Intro
Discover the crucial roles of geneticists in advancing healthcare and research. From diagnosis and treatment to genetic counseling and research, learn about the 5 key roles of geneticists, including genome analysis, gene therapy, and genetic engineering, and how theyre shaping the future of medicine and our understanding of human biology.
Genetics, the study of heredity and variation, has become a crucial aspect of modern biology and medicine. With the rapid advancement of genetic research and technology, the role of geneticists has become increasingly important in various fields. Geneticists play a vital part in understanding the complexities of genetics and its applications in healthcare, agriculture, and biotechnology. Here, we will explore the 5 key roles of geneticists and their significance in shaping the future of genetics.
1. Research and Development
Geneticists are at the forefront of genetic research, exploring the intricacies of genetic inheritance and the mechanisms of genetic variation. They design and conduct experiments to identify and analyze genetic factors contributing to diseases, traits, and characteristics. By understanding the genetic basis of complex diseases, geneticists can develop new diagnostic tools, treatments, and therapies. Their research also informs the development of genetic engineering technologies, enabling the creation of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for agricultural and pharmaceutical applications.
Key Responsibilities:
- Designing and conducting experiments to investigate genetic phenomena
- Analyzing and interpreting genetic data
- Developing and testing new genetic techniques and technologies
- Collaborating with other researchers to advance genetic knowledge
2. Clinical Genetics and Counseling
Geneticists working in clinical settings provide essential services to patients and families affected by genetic disorders. They interpret genetic test results, diagnose genetic conditions, and offer guidance on risk assessment, genetic counseling, and family planning. Clinical geneticists work closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans and provide ongoing support to patients and their families.

Key Responsibilities:
- Interpreting genetic test results and diagnosing genetic conditions
- Providing genetic counseling and risk assessment to patients and families
- Developing personalized treatment plans and collaborating with healthcare professionals
- Staying up-to-date with advances in genetic research and technology
3. Forensic Genetics
Forensic geneticists apply genetic principles to aid in the investigation and resolution of crimes. They analyze DNA evidence to identify suspects, solve crimes, and exonerate the innocent. Forensic geneticists work closely with law enforcement agencies, courts, and forensic laboratories to provide expert testimony and analysis.
Key Responsibilities:
- Analyzing DNA evidence to identify suspects and solve crimes
- Providing expert testimony in court
- Collaborating with law enforcement agencies and forensic laboratories
- Staying current with advances in forensic genetic technology and methodology

4. Agricultural Genetics
Agricultural geneticists work to improve crop yields, disease resistance, and nutritional content through genetic research and breeding. They develop new crop varieties using traditional breeding techniques and genetic engineering. By applying genetic principles, agricultural geneticists contribute to global food security and sustainable agriculture.
Key Responsibilities:
- Developing new crop varieties using traditional breeding and genetic engineering
- Improving crop yields, disease resistance, and nutritional content
- Collaborating with farmers, breeders, and other stakeholders to implement genetic solutions
- Staying current with advances in agricultural genetic research and technology
5. Biotechnology and Industry
Geneticists in biotechnology and industry apply genetic principles to develop innovative products and technologies. They work on the discovery and development of new drugs, vaccines, and diagnostics, as well as the creation of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for various applications. Biotechnology geneticists collaborate with industry partners to bring genetic discoveries to market.

Key Responsibilities:
- Developing new products and technologies using genetic principles
- Collaborating with industry partners to bring genetic discoveries to market
- Conducting research and development in biotechnology and genomics
- Staying current with advances in genetic research and technology
Geneticist Roles Image Gallery








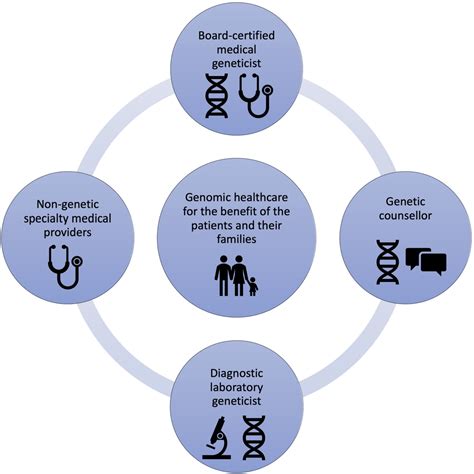
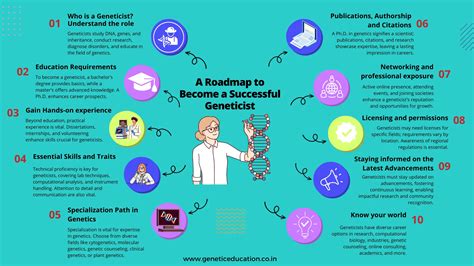
In conclusion, geneticists play a vital role in advancing our understanding of genetics and its applications in various fields. From research and development to clinical genetics and biotechnology, geneticists are working to improve human health, agriculture, and industry. As genetic research and technology continue to evolve, the role of geneticists will become increasingly important in shaping the future of genetics.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the role of geneticists in the comments section below. How do you think geneticists can contribute to solving some of the world's most pressing challenges?
