Discover the concept of Hypotonic Solution, a diluted mixture with low solute concentration, affecting osmosis, cell shrinkage, and isotonic balance, crucial in biology and chemistry.
The concept of a hypotonic solution is crucial in various fields, including biology, chemistry, and medicine. A hypotonic solution is a type of solution that has a lower concentration of solutes compared to another solution. This concept is essential in understanding how cells interact with their environment and how substances are transported across cell membranes. In this article, we will delve into the world of hypotonic solutions, exploring their characteristics, importance, and applications.
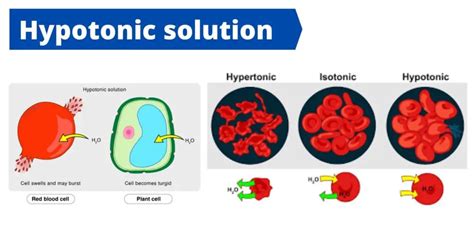
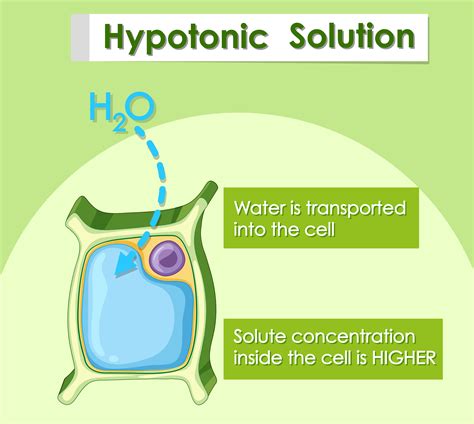
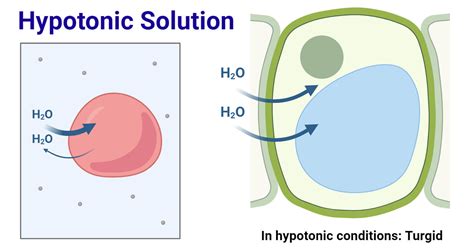
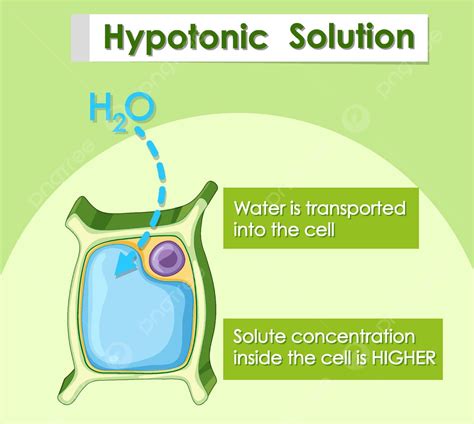
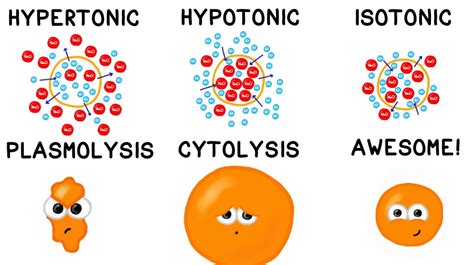
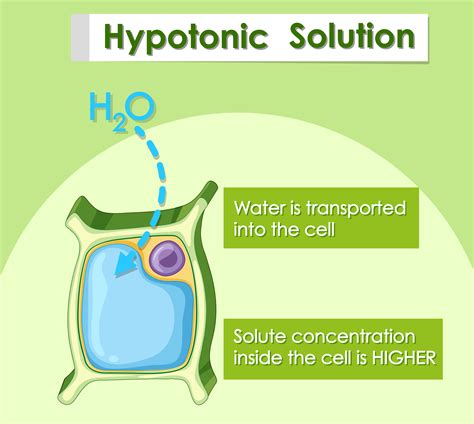
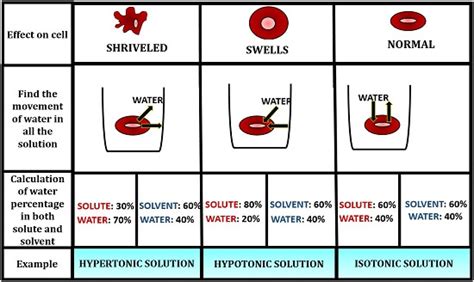
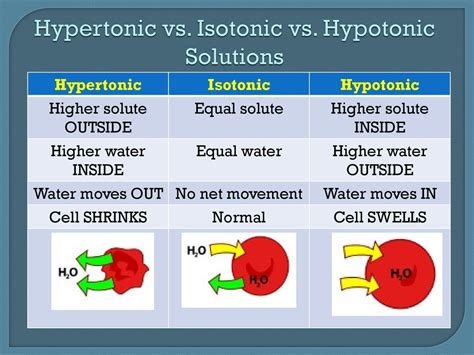
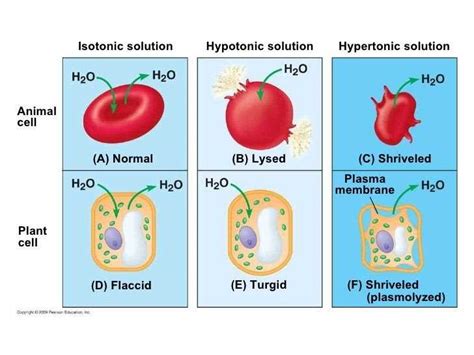
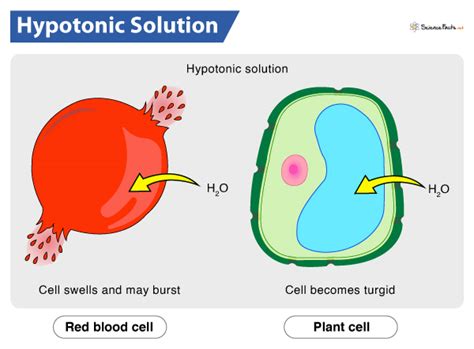
A hypotonic solution is characterized by its low solute concentration, which means it has a lower osmotic pressure compared to a hypertonic solution. Osmotic pressure is the pressure exerted by a solution to prevent the flow of solvent molecules into the solution through a semipermeable membrane. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water molecules flow into the cell, causing it to swell and potentially burst. This is because the cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing water molecules to pass through while keeping larger solute molecules out.
The importance of hypotonic solutions cannot be overstated. In biology, hypotonic solutions are used to study cell membrane transport and the behavior of cells in different environments. For instance, a hypotonic solution can be used to demonstrate the process of osmosis, where water molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration through a semipermeable membrane. This concept is vital in understanding how cells maintain their shape and structure.
What is a Hypotonic Solution?
