Intro
Discover the role and responsibilities of the National Guard in the US military. Learn about its history, organization, and operations, as well as its domestic and overseas missions. Get the facts on this vital force, its difference from the Reserves, and the benefits of serving. Explore the five key things to know about the National Guard.
The National Guard is a unique and vital part of the United States' military forces, playing a critical role in both domestic and international missions. However, many people are unclear about the specifics of the National Guard, its responsibilities, and its differences from other military branches. In this article, we'll delve into the world of the National Guard, exploring five essential things to know about this esteemed organization.

What is the National Guard?
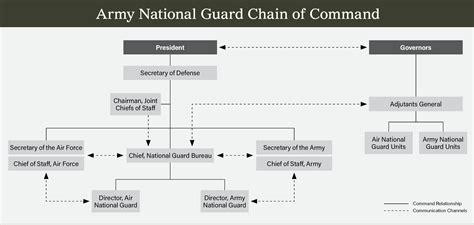
The National Guard is a reserve component of the United States Armed Forces, comprising citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to serve in a variety of capacities. The National Guard is unique in that it is a dual-status organization, meaning it can be activated by either the federal government or individual state governments. This dual role allows the National Guard to respond to both national and state-specific needs.
Origins and History
The National Guard has its roots in the colonial era, when each state maintained its own militia to defend against external threats. After the American Revolution, the Militia Act of 1792 formalized the role of state militias, which would eventually become the National Guard. Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, the National Guard played a significant role in various conflicts, including the Civil War, World War I, and World War II. In the post-9/11 era, the National Guard has been increasingly involved in homeland security and overseas deployments.

Roles and Responsibilities
The National Guard has a diverse range of responsibilities, including:
- Homeland Security: National Guard units can be called upon to respond to natural disasters, terrorist threats, and other domestic emergencies.
- Overseas Deployments: National Guard troops can be deployed to support military operations abroad, such as in Iraq, Afghanistan, and other countries.
- State Missions: National Guard units can be activated by state governors to respond to state-specific emergencies, such as riots, floods, and wildfires.
- Community Support: National Guard units often participate in community events, such as parades, ceremonies, and charity functions.
Organizational Structure
The National Guard is divided into two main components:
- Army National Guard: The Army National Guard is the largest component of the National Guard, with units in all 50 states, three territories, and the District of Columbia.
- Air National Guard: The Air National Guard is a separate component, with units in all 50 states and several territories.
Benefits and Requirements
Serving in the National Guard comes with a range of benefits, including:
- Education Benefits: National Guard members can receive tuition assistance, student loan repayment, and other education benefits.
- Career Opportunities: National Guard service can provide valuable work experience and career skills.
- Health Insurance: National Guard members are eligible for health insurance benefits.
- Retirement Benefits: National Guard members can earn retirement benefits after 20 years of service.
To join the National Guard, individuals must meet certain requirements, including:
- Age: 17-35 years old (with some exceptions)
- Citizenship: U.S. citizen or national
- Education: High school diploma or equivalent
- Physical Fitness: Meet physical fitness standards
- Background Check: Pass a background check

How to Join the National Guard
If you're interested in joining the National Guard, follow these steps:
- Meet the Requirements: Ensure you meet the eligibility requirements.
- Choose Your Role: Select a Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) that aligns with your skills and interests.
- Find a Recruiter: Locate a National Guard recruiter in your area.
- Take the ASVAB: Take the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test.
- Enlist: Enlist in the National Guard and begin your training.

Conclusion
The National Guard is a vital component of the United States' military forces, playing a critical role in both domestic and international missions. By understanding the National Guard's history, roles, and responsibilities, individuals can make informed decisions about joining this esteemed organization. If you're interested in serving your country and community, consider joining the National Guard today.
National Guard Image Gallery









Share your thoughts and experiences with the National Guard in the comments below. Have you or a loved one served in the National Guard? What do you think are the most important benefits and responsibilities of National Guard service?
