Intro
Discover the reality of nuclear engineering careers. Learn the 7 things nuclear engineers actually do, from designing reactors to ensuring safety protocols, and exploring applications in medicine, energy, and space. Get a behind-the-scenes look at this fascinating field, including nuclear power, radiation protection, and nuclear safety regulations.
Nuclear engineers play a vital role in the development and maintenance of nuclear power plants, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of these complex facilities. Their work has a significant impact on the environment, energy production, and public health. Despite their importance, many people are unaware of the various responsibilities and tasks that nuclear engineers perform on a daily basis.
The field of nuclear engineering is often shrouded in mystery, with many people assuming that nuclear engineers only work on designing and building nuclear reactors. However, the reality is that nuclear engineers are involved in a wide range of activities that go beyond reactor design and construction. In this article, we will explore seven things that nuclear engineers actually do, shedding light on the diverse and complex nature of their work.
1. Designing and Developing Nuclear Reactors and Systems
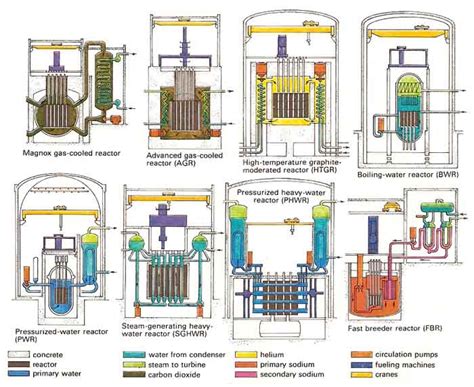
Nuclear engineers are responsible for designing and developing nuclear reactors and systems, including the reactor core, fuel, and cooling systems. They use computer simulations and modeling to optimize reactor performance, safety, and efficiency. This involves collaborating with other engineers and experts to ensure that the design meets regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Types of Reactors Designed by Nuclear Engineers
- Pressurized Water Reactors (PWRs)
- Boiling Water Reactors (BWRs)
- Gas-cooled Reactors
- Liquid Metal Fast Breeder Reactors (LMFBRs)
2. Conducting Safety and Risk Assessments
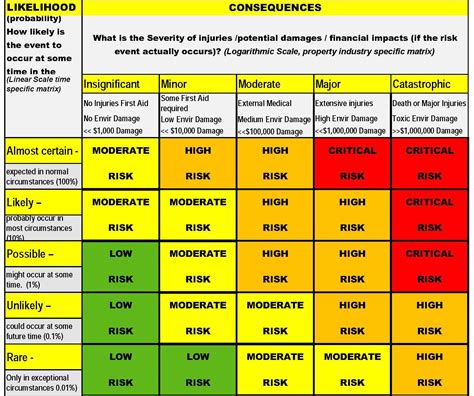
Nuclear engineers conduct safety and risk assessments to identify potential hazards and mitigate risks associated with nuclear power plant operation. This involves analyzing data, modeling scenarios, and conducting experiments to evaluate the likelihood and consequences of accidents or incidents.
Methods Used by Nuclear Engineers for Safety and Risk Assessments
- Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA)
- Deterministic Risk Assessment
- Fault Tree Analysis
- Event Tree Analysis
3. Developing and Implementing Nuclear Waste Management Strategies
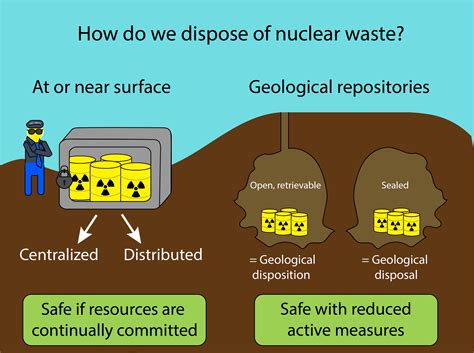
Nuclear engineers develop and implement strategies for managing nuclear waste, including storage, disposal, and remediation. This involves designing and operating facilities for nuclear waste management, as well as developing policies and procedures for waste handling and transportation.
Types of Nuclear Waste Managed by Nuclear Engineers
- Low-Level Waste (LLW)
- Intermediate-Level Waste (ILW)
- High-Level Waste (HLW)
- Transuranic Waste (TRU)
4. Collaborating with Regulators and Industry Partners

Nuclear engineers work closely with regulators, industry partners, and other stakeholders to ensure compliance with regulations and industry standards. This involves participating in regulatory meetings, collaborating on research projects, and sharing best practices.
Regulatory Agencies that Nuclear Engineers Collaborate With
- Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
- World Association of Nuclear Operators (WANO)
5. Conducting Research and Development

Nuclear engineers conduct research and development to improve nuclear power plant design, operation, and safety. This involves investigating new technologies, materials, and methods, as well as publishing research papers and presenting findings at conferences.
Areas of Research Focus for Nuclear Engineers
- Advanced Reactor Designs
- Nuclear Fuel Cycles
- Radiation Detection and Measurement
- Nuclear Security and Non-Proliferation
6. Providing Training and Education
Nuclear engineers provide training and education to colleagues, students, and the public on nuclear power plant operation, safety, and technology. This involves developing and teaching courses, workshops, and seminars, as well as creating educational materials and resources.
Types of Training Provided by Nuclear Engineers
- Operator Training
- Maintenance Training
- Safety Training
- Public Outreach and Education
7. Participating in Emergency Preparedness and Response

Nuclear engineers participate in emergency preparedness and response activities, including developing emergency plans, conducting drills and exercises, and responding to incidents and accidents.
Types of Emergencies that Nuclear Engineers Respond To
- Nuclear Accidents
- Natural Disasters
- Cybersecurity Incidents
- Radiological Incidents
Nuclear Engineering Image Gallery










We hope that this article has provided you with a better understanding of the diverse and complex work that nuclear engineers do. From designing and developing nuclear reactors to conducting research and development, nuclear engineers play a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of nuclear power plants.
