Intro
Unlock the secrets of speed with our simplified explanation of Mach speed. Learn how this fundamental concept in physics measures the velocity of objects in relation to the speed of sound, and discover its significance in aviation, aerospace, and everyday life. Explore the world of supersonic flight and beyond.
The concept of speed has always fascinated humans, from the fastest land animal to the speed of light. One term that is often thrown around in discussions about speed is "Mach speed." But what exactly is Mach speed, and how does it relate to the speed of objects?
Mach speed is a unit of measurement that represents the speed of an object relative to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium, such as air or water. The term "Mach" is named after Austrian physicist Ernst Mach, who first proposed the concept in the late 19th century. In simple terms, Mach speed is a way to express how fast an object is moving compared to the speed of sound.
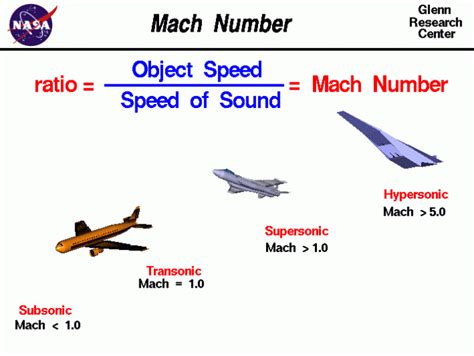
To understand Mach speed, let's consider the speed of sound. The speed of sound is approximately 768 miles per hour (mph) or 1,236 kilometers per hour (km/h) in dry air at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This means that if an object is moving at Mach 1, it is traveling at the same speed as the sound waves around it. If an object is moving at Mach 2, it is traveling twice as fast as the speed of sound.
How is Mach Speed Calculated?
Calculating Mach speed is relatively straightforward. The formula for Mach speed is:
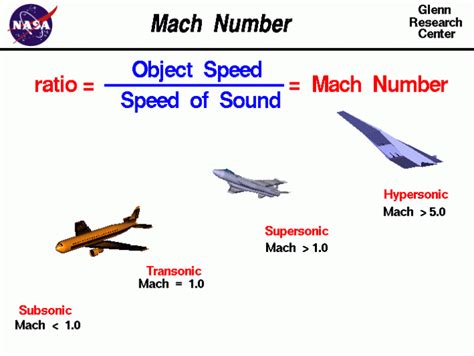
Mach number = (Object speed) / (Speed of sound)
For example, if an object is moving at 1,000 mph and the speed of sound is 768 mph, the Mach number would be:
Mach number = 1,000 mph / 768 mph ≈ 1.3
This means that the object is traveling at approximately Mach 1.3, or 1.3 times the speed of sound.
Subsonic, Supersonic, and Hypersonic Speeds
Mach speed is often used to classify the speed of objects into different categories:
- Subsonic: Objects traveling at speeds below Mach 1, or slower than the speed of sound.
- Supersonic: Objects traveling at speeds between Mach 1 and Mach 5, or faster than the speed of sound but slower than five times the speed of sound.
- Hypersonic: Objects traveling at speeds above Mach 5, or faster than five times the speed of sound.
These categories are important in understanding the behavior of objects at different speeds, particularly in aerospace engineering and military applications.
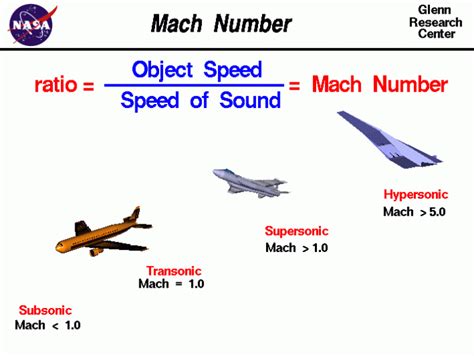
Real-World Applications of Mach Speed
Mach speed has numerous real-world applications in fields such as:
- Aerospace engineering: Understanding Mach speed is crucial in designing aircraft and spacecraft that can withstand the stresses of supersonic and hypersonic flight.
- Military: Mach speed is used to classify the speed of military aircraft and missiles, which is essential for tactical and strategic planning.
- Automotive: Car manufacturers use Mach speed to test the aerodynamics of vehicles and improve their performance.
Mach Speed in Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace engineers use Mach speed to design aircraft and spacecraft that can operate efficiently at different altitudes and speeds. For example, when designing a supersonic aircraft, engineers must consider the effects of air resistance and shock waves on the aircraft's structure and performance.
Mach speed is also used to calculate the sonic boom, which is the shockwave produced when an object breaks the sound barrier. The sonic boom is a critical factor in designing supersonic aircraft, as it can cause damage to structures and disrupt communication systems.

Challenges and Limitations of Mach Speed
While Mach speed is a useful concept, there are several challenges and limitations to consider:
- Air resistance: As objects approach the speed of sound, air resistance increases significantly, making it difficult to achieve supersonic speeds.
- Heat generation: Friction generates heat, which can cause damage to structures and pose a significant challenge in designing hypersonic vehicles.
- Materials science: Developing materials that can withstand the stresses of supersonic and hypersonic flight is a significant challenge.
Future Developments in Mach Speed
Research and development in Mach speed continue to advance, with several promising areas of study:
- Hypersonic flight: Scientists are working on developing vehicles that can achieve hypersonic speeds, which could revolutionize transportation and space exploration.
- Advanced materials: Researchers are developing new materials that can withstand the stresses of supersonic and hypersonic flight.
- Computational modeling: Advances in computational modeling are enabling scientists to simulate and predict the behavior of objects at different Mach speeds.

Conclusion
Mach speed is a fundamental concept in understanding the behavior of objects at different speeds. From subsonic to hypersonic speeds, Mach speed has numerous real-world applications in fields such as aerospace engineering, military, and automotive. While there are challenges and limitations to consider, ongoing research and development are advancing our understanding of Mach speed and pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
Mach Speed Image Gallery

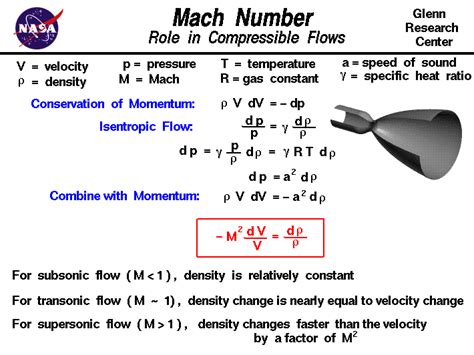
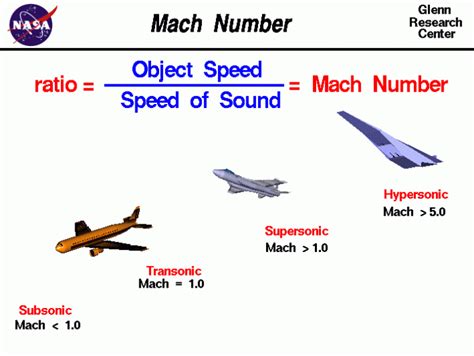





We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of Mach speed and its significance in various fields. Share your thoughts and comments below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues!
