Intro
Discover cell organelles functions, including nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes, and learn about cellular respiration, protein synthesis, and membrane structure in eukaryotic cells.
The human body is composed of approximately 37.2 trillion cells, each of which is a complex and highly specialized unit. Within these cells, there exist various organelles that work together to maintain cellular homeostasis and perform specific functions necessary for the cell's survival. Understanding the functions of cell organelles is essential for grasping the intricacies of cellular biology and appreciating the remarkable complexity of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of cell organelles, exploring their diverse functions and the vital roles they play in maintaining the health and integrity of cells.
The study of cell organelles has become increasingly important in recent years, as researchers seek to understand the underlying mechanisms of cellular function and dysfunction. By examining the structure and function of cell organelles, scientists can gain valuable insights into the causes of various diseases and develop effective treatments. Furthermore, the study of cell organelles has significant implications for fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and agriculture, where understanding cellular function is crucial for advancing our knowledge and improving human health.
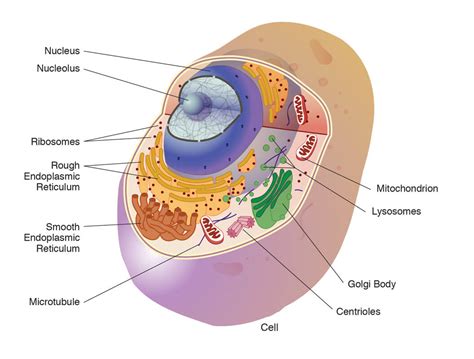
The cell is often referred to as the "building block of life," and its organelles are the functional units that enable it to perform a wide range of tasks. From the nucleus, which houses the cell's genetic material, to the mitochondria, which generate energy for the cell, each organelle plays a unique and essential role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. In the following sections, we will explore the functions of various cell organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes, among others.
Introduction to Cell Organelles
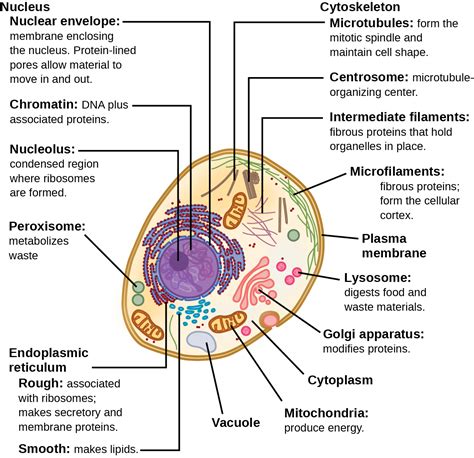
Types of Cell Organelles
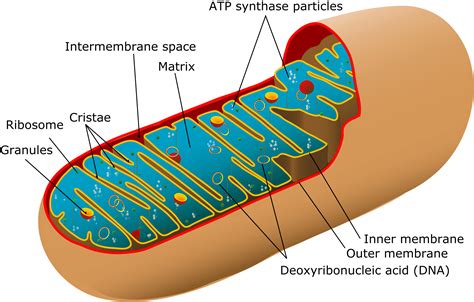
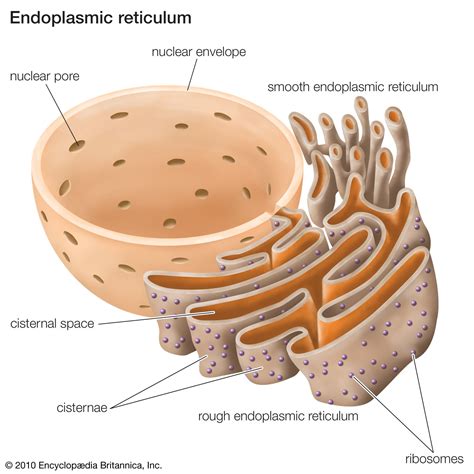
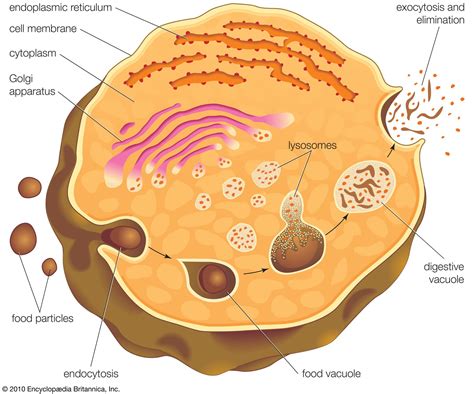
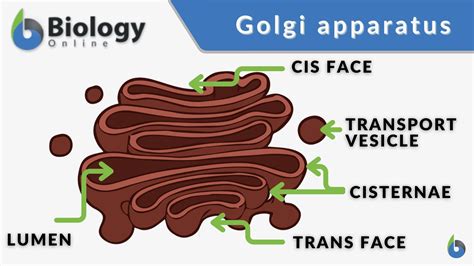
