you have two sheets, "Sheet1" and "Sheet2", with the following data:
Sheet1
| Employee ID | Name | Department |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | John Smith | Sales |
| 102 | Jane Doe | Marketing |
| 103 | Bob Johnson | IT |
Sheet2
| Employee ID | Job Title |
|---|---|
| 101 | Sales Manager |
| 102 | Marketing Manager |
| 103 | IT Manager |
And you want to return the job title for an employee based on their employee ID. You can use the following VLOOKUP formula:
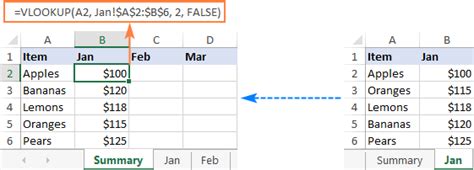
=VLOOKUP(A2, Sheet1!A:C, 2, FALSE)
=VLOOKUP(A2, Sheet2!A:B, 2, FALSE)
These formulas will return the job title for the employee based on their employee ID in both sheets.
Vlookup Another Sheet Image Gallery
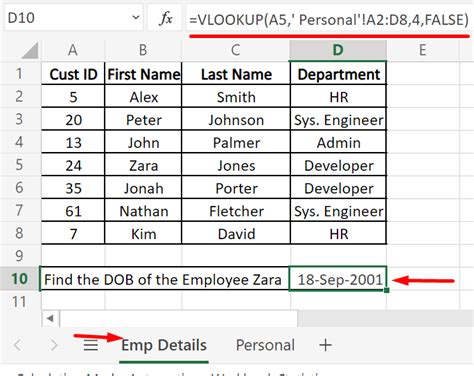
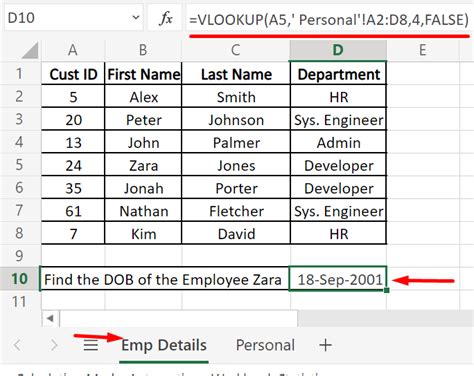
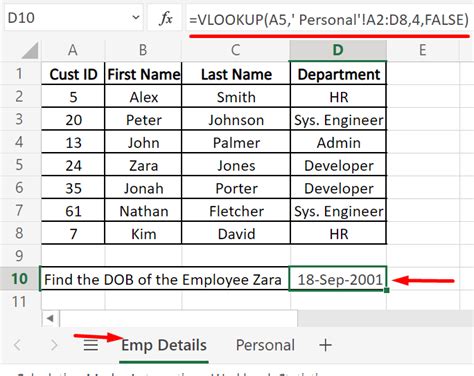
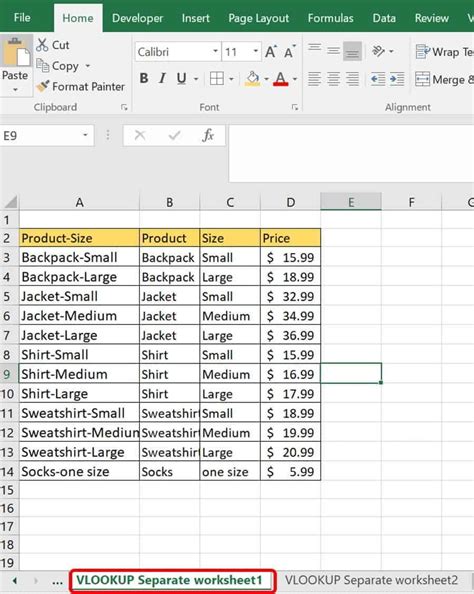
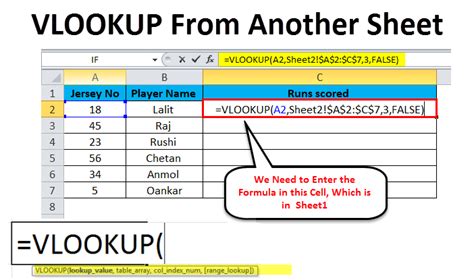
In conclusion, VLOOKUP is a powerful tool that can be used to reference data from one sheet in another. By using the different methods outlined in this article, you can perform lookups and return data from multiple sheets, ranges, and criteria. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced Excel user, VLOOKUP is a tool that can help you to work more efficiently and effectively.
