Master the high seas with confidence! Learn the 7 essential marine definitions you need to know, from Berth to Keelhaul. Understand key nautical terms, including Aft, Bow, and Starboard, and improve your sailing vocabulary. Get familiar with maritime language and navigate the world of boats and ships like a pro!
Marine life has always been a source of fascination for humans, with its intricate ecosystems and incredible diversity of species. From the majestic blue whale to the tiny plankton, marine organisms play a vital role in maintaining the health of our planet. However, understanding the complex world of marine biology requires a familiarity with specialized terms and definitions.
Whether you're a seasoned sailor, a marine biologist, or simply someone who loves the ocean, having a grasp of these key terms will enhance your appreciation and knowledge of the marine world. In this article, we will delve into seven essential marine definitions that will help you navigate the fascinating realm of oceanography.
1. Tides
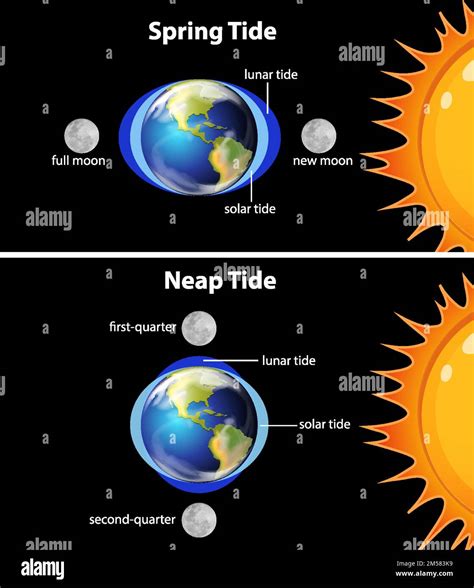
Tides are the periodic rising and falling of the sea level caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and, to a lesser extent, the Sun. This phenomenon results in the movement of water towards or away from the shore, creating high and low tides. Understanding tides is crucial for navigation, as they can significantly impact the depth of the water and the accessibility of certain areas.
Types of Tides
- Diurnal tides: One high tide and one low tide in a 24-hour period
- Semi-diurnal tides: Two high tides and two low tides in a 24-hour period
- Mixed tides: A combination of diurnal and semi-diurnal tides
2. Salinity

Salinity refers to the concentration of dissolved salts in seawater. It is measured in parts per thousand (ppt) or practical salinity units (psu). Salinity plays a critical role in determining the density of seawater, which affects ocean currents and the distribution of marine life.
Factors Affecting Salinity
- Evaporation and precipitation
- Freshwater input from rivers and melting ice
- Geological processes, such as the formation of oceanic crust
3. Marine Debris

Marine debris refers to human-made objects that have been discarded or abandoned in the ocean. This includes plastic bags, bottles, fishing nets, and other waste that can harm marine life and ecosystems. The impact of marine debris is a growing concern, with millions of tons of waste entering the ocean every year.
Types of Marine Debris
- Plastic debris
- Fishing gear and other equipment
- Household waste and litter
4. Phytoplankton
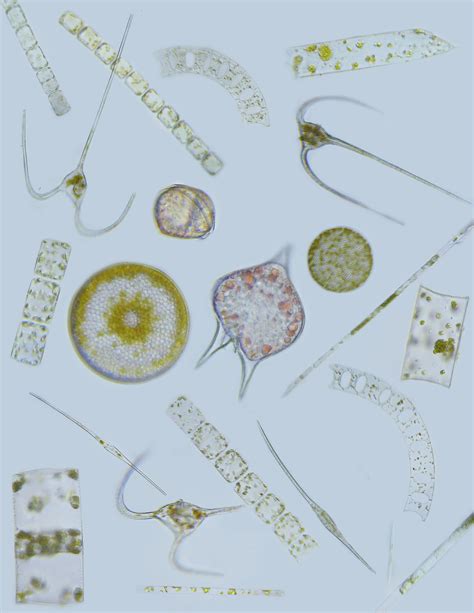
Phytoplankton are microscopic plant-like organisms that drift in the ocean. They are the primary producers of the marine food web, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. Phytoplankton play a vital role in supporting the marine ecosystem and regulating the Earth's climate.
Types of Phytoplankton
- Cyanobacteria
- Diatoms
- Green algae
5. Ocean Acidification

Ocean acidification refers to the decrease in the pH level of the ocean over time, caused by the absorption of excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This increase in acidity can have devastating effects on marine life, particularly organisms with calcium carbonate shells, such as corals and shellfish.
Causes of Ocean Acidification
- Increase in atmospheric CO2 levels
- Release of fossil fuels and other pollutants
- Land use changes and deforestation
6. Eutrophication
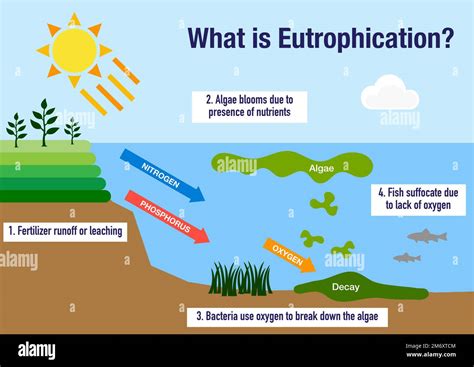
Eutrophication is the process by which excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, enter the ocean, leading to an overgrowth of phytoplankton. This can result in the depletion of oxygen in the water, harming marine life and ecosystems.
Causes of Eutrophication
- Agricultural runoff and fertilizers
- Sewage and wastewater
- Industrial processes and pollution
7. Marine Protected Areas

Marine protected areas (MPAs) are designated regions of the ocean that are protected from human activities that can harm the environment. MPAs can help conserve marine biodiversity, promote sustainable fishing practices, and support ecosystem services.
Types of MPAs
- National parks and wildlife refuges
- Marine sanctuaries and reserves
- Fisheries management areas
Marine Life Image Gallery










In conclusion, understanding these seven marine definitions is essential for anyone interested in the ocean and its inhabitants. By grasping these concepts, you can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of the marine world. Share your thoughts on the importance of marine conservation and education in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with fellow ocean enthusiasts!
