Intro
Discover what Threonate is, a vital component in skincare and supplements, boosting collagen, hydration, and antioxidant levels, with benefits for skin health, anti-aging, and cellular rejuvenation.
Threonate, also known as threonic acid or vitamin C6, is a naturally occurring compound found in various foods and has been gaining attention for its potential health benefits. The importance of threonate lies in its ability to enhance the absorption and utilization of vitamin C in the body. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy immune system, skin, and connective tissue. However, its absorption can be limited due to various factors, such as dietary habits, digestive issues, and individual tolerance. Threonate has been shown to improve the bioavailability of vitamin C, allowing the body to reap its benefits more effectively.
Threonate is a derivative of vitamin C and is found in small amounts in certain foods, including fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. It can also be produced synthetically and is available as a dietary supplement. The unique properties of threonate make it an attractive ingredient in the development of nutritional products and cosmetics. Its ability to enhance vitamin C absorption and utilization has sparked interest in the scientific community, with ongoing research exploring its potential applications in human health and wellness. As the demand for natural and effective health solutions continues to grow, threonate is poised to become a key player in the world of nutrition and supplementation.
The potential benefits of threonate are numerous and varied, ranging from improved immune function and antioxidant activity to enhanced skin health and collagen production. By increasing the bioavailability of vitamin C, threonate may help to protect against oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell damage, which are associated with various chronic diseases. Additionally, threonate has been shown to have a synergistic effect when combined with other nutrients, such as vitamin E and beta-carotene, further enhancing its potential health benefits. As research continues to uncover the mechanisms and effects of threonate, it is likely that this compound will become an increasingly important component of nutritional and therapeutic strategies.
What is Threonate and Its Benefits

The benefits of threonate are not limited to its effects on vitamin C absorption. It has also been shown to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, which may help to protect against cell damage and oxidative stress. Threonate has been found to have a synergistic effect when combined with other antioxidants, such as vitamin E and beta-carotene, further enhancing its potential health benefits. Additionally, threonate may have a role in supporting immune function, with research suggesting that it may help to stimulate the production of white blood cells and activate immune cells.
Threonate and Vitamin C Absorption
Threonate has been shown to enhance the absorption of vitamin C in the body, allowing for greater bioavailability and utilization of this essential nutrient. Vitamin C is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system, skin, and connective tissue, and its deficiency can lead to a range of health problems. Threonate works by increasing the expression of transport proteins that facilitate the uptake of vitamin C into cells, allowing for greater absorption and utilization of this nutrient. This makes threonate a valuable tool for individuals seeking to optimize their vitamin C intake and support overall health and wellness.The mechanisms by which threonate enhances vitamin C absorption are complex and involve the regulation of various transport proteins and signaling pathways. Research has shown that threonate increases the expression of sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters, which are responsible for the uptake of vitamin C into cells. Threonate has also been found to activate signaling pathways that stimulate the production of collagen and other connective tissue proteins, which are essential for maintaining healthy skin, bones, and joints.
Threonate and Antioxidant Activity

The antioxidant activity of threonate is thought to be due to its ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and tissues, leading to inflammation and disease. Threonate has been shown to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which may help to protect against cell damage and promote overall health and wellness.
Threonate and Immune Function
Threonate may have a role in supporting immune function, with research suggesting that it may help to stimulate the production of white blood cells and activate immune cells. The immune system is essential for maintaining health and preventing disease, and its dysfunction can lead to a range of health problems. Threonate has been found to have immunomodulatory effects, which may help to regulate the immune response and prevent excessive inflammation.The mechanisms by which threonate supports immune function are complex and involve the regulation of various signaling pathways and immune cells. Research has shown that threonate increases the production of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that help to coordinate the immune response. Threonate has also been found to activate immune cells, such as macrophages and natural killer cells, which are essential for fighting off infections and diseases.
Threonate and Skin Health

