Intro
Discover the role of a Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) in the US Army. Learn about the responsibilities, ranks, and requirements of NCOs, including their leadership roles, technical expertise, and career advancement opportunities. Understand the importance of NCOs in the Armys structure and their impact on troop morale and mission success.
The United States Army is one of the most respected and formidable military forces in the world, with a long history of protecting the country and its interests. Within the Army, there are various ranks and positions that play crucial roles in its operations. One of the most critical and respected ranks is the Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO).
The NCO is the backbone of the US Army, providing leadership, guidance, and expertise to junior soldiers. They are responsible for leading by example, mentoring, and training their fellow soldiers to ensure they are equipped to perform their duties effectively. NCOs are the link between the enlisted soldiers and the officers, and their role is essential to the success of the Army.

History of NCOs in the US Army
The NCO rank has a long history in the US Army, dating back to the American Revolution. During this time, NCOs were responsible for leading small units of soldiers and providing tactical guidance. Over the years, the role of the NCO has evolved, but their importance has remained constant.
In the late 19th century, the Army formalized the NCO rank, establishing clear guidelines and responsibilities for NCOs. The creation of the Non-Commissioned Officer Corps in 1972 further solidified the importance of NCOs in the Army.
Roles and Responsibilities of NCOs
NCOs play a variety of roles within the Army, including:
- Leading and mentoring junior soldiers
- Providing tactical guidance and expertise
- Training and developing junior soldiers
- Maintaining discipline and enforcing standards
- Providing administrative support
- Advising officers on enlisted matters
NCOs are responsible for ensuring that their soldiers are trained and equipped to perform their duties effectively. They are also responsible for maintaining the morale and welfare of their soldiers.

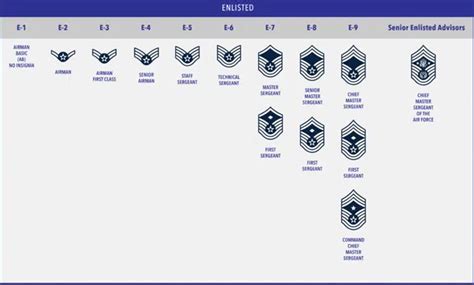
Types of NCOs
There are several types of NCOs in the US Army, each with its own unique responsibilities and requirements. Some of the most common types of NCOs include:
- Corporal (CPL): The lowest NCO rank, responsible for leading small teams of soldiers.
- Sergeant (SGT): A junior NCO rank, responsible for leading squads and providing tactical guidance.
- Staff Sergeant (SSG): A senior NCO rank, responsible for leading platoons and providing administrative support.
- Sergeant First Class (SFC): A senior NCO rank, responsible for leading companies and providing tactical guidance.
- Master Sergeant (MSG): A senior NCO rank, responsible for leading battalions and providing administrative support.
- Sergeant Major (SGM): The highest NCO rank, responsible for leading regiments and providing strategic guidance.
Requirements for Becoming an NCO
To become an NCO, soldiers must meet certain requirements, including:
- Completing Advanced Individual Training (AIT)
- Serving for a minimum of 2-3 years
- Meeting specific performance and promotion requirements
- Completing NCO Professional Development Courses
- Demonstrating leadership and mentorship skills
Benefits of Being an NCO
Being an NCO offers numerous benefits, including:
- Increased pay and allowances
- Greater responsibility and leadership opportunities
- Increased job satisfaction and morale
- Opportunities for advanced education and training
- Respect and recognition from peers and superiors
Challenges Facing NCOs
NCOs face numerous challenges, including:
- Leading and mentoring junior soldiers
- Maintaining discipline and enforcing standards
- Providing tactical guidance and expertise
- Managing administrative tasks and responsibilities
- Adapting to changing situations and environments

Conclusion
In conclusion, the NCO is a critical rank within the US Army, providing leadership, guidance, and expertise to junior soldiers. NCOs play a variety of roles, including leading and mentoring, providing tactical guidance, and maintaining discipline and enforcing standards. To become an NCO, soldiers must meet specific requirements, including completing AIT, serving for a minimum of 2-3 years, and demonstrating leadership and mentorship skills. Being an NCO offers numerous benefits, including increased pay and allowances, greater responsibility and leadership opportunities, and respect and recognition from peers and superiors.
NCO Image Gallery






We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences about NCOs in the US Army. Have you served as an NCO or worked with one? What challenges and benefits did you encounter? Share your story in the comments below.
