Intro
Unlock the secrets of Central Bank Reserves! Discover the 5 key ways to understand how central banks manage foreign exchange, gold reserves, and monetary policy. Learn about reserve requirements, reserve ratios, and the impact of reserve management on global economies, inflation, and currency exchange rates. Boost your financial literacy today!
Central banks play a crucial role in maintaining the economic stability of a country. One of the key tools at their disposal is the management of central bank reserves. However, understanding central bank reserves can be a complex task, even for those with a background in economics. In this article, we will break down the concept of central bank reserves into five manageable parts, making it easier for readers to grasp this critical aspect of monetary policy.
What are Central Bank Reserves?
Central bank reserves refer to the pool of funds held by a central bank to manage the money supply, stabilize the financial system, and implement monetary policy. These reserves are typically made up of foreign currencies, gold, and other liquid assets. The central bank uses these reserves to intervene in the foreign exchange market, provide loans to commercial banks, and maintain the stability of the financial system.
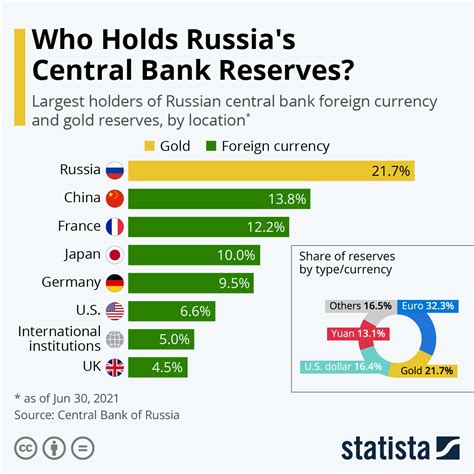
How are Central Bank Reserves Created?
Central bank reserves are created through a combination of factors, including:
- Foreign exchange transactions: When a country's currency is sold in exchange for foreign currency, the central bank receives foreign exchange reserves.
- Gold reserves: Central banks hold gold as a reserve asset, which can be used to back the value of their currency.
- Loans from other central banks: Central banks can borrow from other central banks or international institutions to increase their reserves.
- Monetary policy operations: Central banks can create new reserves by purchasing government securities or providing loans to commercial banks.
Benefits of Central Bank Reserves
Central bank reserves provide several benefits to a country's economy, including:
- Exchange rate stability: Central bank reserves can be used to intervene in the foreign exchange market, stabilizing the value of the currency.
- Financial stability: Reserves can be used to provide emergency loans to commercial banks, preventing the collapse of the financial system.
- Monetary policy implementation: Reserves can be used to implement monetary policy, such as increasing the money supply or reducing interest rates.
- Credibility and confidence: A large pool of reserves can increase confidence in the currency and the central bank, attracting foreign investment and stabilizing the economy.

Challenges Facing Central Bank Reserves
Despite the benefits, central bank reserves also face several challenges, including:
- Managing reserve adequacy: Central banks must balance the need to hold sufficient reserves with the cost of holding them.
- Currency fluctuations: Changes in exchange rates can affect the value of reserves held in foreign currencies.
- Market volatility: Central banks must navigate market volatility, which can impact the value of their reserves.
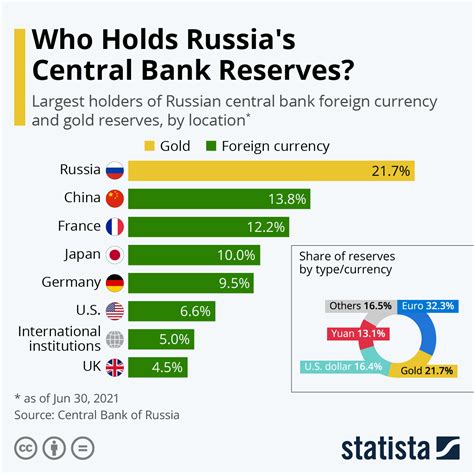
Real-World Examples of Central Bank Reserves
Several countries have successfully utilized central bank reserves to stabilize their economies. For example:
- China's foreign exchange reserves: China's large pool of foreign exchange reserves has enabled it to maintain a stable exchange rate and attract foreign investment.
- Switzerland's gold reserves: Switzerland's central bank has traditionally held a large portion of its reserves in gold, providing a safe-haven asset during times of market volatility.
Best Practices for Managing Central Bank Reserves
To effectively manage central bank reserves, central banks should:
- Maintain a diversified portfolio: Spread reserves across different asset classes to minimize risk.
- Monitor reserve adequacy: Regularly assess the sufficiency of reserves to meet potential demands.
- Implement prudent investment strategies: Invest reserves in low-risk assets to maintain their value.
Central Bank Reserves Image Gallery








In conclusion, central bank reserves play a critical role in maintaining economic stability and implementing monetary policy. By understanding the benefits and challenges of central bank reserves, policymakers and economists can develop effective strategies for managing these reserves and promoting economic growth.