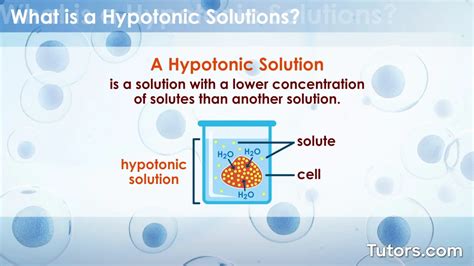
Characteristics of Hypotonic Solutions
Hypotonic solutions have several characteristics that distinguish them from other types of solutions. Some of the key characteristics of hypotonic solutions include: * Low solute concentration: Hypotonic solutions have a lower concentration of solutes compared to other solutions. * Low osmotic pressure: Hypotonic solutions have a lower osmotic pressure, which means they exert less pressure to prevent the flow of solvent molecules into the solution. * Water influx: When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, water molecules flow into the cell, causing it to swell and potentially burst.Importance of Hypotonic Solutions
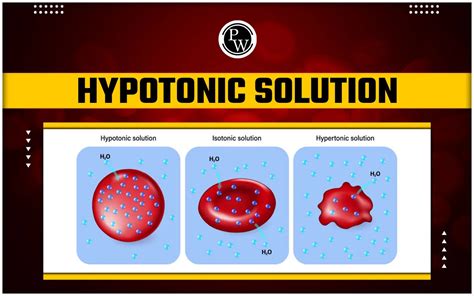
Applications of Hypotonic Solutions
Hypotonic solutions have various applications in different fields. Some of the applications of hypotonic solutions include: * Biology: Hypotonic solutions are used in biology to study cell membrane transport and the behavior of cells in different environments. * Chemistry: Hypotonic solutions are used in chemistry to study the properties of solutions and the behavior of solutes and solvents. * Medicine: Hypotonic solutions are used in medicine to treat various conditions, such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.How Hypotonic Solutions Work
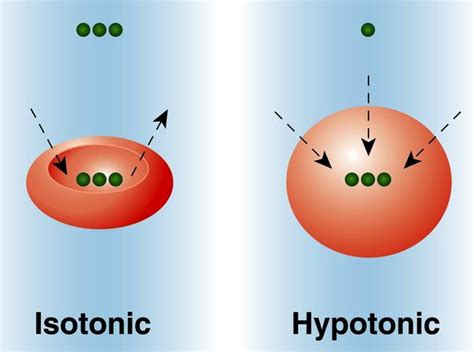
Steps Involved in Hypotonic Solutions
The steps involved in hypotonic solutions include: 1. Preparation of the solution: A hypotonic solution is prepared by dissolving a solute in a solvent to create a solution with a lower solute concentration. 2. Introduction of the cell: A cell is introduced into the hypotonic solution, allowing water molecules to flow into the cell. 3. Osmosis: Water molecules flow into the cell through a semipermeable membrane, causing the cell to swell and potentially burst.Benefits of Hypotonic Solutions
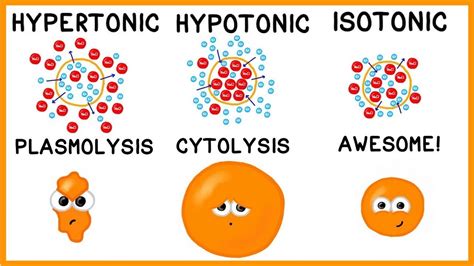
Practical Examples of Hypotonic Solutions
Some practical examples of hypotonic solutions include: * Isotonic saline solution: An isotonic saline solution is a type of hypotonic solution that has the same solute concentration as blood. * Intravenous fluids: Intravenous fluids are used to treat dehydration and electrolyte imbalances and are typically hypotonic solutions. * Cell culture media: Cell culture media are used to grow cells in the laboratory and are typically hypotonic solutions.Challenges and Limitations of Hypotonic Solutions
Solutions to the Challenges and Limitations
Some solutions to the challenges and limitations of hypotonic solutions include: * Using isotonic solutions: Isotonic solutions can be used instead of hypotonic solutions to avoid cell lysis and other complications. * Developing new applications: Researchers are developing new applications for hypotonic solutions, such as using them to study cell membrane transport and the behavior of cells in different environments. * Improving preparation techniques: Improving preparation techniques can make it easier to prepare hypotonic solutions and reduce the risk of complications.Hypotonic Solution Image Gallery
In conclusion, hypotonic solutions are essential in various fields, including biology, chemistry, and medicine. They have several characteristics, importance, and applications, and are used to study cell membrane transport and the behavior of cells in different environments. While they have several challenges and limitations, researchers are developing new applications and improving preparation techniques to make them more effective and efficient. By understanding hypotonic solutions, we can gain a deeper insight into the behavior of cells and the importance of osmosis in maintaining cellular structure and function. We invite you to share your thoughts and comments on this topic, and to explore further the fascinating world of hypotonic solutions.
