Intro
Discover the pivotal moments of the War in the East, a transformative conflict that reshaped world history. From the Eastern Front to the fall of empires, explore the complex web of alliances, military strategies, and geopolitical tensions that defined this epic struggle, including the rise of Soviet power and the fate of Eastern Europe.
The war in the East, specifically the conflict between Japan and China, had far-reaching consequences that reshaped the course of history. This conflict, which began in 1937 and lasted until the end of World War II in 1945, was a pivotal moment in modern history that had significant impacts on the global balance of power, international relations, and the fate of nations.
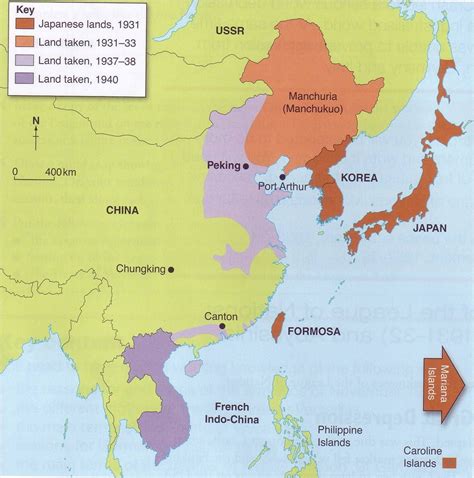
The war in the East was a culmination of years of tensions between Japan and China, fueled by nationalist sentiment, territorial disputes, and economic interests. Japan's invasion of Manchuria in 1931 marked the beginning of a long and bloody conflict that would eventually draw in other major powers, including the United States and the Soviet Union. The war in the East was a complex and multifaceted conflict that involved not only military battles but also economic warfare, propaganda, and diplomatic maneuvering.

The war in the East had significant consequences for the global balance of power. Japan's military expansion in Asia and the Pacific challenged the dominance of Western powers, particularly the United States and the United Kingdom. The war also led to the formation of new alliances and the realignment of old ones, as countries sought to protect their interests and secure their positions in the face of rising tensions.
The Causes of the War in the East
The war in the East was the result of a complex interplay of factors, including nationalist sentiment, territorial disputes, and economic interests. Japan's invasion of Manchuria in 1931 was motivated by a desire to expand its territory, secure resources, and demonstrate its military prowess. China, which had long been subject to foreign domination, saw Japan's aggression as a threat to its sovereignty and territorial integrity.

The war in the East was also fueled by economic interests. Japan needed resources, particularly oil and raw materials, to fuel its military expansion and industrial growth. China, which was rich in natural resources, was seen as a key prize in Japan's quest for economic dominance.
The Role of Nationalism
Nationalism played a significant role in the war in the East. Japan's aggressive expansion in Asia and the Pacific was motivated by a desire to assert its dominance and demonstrate its military prowess. China, which had long been subject to foreign domination, saw Japan's aggression as a threat to its sovereignty and territorial integrity.
The war in the East also saw the rise of nationalist sentiment in other countries, particularly the United States. The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 drew the United States into the conflict, leading to a dramatic shift in the global balance of power.
The Course of the War
The war in the East was a long and bloody conflict that involved multiple theaters and fronts. Japan's military expansion in Asia and the Pacific was marked by brutal violence and atrocities, including the Nanking Massacre and the forced labor camps.

The war in the East also saw significant battles and campaigns, including the Battle of Shanghai, the Battle of Nanjing, and the Burma Campaign. The war was marked by a series of Japanese victories, including the capture of Singapore and the Philippines, but ultimately ended in defeat for Japan.
The Atomic Bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The war in the East ended with the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945. The bombings, which killed hundreds of thousands of people and destroyed entire cities, marked a turning point in the war and led to Japan's surrender.

The war in the East had significant consequences for the global balance of power, international relations, and the fate of nations. The war marked the end of Japan's military expansion in Asia and the Pacific and led to the formation of new alliances and the realignment of old ones.
The Legacy of the War in the East
The war in the East has left a lasting legacy in the modern world. The war marked the end of Japan's military expansion in Asia and the Pacific and led to the formation of new alliances and the realignment of old ones.

The war in the East also saw the rise of nationalist sentiment in other countries, particularly the United States. The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 drew the United States into the conflict, leading to a dramatic shift in the global balance of power.
The War in the East in Popular Culture
The war in the East has been depicted in popular culture, including films, literature, and music. The war has been the subject of numerous films, including "The Last Emperor" and "Letters from Iwo Jima."

The war in the East has also been the subject of numerous literary works, including "The Rape of Nanking" by Iris Chang and "The Burma Road" by Donovan Webster.
War in the East Image Gallery








The war in the East has left a lasting legacy in the modern world, shaping international relations, global politics, and popular culture. As we reflect on this significant event in history, we are reminded of the importance of diplomacy, cooperation, and understanding in preventing future conflicts.
