Intro
Discover the concept of the Reserve Army, a fundamental aspect of Marxist economic theory. Learn about its definition, purpose, and economic impact on labor markets, unemployment rates, and wage dynamics. Understand how this phenomenon affects workers, capitalists, and the overall economy, and explore its relevance in modern times.
The concept of a reserve army has been a crucial aspect of economic theory, particularly in the context of capitalism. The idea of a reserve army, also known as the industrial reserve army, has been debated among economists and scholars for centuries. In this article, we will delve into the definition, purpose, and economic impact of a reserve army.

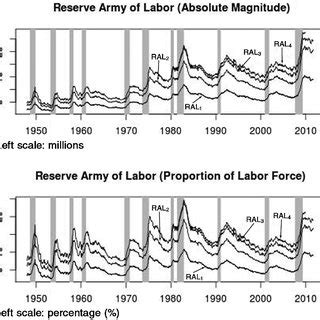
A reserve army refers to a pool of workers who are not currently employed but are available to work. This concept is closely tied to the labor market and the concept of unemployment. The reserve army is composed of individuals who are able and willing to work but are not currently employed due to various reasons such as lack of job opportunities, skills mismatch, or personal circumstances.
The Purpose of a Reserve Army
The primary purpose of a reserve army is to provide a buffer against fluctuations in the labor market. During times of economic boom, the reserve army can be drawn upon to meet the increased demand for labor. Conversely, during times of economic downturn, the reserve army can absorb the shock of layoffs and unemployment, thereby preventing widespread economic disruption.

The reserve army also serves as a means of controlling wages and maintaining social order. By maintaining a pool of unemployed workers, employers can keep wages in check, as workers are less likely to demand higher wages when there are plenty of others willing to work for lower pay. Additionally, the reserve army can be used to quell social unrest and maintain social order, as the threat of unemployment can be used to discipline workers and maintain their compliance.
The Economic Impact of a Reserve Army
The economic impact of a reserve army is multifaceted and far-reaching. On the one hand, a reserve army can provide a source of flexibility and adaptability in the labor market, allowing businesses to respond quickly to changes in demand. This can lead to increased economic efficiency and productivity.
On the other hand, a reserve army can also have negative economic impacts. The existence of a large reserve army can lead to a surplus of labor, driving down wages and working conditions. This can perpetuate poverty and inequality, as workers are forced to accept low-paying jobs or remain unemployed.

Furthermore, the reserve army can also have a negative impact on economic growth. By maintaining a pool of unemployed workers, businesses may be less likely to invest in training and education, as they can simply draw upon the reserve army to meet their labor needs. This can lead to a lack of skills and innovation, ultimately hindering economic growth.
The Marxian Perspective on the Reserve Army
Karl Marx, a prominent economist and philosopher, had a distinct perspective on the concept of a reserve army. According to Marx, the reserve army is a necessary component of capitalism, as it provides a means of controlling wages and maintaining social order.
Marx argued that the reserve army is created by the capitalist system, as workers are forced to sell their labor power in order to survive. The reserve army is a result of the inherent contradictions of capitalism, as the pursuit of profit leads to the creation of a surplus population.

Marx also argued that the reserve army is a means of disciplining workers and maintaining their compliance. By maintaining a pool of unemployed workers, employers can keep wages in check and prevent workers from demanding better working conditions.
Criticisms of the Reserve Army Concept
The concept of a reserve army has been subject to various criticisms and challenges. Some critics argue that the reserve army is not a natural phenomenon, but rather a result of government policies and economic structures.
Others argue that the reserve army is not a fixed entity, but rather a dynamic and constantly changing concept. The rise of the gig economy and precarious work has led some to argue that the traditional concept of a reserve army is no longer relevant.

Despite these criticisms, the concept of a reserve army remains a crucial aspect of economic theory. Understanding the role and impact of the reserve army can provide valuable insights into the workings of the labor market and the broader economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the concept of a reserve army is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that plays a crucial role in the labor market and the broader economy. While the reserve army can provide a source of flexibility and adaptability, it can also perpetuate poverty and inequality.
As the economy continues to evolve and change, it is essential to revisit and rethink the concept of a reserve army. By understanding the role and impact of the reserve army, we can work towards creating a more equitable and sustainable economy.
Reserve Army Image Gallery






We hope you have enjoyed this in-depth article on the reserve army. If you have any comments or questions, please feel free to leave them below.