There are several types of cell organelles, each with distinct functions and characteristics. Some of the most well-known cell organelles include: * Nucleus: The nucleus is the control center of the cell, housing the genetic material and regulating cellular activities. * Mitochondria: Mitochondria are the energy-producing structures of the cell, generating ATP through cellular respiration. * Endoplasmic reticulum: The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that synthesizes proteins and lipids. * Lysosomes: Lysosomes are membrane-bound vesicles that contain digestive enzymes and are responsible for cellular digestion and recycling. * Golgi apparatus: The Golgi apparatus is a complex of flattened sacs and tubules that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or use within the cell.Functions of Cell Organelles
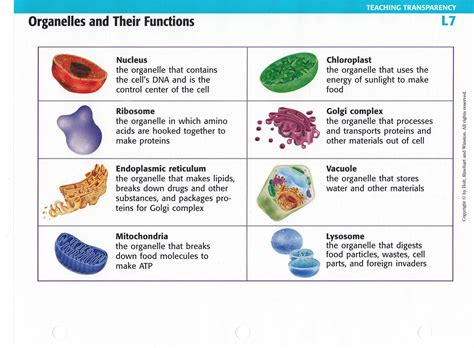
Importance of Cell Organelles
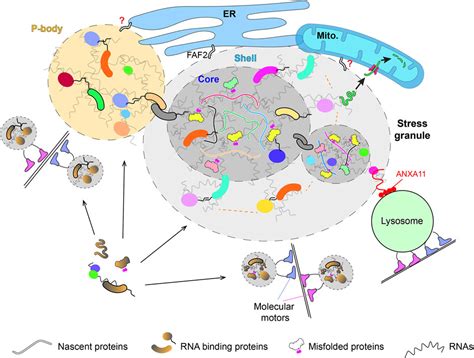
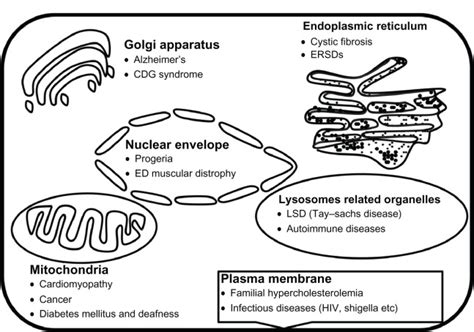
Cell organelles are essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and enabling the cell to perform its various activities. Without functioning cell organelles, the cell would be unable to produce energy, synthesize proteins, or manage waste, leading to cellular dysfunction and potentially death. The importance of cell organelles cannot be overstated, and understanding their functions is crucial for grasping the complexities of cellular biology.Cell Organelles and Disease
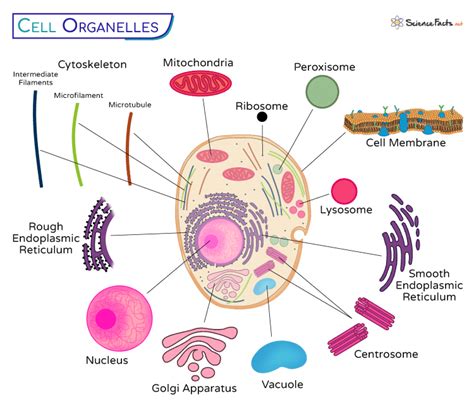
Current Research and Future Directions
Current research on cell organelles is focused on understanding the mechanisms of organelle function and dysfunction, as well as developing new treatments for diseases related to organelle dysfunction. Future directions for research include: * Developing new therapies for diseases related to organelle dysfunction, such as mitochondrial replacement therapy for mitochondrial disorders. * Investigating the role of cell organelles in cancer and developing new cancer therapies that target organelle function. * Understanding the mechanisms of organelle biogenesis and maintenance, and how these processes are regulated in different cell types.Gallery of Cell Organelles
Cell Organelles Image Gallery
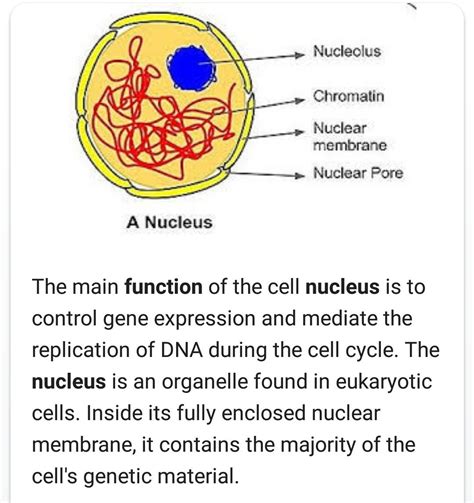
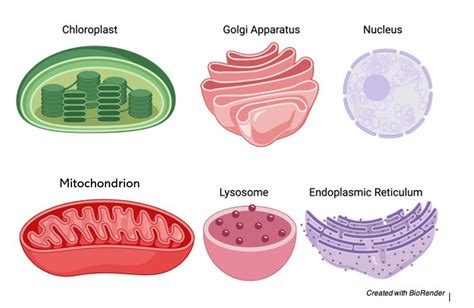
In conclusion, cell organelles play a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and enabling the cell to perform its various activities. Understanding the functions of cell organelles is essential for grasping the complexities of cellular biology and appreciating the remarkable diversity of life on Earth. We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of cell organelles and their functions, and has inspired you to learn more about the fascinating world of cellular biology. If you have any questions or comments, please don't hesitate to share them with us. We would love to hear from you and continue the conversation about the amazing world of cell organelles.
