Intro
Discover the science behind gasoline boiling point, including vapor pressure, flash point, and distillation, to understand fuel properties and behavior.
The boiling point of gasoline is a critical factor in determining its quality and performance. Gasoline, a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, is a volatile liquid that evaporates easily, making its boiling point an essential characteristic. In this article, we will delve into the world of gasoline boiling points, exploring their significance, measurement methods, and the factors that influence them. Whether you are a car enthusiast, a chemistry student, or simply someone interested in learning more about the fuel that powers our vehicles, this article is for you.
The boiling point of gasoline is not just a theoretical concept; it has practical implications for the way we use and handle this fuel. For instance, gasoline with a lower boiling point can evaporate more quickly, potentially leading to vapor lock issues in vehicles. On the other hand, gasoline with a higher boiling point may be less susceptible to evaporation, but it can also be more difficult to ignite, affecting engine performance. Understanding the boiling point of gasoline is crucial for optimizing engine efficiency, ensuring safety, and reducing environmental impact.
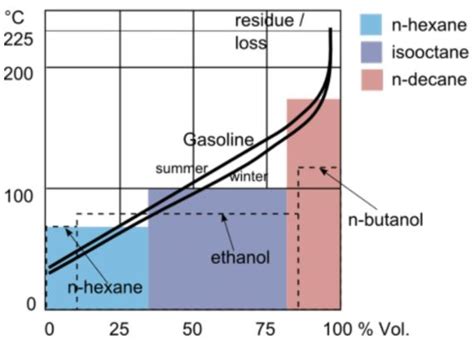
As we explore the concept of gasoline boiling points, it's essential to recognize the complexity of this subject. Gasoline is not a single compound but a mixture of various hydrocarbons, each with its own boiling point. The boiling point of gasoline can vary depending on the specific blend of hydrocarbons, the presence of additives, and even the temperature and pressure conditions under which it is stored and used. This complexity makes the study of gasoline boiling points both fascinating and challenging, as it requires a deep understanding of chemistry, physics, and engineering principles.
Introduction to Gasoline Boiling Point
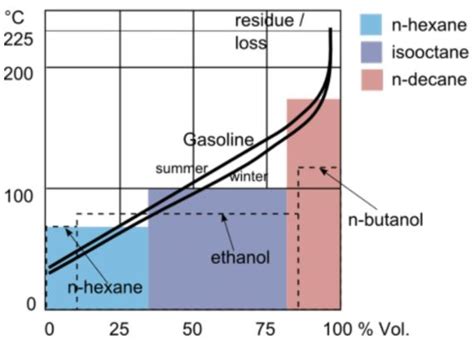
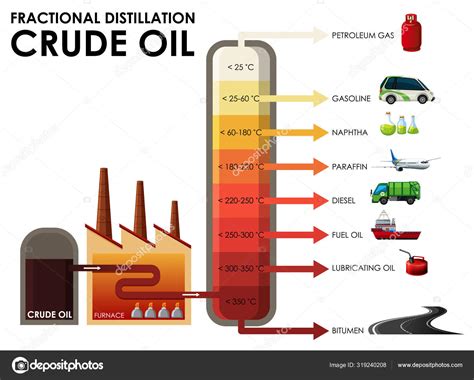
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from a liquid to a gas. For gasoline, this temperature range is typically between 100°F and 400°F (38°C to 204°C), depending on the specific composition of the fuel. The boiling point of gasoline is usually measured using a technique called distillation, where the fuel is heated, and the temperatures at which different fractions of the fuel evaporate are recorded. This process provides a detailed profile of the fuel's volatility, which is critical for determining its suitability for various applications.
