Intro
Unlock the secrets of Signal Intelligence! Discover how SIGINT intercepts and analyzes signals to uncover valuable intel. Learn about its types, methods, and applications in national security, cyber warfare, and more. Explore the importance of signal processing, communications intelligence, and electronic intelligence in the world of signals intelligence.
The world of intelligence gathering is vast and complex, with various forms of intelligence playing crucial roles in national security, defense, and global politics. One of the most critical forms of intelligence is Signal Intelligence (SIGINT). In this article, we will delve into the world of SIGINT, exploring its definition, history, methods, and significance in modern intelligence gathering.
What is Signal Intelligence?
Signal Intelligence (SIGINT) refers to the interception, collection, and analysis of signals or communications transmitted through various media, including radio waves, microwaves, and satellite transmissions. SIGINT involves the gathering of information from these signals to understand the capabilities, intentions, and activities of foreign governments, organizations, or individuals.
SIGINT is a vital component of the intelligence cycle, which includes tasking, collection, processing, analysis, and dissemination of intelligence. The primary goal of SIGINT is to provide strategic and tactical intelligence to support national security decision-making.
History of Signal Intelligence
The origins of SIGINT date back to World War I, when military forces began intercepting and decoding enemy communications. However, it wasn't until World War II that SIGINT became a critical component of military intelligence. The British Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park, for example, played a significant role in breaking German and Japanese codes, providing valuable intelligence to the Allies.
In the post-war era, SIGINT continued to evolve, with the establishment of the National Security Agency (NSA) in the United States in 1952. The NSA is responsible for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating SIGINT to support national security.
Methods of Signal Intelligence
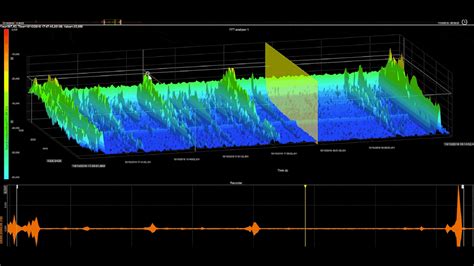
SIGINT involves various methods of intercepting and analyzing signals, including:
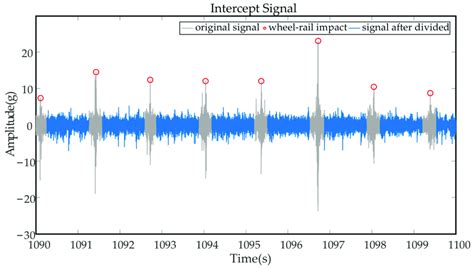
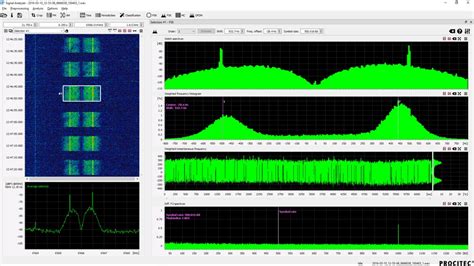
- Radio Frequency (RF) Interception: This involves intercepting radio signals transmitted through the airwaves.
- Satellite Interception: This involves intercepting signals transmitted via satellite communications.
- Microwave Interception: This involves intercepting signals transmitted via microwave communications.
- Computer Network Exploitation (CNE): This involves intercepting and analyzing data transmitted over computer networks.
SIGINT collection platforms include:
- Ground-based stations: These are fixed or mobile stations that intercept signals transmitted via radio waves or satellite communications.
- Airborne platforms: These include aircraft and drones that intercept signals while in flight.
- Satellite-based platforms: These include satellites that intercept signals transmitted via satellite communications.
- Cyber platforms: These include computer networks and systems that intercept and analyze data transmitted over the internet.
Types of Signal Intelligence
There are several types of SIGINT, including:
- Communications Intelligence (COMINT): This involves intercepting and analyzing communications between individuals or organizations.
- Electronic Intelligence (ELINT): This involves intercepting and analyzing electronic signals, such as radar emissions or telemetry data.
- Foreign Instrumentation Signals Intelligence (FISINT): This involves intercepting and analyzing signals emitted by foreign instrumentation, such as missile telemetry data.
Significance of Signal Intelligence
SIGINT plays a critical role in modern intelligence gathering, providing strategic and tactical intelligence to support national security decision-making. SIGINT has been instrumental in:
- Supporting military operations: SIGINT has provided critical intelligence to support military operations, including targeting and situational awareness.
- Countering terrorism: SIGINT has helped identify and disrupt terrorist networks, providing valuable intelligence on terrorist plans and operations.
- Supporting diplomacy: SIGINT has provided intelligence on foreign governments and organizations, supporting diplomatic efforts and informing policy decisions.

Challenges and Controversies
SIGINT faces several challenges and controversies, including:
- Privacy concerns: SIGINT raises concerns about privacy and civil liberties, particularly in the context of domestic surveillance.
- Security risks: SIGINT collection platforms and methods can be vulnerable to security risks, including hacking and eavesdropping.
- International cooperation: SIGINT requires international cooperation, which can be challenging in the context of competing national interests.
Conclusion
Signal Intelligence is a critical component of modern intelligence gathering, providing strategic and tactical intelligence to support national security decision-making. While SIGINT faces several challenges and controversies, its significance in supporting military operations, countering terrorism, and informing policy decisions cannot be overstated.
As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of SIGINT will only continue to grow. It is essential that we continue to invest in SIGINT capabilities, while also addressing the challenges and controversies that surround this critical component of intelligence gathering.
We would love to hear from you! Share your thoughts on the significance of Signal Intelligence and its role in modern intelligence gathering.
Signal Intelligence Image Gallery