Intro
Discover the critical role of EOD military personnel in Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD). Learn about the dangers of unexploded bombs, IEDs, and other explosive threats, and how EOD technicians neutralize these hazards using specialized training, equipment, and tactics to keep people safe and prevent catastrophic consequences.
The military has many specialized branches and units, each with its own unique role and responsibilities. One of the most critical and high-risk jobs in the military is Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD). EOD technicians are trained to detect, disarm, and dispose of explosive devices, making them some of the bravest and most skilled individuals in the military.
What is Explosive Ordnance Disposal?
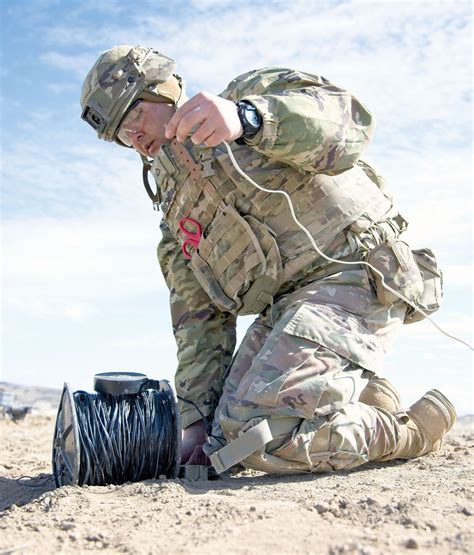

EOD is a specialized field within the military that deals with the detection, identification, and neutralization of explosive threats. EOD technicians are trained to handle a wide range of explosive devices, from hand grenades and landmines to improvised explosive devices (IEDs) and nuclear warheads. Their primary goal is to render these devices safe, preventing harm to people and property.
EOD History and Evolution
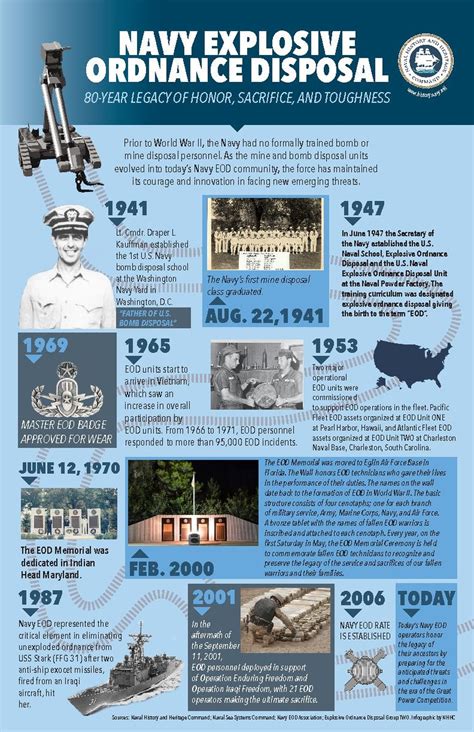
The history of EOD dates back to World War I, when military forces first encountered explosive devices on the battlefield. Initially, EOD was a relatively simple process, with soldiers using basic tools and techniques to disarm and dispose of explosives. However, as the types and complexities of explosive devices increased, so did the need for specialized training and equipment.
During World War II, the military established formal EOD programs, and technicians began to receive specialized training in the detection and disposal of explosive devices. The development of new technologies, such as robotics and x-ray imaging, has continued to improve EOD capabilities, allowing technicians to safely and effectively neutralize a wide range of explosive threats.
EOD Training and Certification

Becoming an EOD technician requires extensive training and certification. EOD technicians must complete a rigorous training program, which includes both classroom instruction and hands-on training. The training program covers topics such as explosive theory, ordnance recognition, and disposal techniques.
EOD technicians must also pass a certification exam, which tests their knowledge and skills in areas such as:
- Explosive device recognition and identification
- Disposal techniques and procedures
- Safety protocols and emergency procedures
- Communication and teamwork
Certified EOD technicians are then assigned to EOD units, where they work under the guidance of experienced technicians to gain hands-on experience and continue their training.
EOD Equipment and Tools
EOD technicians use a range of specialized equipment and tools to detect, disarm, and dispose of explosive devices. Some of the most common EOD tools include:
- Explosive ordnance disposal suits: These suits are designed to protect technicians from explosive blasts and shrapnel.
- Bomb suits: These suits are designed to provide additional protection for technicians working with high-risk devices.
- X-ray imaging equipment: This equipment allows technicians to safely examine explosive devices and determine their composition and configuration.
- Robotics: EOD robots are designed to remotely examine and disable explosive devices, reducing the risk of injury to technicians.
- Disposal equipment: EOD technicians use a range of disposal equipment, including incinerators and fragmentation devices, to safely dispose of explosive devices.
EOD Operations and Procedures

EOD operations involve a range of procedures, from initial response to final disposal. Some of the key EOD procedures include:
- Initial response: EOD technicians respond to explosive device sightings, assessing the situation and determining the best course of action.
- Explosive device recognition: Technicians identify the type and configuration of the explosive device, using visual examination and x-ray imaging equipment.
- Disposal planning: Technicians develop a disposal plan, taking into account the type and risk of the device, as well as environmental and safety factors.
- Disposal execution: Technicians execute the disposal plan, using specialized equipment and techniques to safely neutralize the device.
- Post-disposal procedures: Technicians conduct a thorough examination of the device and surrounding area to ensure that all explosive material has been safely removed.
EOD Safety Protocols and Emergency Procedures
EOD technicians follow strict safety protocols and emergency procedures to minimize the risk of injury or death. Some of the key EOD safety protocols include:
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Technicians wear specialized PPE, including suits, gloves, and masks, to protect themselves from explosive blasts and shrapnel.
- Safe distance protocols: Technicians maintain a safe distance from explosive devices, using robotics and other equipment to minimize their exposure.
- Emergency procedures: Technicians are trained in emergency procedures, including evacuation and first aid, in case of an accident or injury.
EOD Career Paths and Opportunities

A career in EOD can be challenging and rewarding, with opportunities for advancement and specialization. Some of the most common EOD career paths include:
- EOD technician: EOD technicians work in a range of settings, from military bases to civilian law enforcement agencies.
- EOD instructor: Experienced EOD technicians can become instructors, teaching new recruits the skills and procedures they need to succeed.
- EOD supervisor: EOD supervisors oversee EOD operations, coordinating responses and ensuring that safety protocols are followed.
- EOD specialist: EOD specialists work in specialized areas, such as explosive device analysis or robotics development.
EOD Challenges and Future Directions
EOD is a constantly evolving field, with new challenges and technologies emerging all the time. Some of the most significant EOD challenges include:
- Improvised explosive devices (IEDs): IEDs are increasingly sophisticated, requiring EOD technicians to stay up-to-date with the latest threats and countermeasures.
- Nuclear and radiological threats: EOD technicians must be prepared to respond to nuclear and radiological threats, which require specialized training and equipment.
- Cyber threats: EOD technicians must be aware of cyber threats, including hacking and malware, which can compromise explosive devices and EOD operations.
Despite these challenges, EOD remains a vital and rewarding field, with opportunities for career advancement and specialization. As the military and civilian agencies continue to evolve and adapt to new threats, the role of EOD technicians will remain critical to ensuring public safety and security.
EOD Image Gallery









We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Explosive Ordnance Disposal (EOD) and the critical role that EOD technicians play in ensuring public safety and security. Whether you're a military professional or simply interested in learning more about this fascinating field, we encourage you to share your thoughts and comments below.
