Intro
Discover the vital role of Savanna Decomposers, including insects and microorganisms, in ecosystem recycling, nutrient cycling, and organic matter breakdown, supporting savanna biodiversity and ecosystem health.
The savanna ecosystem is a complex and fascinating environment, teeming with life and filled with intricate relationships between organisms. One of the most crucial, yet often overlooked, components of this ecosystem is the decomposers. Decomposers play a vital role in breaking down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients, and maintaining the health and fertility of the savanna soil. Without these microscopic heroes, the savanna would be a barren and lifeless landscape, devoid of the lush grasses and vibrant wildlife that we associate with this ecosystem.
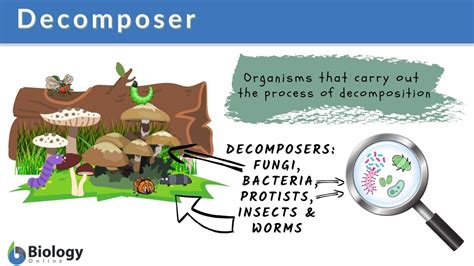
Decomposers are organisms that feed on dead plants and animals, using enzymes to break down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds. This process, known as decomposition, is essential for the savanna ecosystem, as it releases nutrients back into the soil, making them available to other organisms. Decomposers come in many forms, including bacteria, fungi, and insects, each with their unique characteristics and roles in the decomposition process. For example, bacteria are responsible for breaking down proteins and carbohydrates, while fungi specialize in decomposing cellulose and lignin, the tough components of plant cell walls.
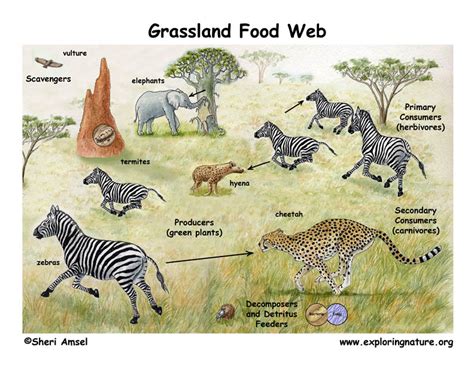
The importance of decomposers in the savanna ecosystem cannot be overstated. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers help to maintain soil quality, structure, and fertility. This, in turn, supports the growth of new plants, which provide food and shelter for the diverse array of wildlife that inhabits the savanna. Additionally, decomposers play a critical role in regulating the savanna's nutrient cycles, ensuring that essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are available to plants and other organisms. Without decomposers, these nutrients would remain locked in dead organic matter, rendering them inaccessible to the rest of the ecosystem.
Introduction to Savanna Decomposers

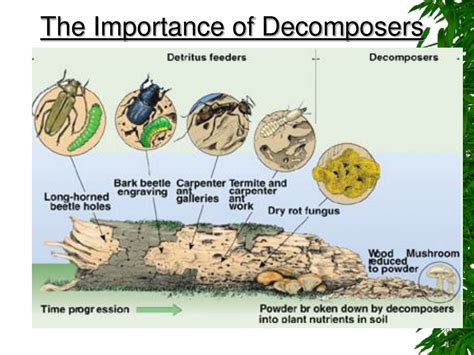
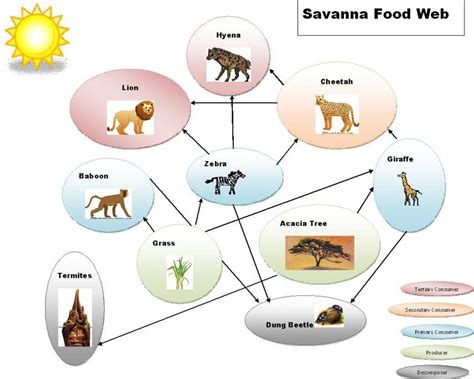
In the savanna ecosystem, decomposers can be broadly categorized into three groups: primary decomposers, secondary decomposers, and tertiary decomposers. Primary decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, are responsible for breaking down fresh organic matter, like dead plants and animals. Secondary decomposers, including insects and other invertebrates, feed on the partially decomposed organic matter, further breaking it down into simpler compounds. Tertiary decomposers, like earthworms and termites, play a crucial role in fragmenting and mixing decomposed organic matter into the soil, creating a nutrient-rich environment that supports plant growth.
Types of Savanna Decomposers
The diversity of decomposers in the savanna ecosystem is staggering, with countless species of bacteria, fungi, insects, and other organisms contributing to the decomposition process. Some of the most common types of savanna decomposers include: * Bacteria: These microscopic organisms are responsible for breaking down proteins, carbohydrates, and other complex organic molecules. * Fungi: Fungi, like mushrooms and molds, specialize in decomposing cellulose and lignin, the tough components of plant cell walls. * Insects: Insects, such as beetles and flies, feed on partially decomposed organic matter, further breaking it down into simpler compounds. * Earthworms: Earthworms play a crucial role in fragmenting and mixing decomposed organic matter into the soil, creating a nutrient-rich environment that supports plant growth.The Decomposition Process

