Intro
Unlock the differences between Warrant Officers and Officers in the military. Discover the distinct roles, responsibilities, and career paths of these two ranks. Learn about the unique skills, training, and leadership styles that set them apart. Get insider knowledge on the key distinctions and similarities between Warrant Officers and Officers.
The military is a complex and multifaceted institution, with a wide range of roles and positions that each play a critical part in the overall functioning of the organization. Two of the most prominent types of military personnel are Warrant Officers and Officers, both of which have distinct responsibilities and requirements. Understanding the key differences between these two groups is essential for anyone considering a career in the military, as well as for those already serving.
What is a Warrant Officer?
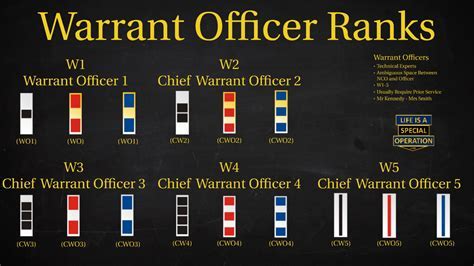
A Warrant Officer is a technical expert in a specific field or specialty, responsible for providing guidance and support to other military personnel. They are highly skilled and experienced individuals who have demonstrated a high level of proficiency in their area of expertise. Warrant Officers are typically responsible for providing technical advice and assistance to commanders and other officers, as well as for training and mentoring junior personnel.
What is an Officer?
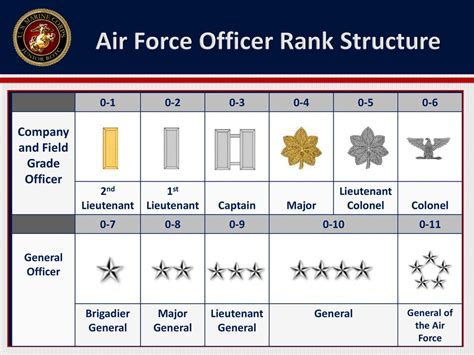
An Officer, on the other hand, is a leader and a manager, responsible for making strategic decisions and overseeing the overall operation of a military unit. Officers are responsible for planning, organizing, and directing the activities of their unit, as well as for making key decisions about personnel, resources, and operations. They are also responsible for representing their unit and the military as a whole, and for upholding the values and traditions of the service.
Key Differences Between Warrant Officers and Officers
While both Warrant Officers and Officers play critical roles in the military, there are several key differences between the two. Some of the most significant differences include:
Education and Training
- Warrant Officers: Typically require a high school diploma or equivalent, as well as specialized training and certification in their area of expertise.
- Officers: Typically require a bachelor's degree from an accredited institution, as well as completion of Officer Candidate School (OCS) or a service academy.
Responsibilities and Duties
- Warrant Officers: Focus on providing technical expertise and support, as well as training and mentoring junior personnel.
- Officers: Focus on leadership and management, including planning, organizing, and directing the activities of their unit.
Rank and Promotion
- Warrant Officers: Hold a unique rank structure, with five grades (W-1 to W-5) that are separate from the enlisted and officer ranks.
- Officers: Hold a traditional rank structure, with 10 grades (O-1 to O-10) that are based on time in service, performance, and other factors.
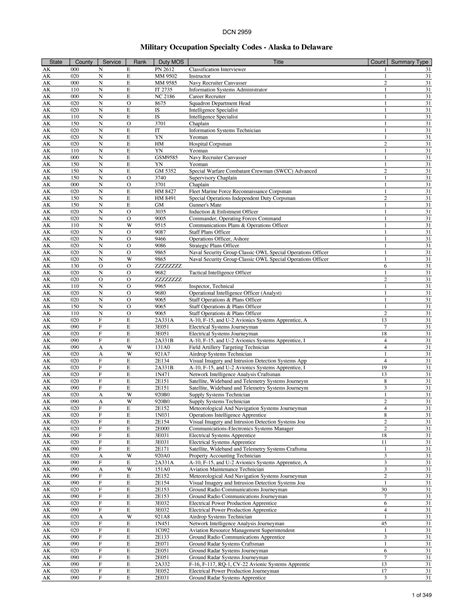
Specialties and Career Paths
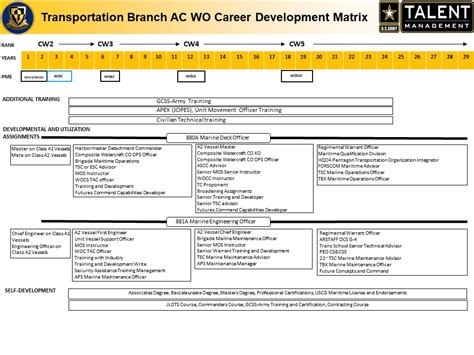
- Warrant Officers: Typically specialize in a specific technical field, such as aviation, communications, or intelligence.
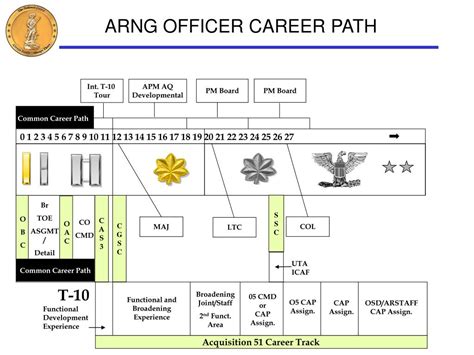
- Officers: Can pursue a wide range of career paths, including combat, logistics, personnel, and more.
Warrant Officer and Officer Career Paths



Conclusion
In conclusion, while both Warrant Officers and Officers play critical roles in the military, there are several key differences between the two. Warrant Officers are technical experts who provide guidance and support, while Officers are leaders and managers who oversee the overall operation of a military unit. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone considering a career in the military, as well as for those already serving.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!
** Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the differences between Warrant Officers and Officers.**
