Intro
Discover the meaning of hijack and its usage in various contexts. Learn how this term originated and evolved, from its roots in aviation to its modern applications in technology, politics, and social media. Understand the different types of hijacking, including website hijacking, email hijacking, and more, and find out how to protect yourself from these malicious activities.
In today's digital age, cybersecurity threats are on the rise, and understanding the terminology used to describe them is crucial. One term that's often thrown around is "hijack." But what does hijack mean, exactly? In this article, we'll delve into the definition and usage of the term "hijack," as well as its implications in the context of cybersecurity.
What is Hijacking?
Hijacking, in general, refers to the act of taking control of something, usually without permission or authority. In the context of cybersecurity, hijacking occurs when an unauthorized entity gains control over a computer system, network, or application, often for malicious purposes.
Types of Hijacking
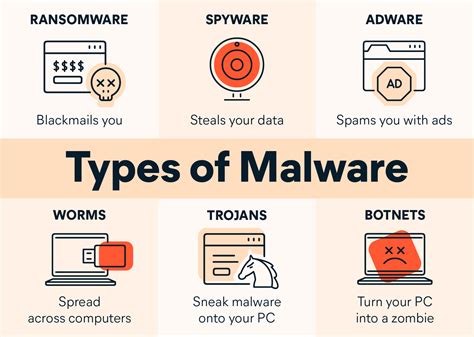
There are several types of hijacking, including:
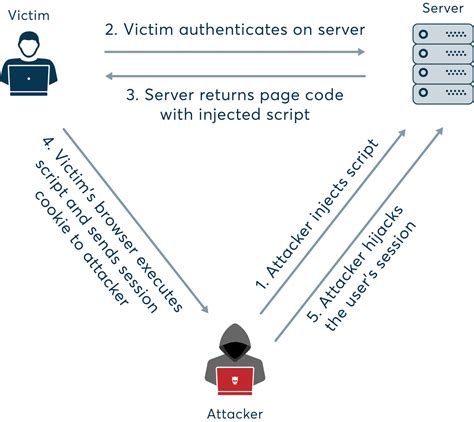
- Session Hijacking: This type of hijacking involves intercepting and taking control of a user's session, allowing the attacker to access sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial data.
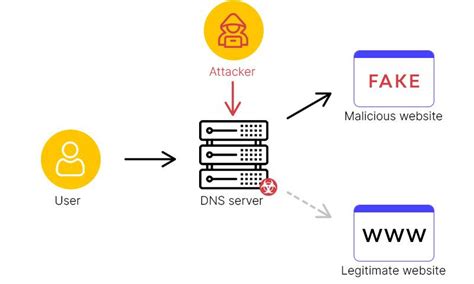
- DNS Hijacking: This type of hijacking involves intercepting and altering DNS (Domain Name System) requests, allowing the attacker to redirect users to fake or malicious websites.
- Email Hijacking: This type of hijacking involves intercepting and taking control of an email account, allowing the attacker to send spam or phishing emails to the victim's contacts.
- Browser Hijacking: This type of hijacking involves taking control of a user's browser, often through malware or viruses, allowing the attacker to redirect the user to malicious websites or display unwanted ads.
How Does Hijacking Happen?
Hijacking can occur through various means, including:
- Phishing: Attackers may use phishing emails or messages to trick victims into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials.
- Malware: Attackers may use malware or viruses to gain control over a system or application.
- Weak Passwords: Attackers may use weak passwords or password cracking tools to gain access to a system or application.
- Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Attackers may exploit unpatched vulnerabilities in software or systems to gain control.

Consequences of Hijacking
The consequences of hijacking can be severe, including:
- Financial Loss: Hijacking can result in financial loss, either through stolen sensitive information or unauthorized transactions.
- Reputation Damage: Hijacking can damage a company's reputation, leading to a loss of customer trust and loyalty.
- Data Breach: Hijacking can result in a data breach, exposing sensitive information to unauthorized parties.
Prevention and Mitigation**
To prevent and mitigate hijacking, individuals and organizations can take several steps, including:
- Using Strong Passwords: Using strong, unique passwords and enabling two-factor authentication can help prevent hijacking.
- Keeping Software Up-to-Date: Keeping software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches can help prevent hijacking.
- Using Anti-Virus Software: Using anti-virus software and regularly scanning for malware can help prevent hijacking.
- Being Cautious with Emails: Being cautious with emails and avoiding suspicious links or attachments can help prevent hijacking.

Gallery of Hijacking Examples
Hijacking Image Gallery






Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is hijacking? A: Hijacking is the act of taking control of something, usually without permission or authority.
Q: What are the types of hijacking? A: There are several types of hijacking, including session hijacking, DNS hijacking, email hijacking, and browser hijacking.
Q: How does hijacking happen? A: Hijacking can occur through various means, including phishing, malware, weak passwords, and unpatched vulnerabilities.
Q: What are the consequences of hijacking? A: The consequences of hijacking can be severe, including financial loss, reputation damage, and data breach.
Q: How can I prevent and mitigate hijacking? A: To prevent and mitigate hijacking, individuals and organizations can take several steps, including using strong passwords, keeping software up-to-date, using anti-virus software, and being cautious with emails.
Final Thoughts
Hijacking is a serious cybersecurity threat that can have severe consequences. By understanding the definition and usage of the term "hijack," individuals and organizations can take steps to prevent and mitigate hijacking. Remember to use strong passwords, keep software up-to-date, and be cautious with emails to stay safe online.