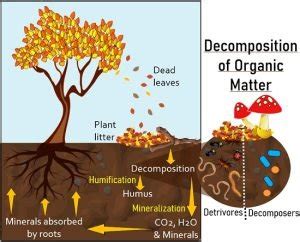
The decomposition process in the savanna ecosystem is a complex and highly regulated process, involving a multitude of organisms and chemical reactions. The process can be broadly divided into four stages: fragmentation, leaching, decomposition, and humification. Fragmentation occurs when larger organic matter, like dead plants and animals, is broken down into smaller pieces by insects and other organisms. Leaching involves the loss of soluble nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus, from the decomposing organic matter. Decomposition is the breakdown of complex organic molecules into simpler compounds, facilitated by bacteria, fungi, and other decomposers. Humification is the final stage, where the decomposed organic matter is transformed into a stable, nutrient-rich humus that supports plant growth.
Factors Influencing Decomposition
Several factors influence the decomposition process in the savanna ecosystem, including: * Temperature: Decomposition rates increase with temperature, as higher temperatures stimulate microbial activity. * Moisture: Adequate moisture is essential for decomposition, as it facilitates the growth and activity of decomposers. * Oxygen: Oxygen is necessary for decomposition, as it supports the growth and activity of aerobic decomposers. * Soil pH: Decomposition rates are optimal in slightly acidic to neutral soils, as extreme pH values can inhibit decomposer activity.Importance of Savanna Decomposers
The importance of savanna decomposers cannot be overstated, as they play a critical role in maintaining the health and fertility of the savanna ecosystem. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release nutrients back into the soil, supporting the growth of new plants and maintaining the diversity of wildlife that inhabits the savanna. Additionally, decomposers help to regulate the savanna's nutrient cycles, ensuring that essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are available to plants and other organisms.
Benefits of Decomposers
The benefits of decomposers in the savanna ecosystem are numerous, including: * Nutrient cycling: Decomposers release nutrients back into the soil, supporting plant growth and maintaining ecosystem fertility. * Soil structure: Decomposers help to maintain soil structure, creating a porous and well-draining environment that supports plant growth. * Biodiversity: Decomposers support biodiversity, as they provide a source of food and shelter for a wide range of organisms. * Ecosystem resilience: Decomposers help to maintain ecosystem resilience, as they facilitate the recovery of ecosystems from disturbances and stressors.Challenges Facing Savanna Decomposers
Despite their importance, savanna decomposers face numerous challenges, including climate change, habitat fragmentation, and human activities like agriculture and urbanization. Climate change, for example, can alter decomposition rates, as higher temperatures and changing precipitation patterns affect decomposer activity. Habitat fragmentation can reduce decomposer populations, as fragmented habitats can isolate decomposer populations and reduce their ability to disperse and colonize new areas.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are necessary to protect and preserve savanna decomposers, including: * Habitat preservation: Preserving and restoring savanna habitats can help to maintain decomposer populations and ecosystem function. * Sustainable land use: Promoting sustainable land use practices, like agroforestry and permaculture, can help to reduce the impact of human activities on decomposers and ecosystem function. * Climate change mitigation: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change can help to maintain decomposition rates and ecosystem function.Savanna Decomposers Image Gallery






In conclusion, savanna decomposers play a vital role in maintaining the health and fertility of the savanna ecosystem. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release nutrients back into the soil, supporting plant growth and maintaining ecosystem function. However, decomposers face numerous challenges, including climate change, habitat fragmentation, and human activities. Conservation efforts are necessary to protect and preserve savanna decomposers, including habitat preservation, sustainable land use, and climate change mitigation. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on the importance of savanna decomposers and the challenges they face. Let's work together to protect and preserve these microscopic heroes and the ecosystem they inhabit.