Factors Influencing Gasoline Boiling Point
Several factors can influence the boiling point of gasoline, including the type of crude oil from which it is derived, the refining process, and the presence of additives. The boiling point can also be affected by environmental conditions such as temperature, pressure, and humidity. Understanding these factors is essential for the production and use of gasoline, as they can impact the fuel's performance, safety, and environmental impact.Measurement of Gasoline Boiling Point
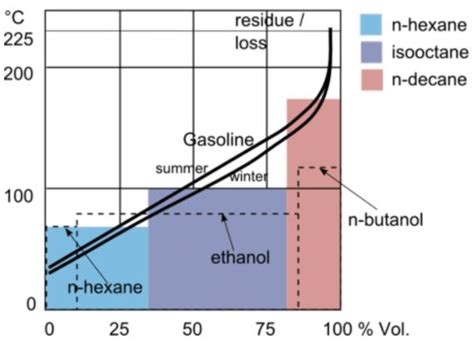
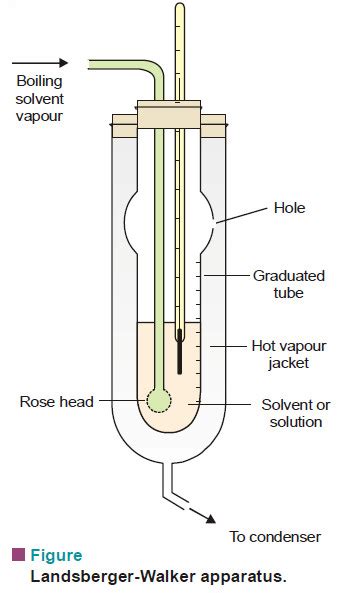
The measurement of gasoline boiling point is a precise process that involves heating a sample of the fuel in a controlled environment and observing the temperatures at which it evaporates. This can be done using various techniques, including distillation, gas chromatography, and thermogravimetry. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of technique depends on the specific requirements of the analysis and the resources available.
Importance of Accurate Measurement
Accurate measurement of the boiling point of gasoline is crucial for ensuring the quality and safety of the fuel. A fuel with an incorrectly measured boiling point can lead to poor engine performance, increased emissions, and even safety hazards. Furthermore, accurate measurement is essential for regulatory compliance, as many countries have strict standards for the boiling point of gasoline to ensure environmental protection and public safety.Applications of Gasoline Boiling Point
The boiling point of gasoline has numerous applications in the petroleum industry, automotive sector, and environmental science. It is used to optimize engine design, improve fuel efficiency, and reduce emissions. The boiling point is also a critical factor in the development of alternative fuels and in the assessment of fuel quality and safety.
Optimizing Engine Performance
Understanding the boiling point of gasoline is essential for optimizing engine performance. Engines are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges, and the boiling point of the fuel can significantly impact engine efficiency and power output. By matching the boiling point of the fuel to the engine's design specifications, manufacturers can improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance overall vehicle performance.Environmental Impact of Gasoline Boiling Point
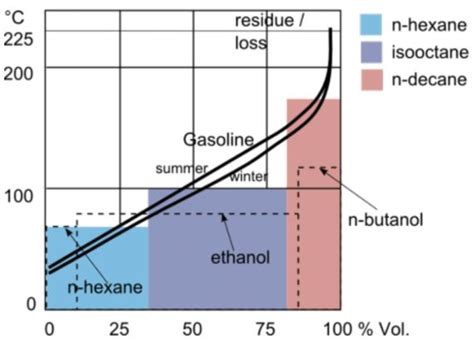
The boiling point of gasoline can have a significant environmental impact, particularly in terms of air quality and climate change. Gasoline with a higher boiling point can lead to increased emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and negative health effects. On the other hand, optimizing the boiling point of gasoline can help reduce emissions, improve air quality, and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Sustainability and Future Directions
As the world moves towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solutions, the study of gasoline boiling points remains relevant. Researchers are exploring alternative fuels with improved boiling point characteristics, such as biofuels and hydrogen fuel cells. Understanding the boiling point of these alternative fuels is crucial for their development and integration into existing energy infrastructure.Gallery of Gasoline Boiling Point Images
Gasoline Boiling Point Image Gallery








Final Thoughts on Gasoline Boiling Point
In conclusion, the boiling point of gasoline is a complex and multifaceted topic that plays a critical role in the production, use, and environmental impact of this fuel. By understanding the factors that influence the boiling point of gasoline, measuring it accurately, and optimizing its applications, we can improve engine performance, reduce emissions, and contribute to a more sustainable energy future. We invite readers to share their thoughts, ask questions, and explore further the fascinating world of gasoline boiling points. Whether through comments, social media, or further research, we hope this article has inspired a deeper appreciation for the science and technology behind the fuel that powers our daily lives.