The mechanisms by which threonate supports skin health are complex and involve the regulation of various signaling pathways and connective tissue proteins. Research has shown that threonate increases the expression of collagen genes and stimulates the production of collagen proteins. Threonate has also been found to reduce the activity of matrix metalloproteinases, which are enzymes that break down collagen and other connective tissue proteins.
Threonate and Collagen Production
Threonate may have a role in supporting collagen production, with research suggesting that it may help to stimulate the production of collagen and other connective tissue proteins. Collagen is an essential protein that gives structure and elasticity to the skin, bones, and joints, and its deficiency can lead to a range of health problems. Threonate has been found to increase the production of collagen and other connective tissue proteins, which may help to improve skin texture, reduce the signs of aging, and support joint health.The mechanisms by which threonate supports collagen production are complex and involve the regulation of various signaling pathways and connective tissue proteins. Research has shown that threonate increases the expression of collagen genes and stimulates the production of collagen proteins. Threonate has also been found to reduce the activity of matrix metalloproteinases, which are enzymes that break down collagen and other connective tissue proteins.
Threonate and Joint Health

The mechanisms by which threonate supports joint health are complex and involve the regulation of various signaling pathways and connective tissue proteins. Research has shown that threonate reduces the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation. Threonate has also been found to increase the production of collagen and other connective tissue proteins, which may help to improve joint health and reduce the signs of aging.
Threonate and Inflammation
Threonate may have a role in reducing inflammation, with research suggesting that it may help to reduce the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increase the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines. Inflammation is a natural response to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to a range of health problems, including arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Threonate has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects, which may help to reduce joint pain and inflammation.The mechanisms by which threonate reduces inflammation are complex and involve the regulation of various signaling pathways and immune cells. Research has shown that threonate reduces the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-alpha and IL-1beta, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation. Threonate has also been found to increase the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10 and TGF-beta, which are signaling molecules that reduce inflammation.
Threonate and Oxidative Stress
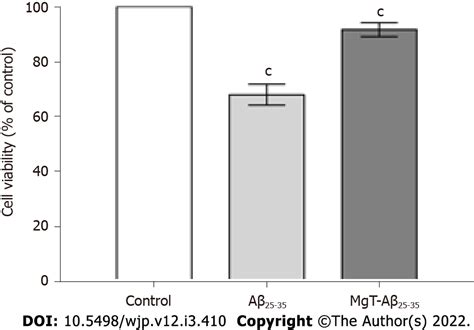
The mechanisms by which threonate reduces oxidative stress are complex and involve the regulation of various signaling pathways and antioxidant enzymes. Research has shown that threonate increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, which are essential for neutralizing free radicals. Threonate has also been found to reduce the production of reactive oxygen species, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative damage.
Threonate and Cell Damage
Threonate may have a role in reducing cell damage, with research suggesting that it may help to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. Cell damage is a natural process that occurs as a result of aging, injury, or disease, but excessive cell damage can lead to a range of health problems, including cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Threonate has been found to have antioxidant effects, which may help to reduce cell damage and promote overall health and wellness.The mechanisms by which threonate reduces cell damage are complex and involve the regulation of various signaling pathways and antioxidant enzymes. Research has shown that threonate increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase and catalase, which are essential for neutralizing free radicals. Threonate has also been found to reduce the production of reactive oxygen species, which are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative damage.
Threonate Image Gallery





In conclusion, threonate is a naturally occurring compound that has been shown to have a range of benefits, including improved vitamin C absorption, enhanced antioxidant activity, and potential anti-inflammatory effects. Its ability to increase the bioavailability of vitamin C makes it an attractive ingredient in the development of nutritional products and supplements. Threonate has been found to be effective in enhancing the absorption of vitamin C in both healthy individuals and those with impaired digestive function. As research continues to uncover the mechanisms and effects of threonate, it is likely that this compound will become an increasingly important component of nutritional and therapeutic strategies. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with threonate in the comments below, and to explore the potential benefits of this exciting compound for yourself.
